Abstract
A model was developed to describe the mixed rate control kinetics in systems with MnO-SiO2-CaO-Al2O3 slags and Fe-Si metal droplets. During the reaction of Fe-Si droplets and slag, Mn2+ transport was found to be part of controlling the system but could not sufficiently describe all initial conditions (chiefly, changes to initial silicon content). The current model describes the kinetics of the stated system and offers answers to the question of rate control; the model has been fitted to nine datasets of varying initial conditions including initial [Si], initial (MnO), initial droplet size, and reaction temperature. The fitted mass transfer coefficients for metal and slag were 2.3 × 10−4 and 6.7 × 10−4 m/s, respectively; these values are constant across the nine datasets. Previous claims about the efficiency of silicon usage in reducing manganese have been modified; it appears that the formation of silica is favored throughout the reaction, but that the formation of a silicon monoxide gas layer on the metal surface dramatically impacts the rate of reaction. As a measure of overall fit of the model, the average of the root-mean-square errors for all datasets is 14 pct. Mass transport in slag is twice as influential on rate control as the metal phase. The simultaneous transport of both Mn2+ and silicate dimers controls mass transport in the slag. Both [Si] and [Mn] can control from the metal side but are dependent on the initial conditions.

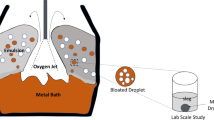
Reprinted from Ref. [7]



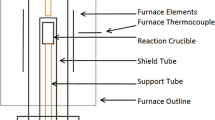
Reprinted from Ref. [7]















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.K. Lee and J. Han: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2015, vol. 31, pp. 843–56.
G. Kim, S.K. Kim, S.C. Kang, and I.R. Sohn: CAMP-ISIJ, 2008, vol. 21, p. 593.
O.S. Bobkova and V.V. Barsegyan: Metallurgist, 2006, vol. 50, pp. 463–68.
L.N. Kologrivova, A.Y. Nakonechnyi, Z.G. Trofimova, O.V. Nosochenko, and N.N. Kulik: Metallurgy, 1987, vol. 5, pp. 28–29.
O.I. Nokhrina, V.P. Komshukov, and V.I. Dmitrienko: Metallurgist, 2004, vol. 48, pp. 264–65.
M. Eissa, H. El-Faramawy, and G. Farid: Steel Res., 1998, vol. 69, pp. 373–80.
B.J. Jamieson and K.S. Coley: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48B, pp. 1613–24.
W.L. Daines and R.D. Pehlke: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1968, vol. 242, pp. 565–75.
E. Shibata, H. Sun, and K. Mori: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1999, vol. 30B, pp. 279–86.
H. Sohn, Z. Chen, and W. Jung: Steel Res., 2000, vol. 71, pp. 145–52.
J.H. Heo, Y. Chung, and J.H. Park: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46B, pp. 1154–61.
S.K. Tarby and W.O. Philbrook: Trans. TMS-AIME, 1967, vol. 239, pp. 1005–17.
R.J. Pomfret and P. Grieveson: Ironmak. Steelmak., 1978, vol. 5, pp. 191–97.
M. Ashizuka, A. Moribe, and K. Sawamura: Tetsu-to-Hagané, 1975, vol. 61, pp. 36–45.
K. Xu, G. Jiang, W. Ding, L. Gu, S. Guo, and B. Zhao: ISIJ Int., 1993, vol. 33, pp. 104–08.
H. Sun, M.Y. Lone, S. Ganguly, and O. Ostrovski: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 639–46.
M.W. Chase, Jr., C.A. Davies, J.R. Downey, Jr., D.J. Frurip, R.A. McDonald, and A.N. Syverud: NIST Stand. Ref. Database 13, vol. 1, 1985.
C.W. Bale, E. Bélisle, P. Chartrand, S.A. Decterov, G. Eriksson, A.E. Gheribi, K. Hack, I.H. Jung, Y.B. Kang, J. Melançon, A.D. Pelton, S. Petersen, C. Robelin, J. Sangster, and M.A. Van Ende: Calphad, 2016, vol. 54, pp. 35–53.
Y.E. Lee and J.H. Downing: Can. Metall. Q., 1980, vol. 19, pp. 315–22.
A. Gilat and V. Subramaniam: Numerical Methods for Engineers and Scientists: An Introduction with Applications Using MatLab, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY, 2008.
NIST/SEMATECH: E-Handb. Stat. Meth., 2013, pp. 1–4.
W. Ding and S.E. Olsen: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol. 40, pp. 850–56.
E.T. Turkdogan, G.J.W. Kor, and R.J. Fruehan: Ironmak. Steelmak., 1980, vol. 7, pp. 268–80.
A. Wu, P.C. Hayes, and H.G. Lee: ISIJ Int., 1998, vol. 38, pp. 213–19.
K. Gu, N. Dogan, and K.S. Coley: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48B, p. 3408.
K. Gu, N. Dogan, and K.S. Coley: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49B, pp. 1119–35.
P.K. Iwamasa and R.J. Fruehan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1997, vol. 28B, pp. 47–57.
J. Lee, J.S. Oh, and J. Lee: JOM, 2016, vol. 68, pp. 2359–64.
K. Narita, T. Makino, H. Matsumoto, A. Hikosaka, and J. Katsuda: ISIJ, 1983, vol. 69, pp. 1722–29.
P.V.V. Riboud and L.D.D. Lucas: Can. Metall. Q., 1981, vol. 20, pp. 199–208.
E. Chen and K.S. Coley: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2010, vol. 37, pp. 541–45.
M.D. Dolan and R.F. Johnston: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35B, pp. 675–84.
I. Sohn and D.J. Min: Steel Res. Int., 2012, vol. 83, pp. 611–30.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Science and Research Council of Canada (NSERC, Grant No. STPGP463252-14) for funding support. They also extend special thanks to ArcelorMittal Dofasco, Stelco, Praxair, and Hatch Ltd. for their in-kind support, technical expertise, and many helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 19, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamieson, B.J., Tabatabaei, Y., Barati, M. et al. Kinetic Modeling of the Silicothermic Reduction of Manganese Oxide from Slag. Metall Mater Trans B 50, 192–203 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1437-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-018-1437-y