Abstract
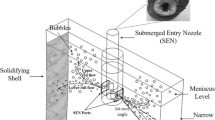
Momentum transfer of argon–steel flows in a slab mold were studied through an air–water physical model and particle image velocimetry measurements under the effects of nozzle design (nozzles with square ports S, square ports with bottom design U and circular ports C) and gas flow rate. The ratio of drag momentum of the gas phase over the liquid phase defines the conditions for coupled (existence of momentum transfer between the phases) and channeled flows (defined as those conditions where there is not further momentum transfer between both phases). When the ratio of superficial velocities of the gas phase over the liquid phase in the nozzle bore is less than 0.14, the flow pattern in the mold is dependent on the nozzle design and flow rate of gas (2 to 10 L/minute). Above this magnitude, the flow pattern becomes uncoupled and independent from the nozzle design and from the flow rate of gas. The ratios of drag velocities of the gas phase on the liquid phase and their superficial velocities in the nozzle bore are strongly dependent on the volume fraction of the gas phase. Nozzle U delivers the smallest sizes of bubbles and the smaller amount of bubble swarms per unit time impacting on the narrow face of the mold. It is, therefore, the most recommendable to cast ultra-low carbon steels. Practical implications derived from these results are written down in the text.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.M. Salazar-Campoy, R.D. Morales, A. Nájera-Bastida, I. Calderón-Ramos, V. Cedillo-Hernández, and J.C. Carlos Delgado-Pureco: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016 (under review).
J. Sengupta, B.G. Thomas, H.J. Lee, and S.H. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2006, vol. 37, pp. 1597–1611.
K. Jin, B.G. Thomas, and X.M. Ruan: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 548–65.
Z. Liu, F. Qi, B. Li, and M. Jiang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46 B, pp. 933–52.
I. Calderón-Ramos and R.D. Morales: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46 B, pp. 1314–25.
J. Zhou, R.J. Adrian, S. Balachandar, and T.M. Kendall: J. Fluid Mech., 1999, vol. 387, pp. 353–96.
P. Chakraborty, S. Balachandar, and R.J. Adrian: J. Fluid Mech., 2005, vol. 535, pp. 189–214.
R. Sánchez-Pérez, R.D. Morales, L. García-Demédices, J. Palafox-Ramos, and M. Díaz-Cruz: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2004, vol. 35 B, pp. 85–99.
O. Levenspiel: Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed., Wiley, New York, 1999, p. 258–60.
ImageJ-1.49 (Image Processing and Analysis in Java). http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/index.html. Accessed 10 December 2015.
H. Bai and B. Thomas: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2001, vol. 32 B, pp. 1143–59.
A. Berlement and C.T. Crowe: Multiphase Flow Handbook, 3rd ed., CRC Taylor and Francis, New York, 2006, p. 17–9.
N.I. Kolev: Multiphase Flow Dynamics, Turbulence, Gas Absorption and Release, Diesel Fuel Properties, vol. 3, Springer, Berlin, 2007, pp. 109–17.
L.C. Hibbeler and B.G. Thomas: AISTech Proceedings, 2013, pp. 1215–30.
K. Uemura, M. Takahashi, S. Koyama, and M. Nitta: ISIJ Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 150–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 17, 2016.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (WMV 15794 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (WMV 8041 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (WMV 18801 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salazar-Campoy, M.M., Morales, R.D., Nájera-Bastida, A. et al. A Physical Model to Study the Effects of Nozzle Design on Dense Two-Phase Flows in a Slab Mold Casting Ultra-Low Carbon Steels. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 1376–1389 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-0918-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-0918-8