Abstract
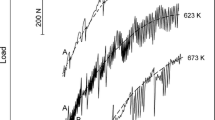
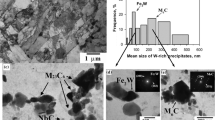
The effect of temperature and strain rate on the tensile flow behavior of Fe-0.3 pct C-CrMoV grade steel was studied over a wide range of strain rates (10−4 to 10−1 s−1) and temperatures (700 °C to 950 °C). The flow curves of the steel showed typical dynamic recovery (DRV)-type characteristics at low temperature, high strain rate, and dynamic recrystallization (DRX) type at high temperature > 775 °C. Stress regimes with stress exponent (n) of 3.6 to 5.5 for low–high stresses were observed. The ‘n’ values at temperatures of 850 °C and 900 °C were found to be > 4, which correspond to dislocation climb as the rate controlling mechanism. At 950 °C, ‘n’ value was found to be < 4, where viscous glide is the rate controlling mechanism. The apparent activation energy (Q) was found to be 320 ± 12 kJ mol−1. Hence, the dominant high-temperature deformation mechanism was identified as high-temperature climb of edge dislocations. The strain rate sensitivity index (m) of the steel was evaluated using jump strain rate tests and cyclic temperature and strain rate jump tests over temperatures of 700 °C to 950 °C and strain rates of 10−4 to 10−3 s−1 . Although, ‘m’ value as high as 0.5 was observed, cavitation resulted in premature failure during deformation resulting in low elongation. The volume fraction of cavities was inversely proportional to the strain rate at all temperatures. The fine-grained microstructure aids grain boundary sliding, and diffusion thereby favors the cavity growth at low strain rates. Microstructures evolved during the high-temperature tensile tests were analyzed and the optimum conditions for hot deformation i.e., hot rolling/hot forming schedules were determined as the temperature range of 850 °C to 950 °C and strain rate range of 10−3 to 10−4 s−1. The flow stress data for the steel were found to follow the universal Dorn sine hyperbolic equation.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.V. Philip and T.J. McCaffy: Metals Handbook, vol. 1, 10th ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1990, pp. 20–24.
K. Sreekumar, M. S. P. Murthy, A. Natarajan, P. P. Sinha, and K. V. Nagarajan: Trans. Ind. Inst. Met., 1982, vol. 35, pp. 349–55.
G. M. Padki, M. S. N. Balasubramanian, K. M. Gupta, and P. K. Rao: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1983, vol. 10, pp.180–85.
M. Chatterjee, M. S. N. Balasubramanian, K. M. Gupta, and P.K. Rao: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1990, vol. 17, pp. 38–42.
K. Saravanan, R. Suresh Kumar, V.M.J. Sharma, D. Sivakumar, P. Ramkumar, P. Ramesh Narayanan, K. Sreekumar and P.P. Sinha: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2012, vol. 710, pp. 433–38.
S. K. Maity, N. B. Ballal and R. Kawalla: The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan International, 2006, vol. 46, pp. 1361-70.
S. K. Maity, N. B. Ballal, R. Kawalla and G. Goldhahn: The Iron and Steel Institute of Japan International, 2008, vol. 49, pp. 902-10.
M.R. Suresh: Development of a new ultrahigh strength steel and studies of its microstructure and properties, Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Metallurgical Engineering and Material Science, IIT Bombay, India, 2002.
M. R. Suresh: Trans. Ind. Inst. Met., 2011, vol. 64, pp. 483–92.
M. R. Suresh, I. Samajdar, A. Ingle, N. B. Ballal, P. K. Rao and P. P. Sinha: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2003, vol. 30, pp. 379-86.
T.R. Bandyopadhyay: Ultrahigh strength steel development using electroslag refining with inoculation, Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Metallurgical Engineering and Material Science, IIT Bombay, India, 2006.
P. Ramkumar, V. Anil Kumar, R.K. Gupta, M.K. Karthikeyan, S. Narahari Prasad, F. Gino Prakash, K.V.A. Chakravarthi, Y. Maruthi Prasad and P. V. Venkitakrishnan: Trans. Ind. Inst. Met., 2018, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1283-2.
T. R Bandyopadhyay, P. K. Rao and N. Prabhu: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2006, vol. 33, pp. 331-36.
T. Gladman: The physical Metallurgy of microalloyed steels, 1st Ed., Institute of Matetrials, The University Press, London, 1997, pp. 28-34.
F.B. Pickering and T. Gladman: ISI Special Report, pp. 81–83, 1961.
S. K. Mishra, S. Das and S. Ranganathan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 2002, vol. 323, pp. 285–90.
P. Ramkumar, V. Anil Kumar, R.K. Gupta, M.K. Karthikeyan, C. Magadum and V. Muthupandi: Trans. Ind. Inst. Met., 2016, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-016-0927-3.
M.R. Suresh, P.P. Sinha, D.S. Sarma, N.B. Ballal and P. Krishna Rao: J. Mater. Sci., 2007, vol. 42, pp. 5602–12.
S. Alsagabi, T. Shrestha and I. Charit: J. Nucl. Mater., 2014, vol. 453 pp. 151–7.
Y. C. Huang, Y. C. Lin, J. Deng, G. Liu, M. S. Chen: Mater. Des., 2014, vol. 53, pp. 349-56.
A. K. Mukerjee, J. E. Bird and J. E. Dorn: Trans. ASM, 1969, vol. 62, pp.155-79.
H. J Frost and M. F. Ashby: Deformation mechanism maps, The plasticity and creep of metals and ceramics, 1st Ed., Pergoman press, Oxford, UK, 1982, pp. 1-11.
C. M. Sellars and W.T. M. Tegart: Int. Metal. Rev., 1972, vol. 17, pp. 1-24.
B.P. Kashyap and A.K. Mukherjee: Res. Mechanica., 1986, vol. 17, pp. 293-355.
A. H. Chokshi: Met. Trans. A., 1987, vol. 18, pp. 63-7.
N. Ridley and Z.C. Wang: Mater. Sci. For., 1994, vol. 170-172, pp. 177-86.
N. Ridley and Z.C. Wang: Mater. Sci. For., 1997, vol. 233-234, pp. 63-80.
J.P. Speer, C.M. Enloe, K.O. Findley, C.J. Van Tyne and E.J. Pavlina, in Fundamentals and Applications of Mo and Nb Alloying in High Performance Steels, vol. 2, TMS, UK, 2015, pp. 85–98.
R. Okamoto, A. Borgenstam and J. Argen: Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 4783-90.
V. Nagarajan: Int. Heat. Treat. Surf. Eng., 2014, vol 8-2, pp.80-5.
P. Gong, E.J. Palmiere and W.M. Rainforth: Acta Mater., 2015, vol. 97, pp.392-403.
R. Schwaiger, B. Moser, M. Dao, N. Chollacoop and S. Suresh: Acta Mater., 2003, vol. 51, pp.5159-72.
Y. Maehara and T. G. Langdon: Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 1990, vol. 128, pp. 1-13.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank National Facility for texture and OIM Lab, IIT Bombay for the support provided in EBSD work. The authors also acknowledge the support of FIST lab, MEMS department, for the support extended for testing and IFF/MME/VSSC for the fabrication support extended by them. The authors also thankfully acknowledge GM and DD, MME/VSSC for providing guidance during this work and Director, VSSC for kind permission to publish the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 29, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dilip Chandra Kumar, G., Anil Kumar, V., Gupta, R.K. et al. Effect of Strain Rate and Temperature on the Tensile Flow Behavior and Microstructure Evolution in Fe-0.3 Pct C-CrMoV Grade Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 50, 161–178 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4963-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-018-4963-y