Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effect of Chinese medicine (CM) treatment on survival time and quality of life (QOL) in patients with small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Methods
This was an exploratory and prospective clinical observation. Patients diagnosed with SCLC receiving CM treatment were included and followed up every 3 months. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS), and the secondary outcomes were progression-free survival (PFS) and QOL.
Results
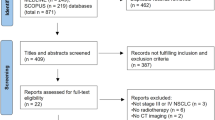
A total of 136 patients including 65 limited-stage SCLC (LS-SCLC) patients and 71 extensive-stage SCLC (ES-SCLC) patients were analyzed. The median OS of ES-SCLC patients was 17.27 months, and the median OS of LS-SCLC was 40.07 months. The survival time was 16.27 months for SCLC patients with brain metastasis, 9.83 months for liver metastasis, 13.43 months for bone metastasis, and 18.13 months for lung metastasis. Advanced age, pleural fluid, liver and brain metastasis were risk factors, while longer CM treatment duration was a protective factor. QOL assessment indicated that after 6 months of CM treatment, scores increased in function domains and decreased in symptom domains.
Conclusion
CM treatment might help prolong OS of SCLC patients. Moreover, CM treatment brought the trend of symptom amelioration and QOL improvement. These results provide preliminary evidence for applying CM in SCLC multi-disciplinary treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zou X, Jia M, Wang X, Zhi X. Changing epidemic of lung cancer & tobacco and situation of tobacco control in China. Chin J Lung Cancer (Chin) 2017;20:505–510.
Tartarone A, Giordano P, Lerose R, Rodriquenz MG, Conca R, Aieta M. Progress and challenges in the treatment of small cell lung cancer. Med Oncol 2017;34:110.
Stinchcombe TE. Current treatments for surgically resectable, limited-stage, and extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Oncologist 2017;22:1510–1517.
Byers LA, Rudin CM. Small cell lung cancer: where do we go from here? Cancer 2015;121:664–672.
Parikh M, Riess J, Lara PN Jr. New and emerging developments in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer therapeutics. Curr Opin Oncol 2016;28:97–103.
Baize N, Monnet I, Greillier L, Quere G, Kerjouan M, Janicot H, et al. Second-line treatments of small-cell lung cancers. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2017;17:1033–1043.
van Meerbeeck JP, Fennell DA, De Ruysscher DK. Small-cell lung cancer. Lancet 2011;378:1741–1755.
Nosaki K, Seto T. The role of radiotherapy in the treatment of small-cell lung cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2015;16:56.
Qi F, Zhao L, Zhou A, Zhang B, Li A, Wang Z, et al. The advantages of using traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy in the whole course of cancer treatment instead of only terminal stage of cancer. Biosci Trends 2015;9:16–34.
Liao YH, Li CI, Lin CC, Lin JG, Chiang JH, Li TC. Traditional Chinese medicine as adjunctive therapy improves the long-term survival of lung cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2017;143:2425–2435.
Tang WR, Yang SH, Yu CT, Wang CC, Huang ST, Huang TH, et al. Long-term effectiveness of combined treatment with traditional chinese medicine and western medicine on the prognosis of patients with lung cancer. J Altern Complement Med 2016;22:212–222.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) small cell lung cancer (Version 1. 2015). Fort Washington; 2015.
Sun T, Chen XY. Study on TCM syndrome characteristics of patients with primary small cell lung cancer before and after chemotherapy. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm (Chin) 2002;17:378–379.
Wang ZW, Wang JY, Hu J, Liu CQ, Wu Q, Yan J, et al. Association between traditional Chinese medicine syndrome elements before radiotherapy and radiation-induced lung injury in lung cancer patietns: a prospective cohort study. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2019;46:1233–1236.
Guo MX, Wu C, Tong WH. Research progress in equivalence study of TCM dispensing granule and traditional herbal decoction. Modern Chin Med (Chin) 2016;18:1107–1110.
Zhao YD, Ye HJ. Review of pharmacodynamics equivalence between decotion pieces and formula granules of traditional Chinese medicine. J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2010;12:227–229.
Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst 1993;85:365–376.
Bergman B, Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Kaasa S, Sullivan M. The EORTC QLQ-LC13: a modular supplement to the EORTC Core Quality of Life Questionnaire (QLQ-C30) for use in lung cancer clinical trials. EORTC Study Group on Quality of Life. Eur J Cancer 1994;30a:635–642.
Xia B, Hong LZ, Cai XW, Zhu ZF, Liu Q, Zhao KL, et al. Phase 2 study of accelerated hypofractionated thoracic radiation therapy and concurrent chemotherapy in patients with limited-stage small-cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2015;91:517–523.
Zhang W, Zhu H, Zhou Z, Feng Q, Chen D, Zhang H, et al. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in limited-stage small cell lung cancer: a single institution experience. Chin J Oncol (Chin) 2015;37:223–226.
Zhou L, Xie Z, Shao Z, Chen W, Xie H, Cui X, et al. Modeling the relationship between baseline lactate dehydrogenase and prognosis in patients with extensive-disease small cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study. J Thorac Dis 2018;10:1043–1049.
Qin T, Zhou N, Zeng YD, Dinglin X, Zhao Y, Liu H, et al. Benefit from thoracic radiotherapy in patients with extensive-disease small-cell lung cancer with elevated lactate dehydrogenase. Onco Targets Ther 2016;9:1095–1103.
Elegbede AA, Gibson AJ, Fu H, Dean ML, Ezeife DA, Lau H, et al. Real-world adherence to guideline-recommended treatment for small cell lung cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 2019;43:1.
Ogino H, Hanibuchi M, Kakiuchi S, Saijo A, Tezuka T, Toyoda Y, et al. Analysis of the prognostic factors of extensive disease small-cell lung cancer patients in Tokushima University Hospital. J Med Invest 2016;63:286–293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xu XQ was responsible for study execution and drafting the manuscript; Deng WQ and Li M were responsible for data acquisition; Wang DY conducted data analysis; Kou DL drafted the manuscript; Zhang PT raised the study concept and design, and revised the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
All authors report no conflict of interest.
Surpported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81673797), and Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. 7182142)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Xq., Deng, Wq., Wang, Dy. et al. Chinese Medicine Treatment Prolonged Survival in Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Clinical Observation. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 27, 496–501 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-020-3197-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-020-3197-1