Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effificacy of oral Chinese medicine (CM) in comparison with donepezil, a cholinesterase inhibitor (ChEI), for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Methods
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have been searched, and the effect of CM compared with donepezil in AD has been investigated. An electronic search of MEDLINE, Excerpta Medica Database (EMBASE), Cochrane Library, Chinese Biological Medicine Database (CBMdisc), and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI) to identify articles in English and Chinese from the inception of the database until October 18, 2015. A modifified Jadad score (7-points) to judge the methodological quality of studies, comprehensive meta-analysis was performed with Cochrane Collaboration Revman 5.3. Dichotomous data were analyzed by relative risk (RR) with a 95% confifidence interval (CI), while continuous variables were analyzed by using mean differences (MD) with 95% CI for effect size.
Results
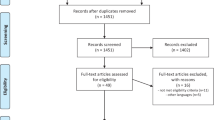
Six studies involving 596 AD patients through Jadad assessment with low bias were included in the meta-analysis. No signifificant difference was observed in cognitive improvement and daily abilities of patients using the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) (MD: 0.69, 95% CI:–0.17 to 1.56) and Activities of Daily Living (ADL) scale (MD: 0.94, 95% CI:–1.54 to 3.43). There were no signifificant differences in status of illness or MD for mild-moderate AD patients at 24 weeks (MD: 0.62, 95% CI:–2.99 to 4.23) and 48 weeks (MD:–0.73, 95% CI:–5.02 to 3.56). Severe AD patients were also assessed at 24 weeks (MD: 3.13, 95% CI:–6.92 to 13.18) and 48 weeks (MD: 4.23, 95% CI:–6.38 to 14.84). Furthermore, compared with donepezil, Xin (Heart)-regulating CM and Shen (Kidney)-tonifying groups were observed (MD:–1.50, 95% CI:–3.08 to 0.08; MD:–1.92, 95% CI:–3.50 to–0.33; respectively). CM had fewer side effects in AD patients.
Conclusion
Compared with donepezil, oral CM showed no signifificant difference in effectiveness in AD patients, and more evidence is needed to verify the fifindings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzheimer's Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2015: The Global Impact of Dementia. The United Kingdom: Alzheimer's Disease International. http://www.alz.co.uk/research/world-report-2015.
Wang J. The state of prevalent and prevention on Alzheimer's disease in China. Asia-Pacific Tradit Med (Chin) 2011;7:156–157.
National Institute for Health Research. Donopezil, galantamine, rivastigmine and memantine for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (review). 2011,3. Available at: www.nice.org.uk.
Yang NZ, Yun XH, Zhou YY. Systematic assessment of donepezil in treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Chin J Geriatric Heart Brain Vessel Dis (Chin) 2015;17:61–66.
Li L, Zhang L. Action characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Prog Biochem Biophysics 2012;39:816–828.
Wang LY, Guo DM, Zhang K. A bibliometric analysis on articles of research on Alzheimer's disease with traditional Chinese medicine from 2002 to 2011. Modern Chin Med (Chin) 2012;14(12):18–21.
Mckhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 1984;34:939–944.
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorder. 4th ed. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2000:143-147.
Jack CR, Albert MS, Knopman DS. Introduction to the recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 2011;7:257–262.
Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer's disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 2011;7:280–292.
Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 2011;7:270–279.
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trails: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 1996;17:1–12.
Gang BZ, Wang DS, Wang CL. The efficacy of Fuzhisan in patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Apoplexy Nervous Dis (Chin) 2005;22:527–529.
Zhou RQ, Lin SM, Wang J. Clinical study on Chinese Herbal Heart-Regulating Formula and Kidney-Tonifying Formula in improving cognitive ability in Alzheimer's. Modern Rehabil (Chin) 2001;5(6):46–47.
Wang J, Lin SM, Zhou RQ. Clinical study on Kidney-Nourshing Formula in treating Alzheimer's disease. Shanghai J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2002;4:4–6.
Lin SM, Wang J, Zhou RQ, Yu ZH. Clinical study on treatment of Alzheimer's disease from the viewpoint of Xin and Shen. Chin J Integr Med (Chin) 2006;10:162–164.
Yu L, Lin SM, Zhou RQ, Tang WJ, Huang PX. Chinese herbal medicine for patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease based on syndrome differentiation: a randomized controlled trial. J Chin Integr Med (Chin) 2012;10:766–776.
Yu L, Lin SM, Zhou RQ. Clinical study on treatment based on syndrome differentiation for improving quality of life of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Acta Univ Tradit Med Sin Pharmacol Shanghai (Chin) 2012;26(4):41–45.
Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.3.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2015. Available at: www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Zhu H, Dong KL, Wu Y, Zhang T, Li MR, Hu SH. Effect of tonifying Kidney and activating blood circulation on cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Chin J Gerontol (Chin) 2010;30:1493–1495.
Wang EL. Using herbs of reinforcing Kidney and activating blood to treat AD. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2013;40:1867–1868.
He HL, Zhou RM. Revised Buyang Huanwu Decoction treat senile dementia 35 cases. J Zhejiang Univ Chin Med (Chin) 2013;37:723–724.
Chen L. Chinese medicine "Bu Yuan Cong Nao Tang" treating Kidney essence deficiency and phlegm and blood stasis resistance winding type senile dementia (Alzheimer's disease, AD) patients [dissertation]. Shenyang: Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine; 2011.
Li Y. Shenrong Yizhi Decoction in treating patients with senile dementia clinical research [dissertation]. Wuhan: Hubei University of Chinese Medicine; 2008.
Liu J. The clinical study of 30 cases of senile dementia treated by Didang Decoction. Shandong J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2014;31(10):22–23.
Wang SH. Clinical observation on 34 cases of Alzheimer's disease treated by compound Congrong Yizhi Capsule. Zhejiang J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2015;50:386–387.
Chen F, Fei YE, Lin Y. Effect of compound sea snake Capsule on Alzheimer's disease. Chin J Rural Med Pharm (Chin) 2014;21(23):32–33.
Na WQ, Li JH, Chen K, Xia QC, Guan TF. A comparative study of Sea Cucumber Capsule in treatment of aged Alzheimer disease. Chin J Mar Drugs (Chin) 2012;31:42–45.
Li XC, He MD. Effect of Naoling Decoction on MMSE and pro-inflammatory cytokines of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Pract Prev Med (Chin) 2010;17:959–961.
Ding XD, Zhang QY, Sun QS, Zhang JX. Clinical research of Shenghuang Yizhi Granule on Alzheimer's disease. Chin J Gerontol (Chin) 2009;29:2023–2024.
Pang SH, Kang BR. Modified Yiqi Congming Decoction in treatment of Spleen and Kidney deficiency type of Alzheimer's disease. Liaoning J Traditional Chin Med (Chin) 2014;41:967–969.
Yang P, Dong KL. Clinical study on Yizhi Jiannao Granule in treating Alzheimer's disease. J New Chin Med (Chin) 2013;45(12):56–58.
Zhang XP. Clinical observation on Yizhi Decoction on Alzheimer's disease patients. J Hubei Univ Chin Med (Chin) 2014;16:81–82.
Zhang FL. Treating 38 cases of senile dementia in Yizhi Decoction. Acta Chin Med (Chin) 2009;24(5):45–46.
Yan SD, Yan SY, Qi DQ, Niu Y, Wang MJ. Clinical observation on 93 cases of Alzheimer's disease treated by Zhijing Oral Liquid. Guangxi J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2007;30(3):30–32.
Xu J. Zuoguiwan flavored type of kidney essence deficiency in patients with senile dementia clinical efficacy and safety of the drug research [dissertation]. Shenyang: Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine; 2013.
Chang FY, Yuan Y, Sun Y, Lai J, Song X. Clinical research on Refined Xingnao Power in treatment of senile dementia. Chin Arch Tradit Chin Med 2013;31:1253–1254.
Li H. Effect of Bupi Yishen Decoction in treating 35 cases with Alzheimer's disease. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formula (Chin) 2015;21:193–196.
Acknowledgments
We thank for the help of Evidence Based Clinical Club (EBCC) in providing conference room and organizing meetings among the meta-analysis lovers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Youth Found Project (No. 81503450)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Hk., Liu, Y., Li, B. et al. Chinese Medicine for Alzheimer's Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 24, 938–943 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-018-2567-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-018-2567-4