Abstract
Objective
To assess the effectiveness of Tongjiang Granule (TJG, 通降颗粒) on the patients with nonerosive reflux disease (NERD) of Gan (肝)-Wei (胃) incoordination syndrome, its impact on their quality of life, and its safety.
Method
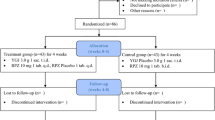
A randomized, controlled, double-blinded, and double-dummy method was adopted in the trial. There were 120 NERD patients enrolled in the study and randomly divided into the experiment and control groups, each with 60 patients; drugs were distributed according to the drug number by patients’ inclusion sequences. In the experiment group, patients were given TJG 10 g and mosapride citrate dummy 5 mg three times a day, and in the control group, patients were given mosapride citrate 5 mg and TJG dummy 10 g three times a day. The treatment courses of both groups were 4 weeks.
Results
Among 120 included patients, 112 were screened for full analysis set (FAS), and 105 were screened per-protocol set (PPS). The results were as follows: (1) the improvement of total scores of symptom in the experiment group (0–4 week) were 15.93±7.88 scores by FAS and 16.22 ±7.75 scores by PPS, and they were 10.43±10.16 scores and 10.79±10.27 scores in the control group, respectively. The 95% CI of net scores improvement between the two groups were 2.10–8.90 scores and 1.92–8.94 scores in FAS and PPS; it was significantly better in the experiment group than that in the control group (P<0.05). (2) The improvement of scores of major symptom in the experiment group (0–4 week) were 10.68±5.35 by FAS and 10.89±5.29 by PPS and 7.40±7.41 and 7.60±7.46 in the control group, respectively. The 95% CI of net scores improvement in the two groups were 0.85–5.71 and 0.71–5.69 in FAS and PPS separately, and the improvement in the experiment group was significantly better than that in the control group (P<0.05). (3) The total effective rates were 86.0% and 61.8% in the experiment and the control group separately, and the Ridit analysis results showed that it was better in the experiment group (P<0.05). (4) The improvement quality of life in the domain of physical functioning and general health in the experiment group was better than that in the control group (P<0.05). (5) One case of experiment group caught a cold and recovered in six days without drug suspension. No adverse event was found in the other cases. There was no meaningful safety examination indices change in pretreatment and posttreatment periods in both groups.
Conclusion
TJG showed a definite effect on the treatment of NERD with Gan-Wei incoordination syndrome, and it could improve the quality of life of NERD patient without obvious toxic and side effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin SR, Xu GM, Hu PJ, Zhou LY, Chen MH, Ke MY, et al. Chinese consensus on gastroesophageal reflux disease. Chin J Gastroenterol (Chin) 2007;12:233–239.
Pan GZ, Xu GM, Guo HP, Ke MY, Han SM, Li ZS, et al. An epidemiologic study on symptomatic GER in Beijing and Shanghai. Chin J Digest (Chin) 1999;19:223–226.
Kouzu T, Hishikawa E, Watanabe Y, Inoue M, Satou T. Epidemiology of GERD in Japan. Nippon Rinsho 2007;65:791–794.
Rosaida MS, Goh KL. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, reflux oesophagitis and non-erosive reflux disease in a multiracial Asian population: a prospective, endoscopy based study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;16:495–501.
Zhao YF, Wang R, Yan XY, Ma XQ, He J. Impacts of gastroesophageal reflux disease on health-related quality of life of residents in Shanghai. Chin J Health Statistics (Chin) 2009;26:363–366.
Ronkainen J, Aro P, Storskrubb T, Lind T, Bolling-Sternevald E, Junghard O, et al. Gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms and health related quality of life in the adult general population-the Kalixanda study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006;23:1725–1733.
Tang XD, Wu HM, Wang ZB, Shao Y, Hu YC. Study on reflux esophagitis treated by Tongjiang Granule. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2006;31:136–138.
Tang XD, Wu HM, Wang ZB, Shao Y, Hu YC. Assessment on effects of Tongjiang Granule on experimental reflux esophagitis in rats. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2006;26:818–821.
Tang XD, Wu HM, Wang ZB, Liu XM, Hu YC. Impact of Tongjiang Granule in gastric emptying function on experimental animals. Chin J Experiment Tradit Med Formulae (Chin) 2006;12:24–26.
Zhen XY, ed. Guiding principle for clinical researches on new drugs of Chinese medicine. Beijing: China Medical Science Press; 2002:366–368.
Shaw M, Dent J, Beebe T, Junghard O, Wiklund I, Lind T, et al. The reflux disease questionnaire: a measure for assessment of treatment response in clinical trials. Health Quality Life Outcomes 2008;6:31.
Li L, Wang HM, Shen Y. Development and psychometric tests of a Chinese version of the SF-36 Health Survey Scales. Chin J Prevent Med (Chin) 2002;36:109–113.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Fund of Capital Medical Development and Research (No. 03 III 10).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Bs., Li, Zh., Tang, Xd. et al. A randomized, controlled, double-blinded and double-dummy trial of the effect of Tongjiang Granule (通降颗粒) on the nonerosive reflux disease of and Gan (肝)-Wei (胃) incoordination syndrome. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 17, 339–345 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0724-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0724-0