Abstract
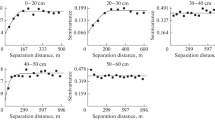
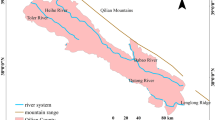
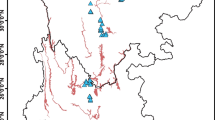
Soil nitrogen (N) is critical to ecosystem services and environmental quality. Hotspots of soil N in areas with high soil moisture have been widely studied, however, their spatial distribution and their linkage with soil N variation have seldom been examined at a catchment scale in areas with low soil water content. We investigated the spatial variation of soil N and its hotspots in a mixed land cover catchment on the Chinese Loess Plateau and used multiple statistical methods to evaluate the effects of the critical environmental factors on soil N variation and potential hotspots. The results demonstrated that land cover, soil moisture, elevation, plan curvature and flow accumulation were the dominant factors affecting the spatial variation of soil nitrate (NN), while land cover and slope aspect were the most important factors impacting the spatial distribution of soil ammonium (AN) and total nitrogen (TN). In the studied catchment, the forestland, gully land and grassland were found to be the potential hotspots of soil NN, AN and TN accumulation, respectively. We concluded that land cover and slope aspect could be proxies to determine the potential hotspots of soil N at the catchment scale. Overall, land cover was the most important factor that resulted in the spatial variations of soil N. The findings may help us to better understand the environmental factors affecting soil N hotspots and their spatial variation at the catchment scale in terrestrial ecosystems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber JD, Nadelhoffer KJ, Steudler P, et al. (1989) Nitrogen saturation in northern forest ecosystems. Bioscience 39(6): 378–386. https://doi.org/10.2307/1311067
Agehara S, Warncke DD (2005) Soil moisture and temperature effects on nitrogen release from organic nitrogen sources. Soil Science Society of America Journal 69(6): 1844–1855. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2004.0361
Andrews DM, Lin H, Zhu Q, et al. (2011) Hot spots and hot moments of dissolved organic carbon export and soil organic carbon storage in the Shale Hills catchment. Vadose Zone Journal 10(3): 943–954. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2010.0149
Andrews SS, Carroll CR (2001) Designing a soil quality assessment tool for sustainable agroecosystem management. Ecological Applications 11(6): 1573–1585. https://doi.org/10.1890/1051-0761(2001)011[1573:DASQAT]2.0.CO;2
Armstrong A, Quinton JN, Francis B, et al. (2011) Controls over nutrient dynamics in overland flows on slopes representative of agricultural land in North West Europe. Geoderma 164: 2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.04.011
Assouline S, Ben-Hur M (2006) Effects of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on the dynamics of interrill erosion during soil surface sealing. Catena 66(3): 211–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2006.02.005
Bennie J, Huntley B, Wiltshire A, et al. (2008) Slope, aspect and climate: Spatially explicit and implicit models of topographic microclimate in chalk grassland. Ecological Modelling 216(1): 47–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2008.04.010
Bernard-Jannin L, Sun XL, Teissier S, et al. (2017) Spatio-temporal analysis of factors controlling nitrate dynamics and potential denitrification hot spots and hot moments in groundwater of an alluvial floodplain. Ecological Engineering 103: 372–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.12.031
Bernhardt ES, Blaszczak JR, Ficken CD, et al. (2017) Control points in ecosystems: Moving beyond the hot spot hot moment concept. Ecosystems 20: 665–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-016-0103-y
Boring LR, Swank WT (1984) The role of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) in forest succession. Journal of Ecology 72(3): 749–766. https://doi.org/10.2307/2259529
Brejda JJ, Moorman TB, Karlen DL, et al. (2000) Identification of regional soil quality factors and indicators. I. Central and Southern High Plains. Soil Science Society of America Journal 64: 2115–2124. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2000.6462115x
Breuer L, Kiese R, Butterbachbahl K (2002) Temperature and moisture effects on nitrification rates in tropical rain-forest soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 66(3): 399–402. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2002.8340
Brockett BFT, Prescott CE, Grayston SJ (2012) Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven biogeoclimatic zones in western Canada. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 44(1): 9–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.09.003
Burt TP, Butcher DP (2010) Topographic controls of soil moisture distributions. European Journal of Soil Science 36(3): 469–486. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1985.tb00351.x
Cambardella CA, Moorman TB, Parkin TB, et al. (1994) Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 58: 1501–1511. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800050033x
Cao YZ, Wang XD, Lu XY, et al. (2013) Soil organic carbon and nutrients along an alpine grassland transect across Northern Tibet. Journal of Mountain Science 10(4): 564–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-012-2431-5
Castellano MJ, Schmidt JP, Kaye JP, et al. (2010) Hydrological and biogeochemical controls on the timing and magnitude of nitrous oxide flux across an agricultural landscape. Global Change Biology 16(10): 2711–2720. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02116.x
Causse J, Baurè SE, Mery Y, et al. (2015) Variability of N export in water: A review. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 45(20): 2245–2281. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2015.1010432
Córdova C, Sohi SP, Lark RM, et al. (2012) Resolving the spatial variability of soil N using fractions of soil organic matter. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 147: 66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2011.06.016
Edokpa DA, Evans MG, Rothwell JJ (2015) High fluvial export of dissolved organic nitrogen from a peatland catchment with elevated inorganic nitrogen deposition. Science of the Total Environment 532: 711–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.072
Alkheir A, et al. (2014) Spatial variation of soil carbon and nitrogen pools by using ordinary kriging method in an area of north Nile Delta, Egypt. Catena 113: 70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.09.008
Foster N, Spoelstra J, Hazlett P, et al. (2005) Heterogeneity in soil nitrogen within first-order forested catchments at the Turkey Lakes watershed. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 35(4): 797–805. https://doi.org/10.1139/x05-016
Franzluebbers AJ, Stuedemann JA (2009) Soil-profile organic carbon and total nitrogen during 12 years of pasture management in the southern piedmont USA. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment 129: 28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2008.06.013
Frei S, Knorr KH, Peiffer S, et al. (2012) Surface micro-topography causes hot spots of biogeochemical activity in wetland systems: A virtual modeling experiment. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 117: G00N12. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012jg002012
Gilliam FS, Galloway JE, Sarmiento JS (2015) Variation with slope aspect in effects of temperature on nitrogen mine. Canadian Journal of Forest Research 45: 958–962. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjfr-2015-0087
Huang YM, Liu D, An SS (2015) Effects of slope aspect on soil nitrogen and microbial properties in the Chinese Loess region. Catena 125: 135–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.09.010
Gong X, Brueck H, Giese KM, et al. (2008) Slope aspect has effects on productivity and species composition of hilly grassland in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Arid Environments 72(4): 483–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2007.07.001
Gu C, Anderson W, Maggi F (2012) Riparian biogeochemical hot moments induced by stream fluctuations. Water Resources Research 48(9): W09546. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011wr011720
Ihori T, Burke IC, Lauenroth WK, et al. (1995) Effects of cultivation and abandonment on soil organic matter in northeastern Colorado. Soil Science Society of America Journal 59(4): 1112–1119. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1995.03615995005900040024x
Jackson-Blake L, Helliwell RC, Britton AJ, et al. (2012) Controls on soil solution nitrogen along an altitudinal gradient in the Scottish uplands. Science of the Total Environment 431: 100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.019
Jenson SK, Domingue JO (1988) Extracting topographic structure from digital elevation data for geographic information system analysis. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 54(11): 1593–1600.
Jin Z, Guo L, Lin H, et al. (2018) Soil moisture response to rainfall on the Chinese Loess Plateau after a long-term vegetation rehabilitation. Hydrological Processes 32(12): 1738–1754. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13143
Jin Z, Li XR, Wang YQ, et al. (2016) Comparing watershed black locust afforestation and natural revegetation impacts on soil nitrogen on the Loess Plateau of China. Scientific Reports 6: 25048. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25048
Johnson DW, Glass DW, Murphy JD, et al. (2010) Nutrient hot spots in some sierra Nevada forest soils. Biogeochemistry 101: 93–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-010-9423-8
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982). Nitrogen-inorganic forms. Methods of Soil Analysis, 2nd ed. Madison, WI: ASA and SSSA. pp 643–698.
Klemmedson JO, Wienhold BJ (1991) Aspect and species influences on nitrogen and phoshorus availability in Arizona chaparral soils. Soil Science Society of Americal Journal 55: 1735–1740. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1991.03615995005500060038x
Kravchenko AN (2003) Influence of spatial structure on accuracy of interpolation methods. Soil Science Society of Americal Journal 67: 1564–1571. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2003.1564
Kuzyakov Y, Blagodatskaya E (2015) Microbial hotspots and hot moments in soil: Concept & review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 83: 184–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.01.025
Leonelli G, Pelfini M, Battipaglia G, et al. (2009) Site-aspect influence on climate sensitivity over time of a high-altitude Pinus cembra tree-ring network. Climatic Change 96: 185–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-009-9574-6
Lescop B, Fanjoux G, Arfa MB, et al. (2014) Residence time control on hot moments of net nitrate production and uptake in the hyporheic zone. Hydrological Processes 28(11): 3741–3751. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9921
Lewis MPL (2010) Influence of antecedent moisture and rainfall rate on the leaching of nitrate and phosphate from intact monoliths of agricultural soil. Master thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo. p 92.
Liu ZP, Shao MA, Wang YQ (2013) Spatial patterns of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus across the entire Loess Plateau region of China. Geoderma 197–198: 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.12.011
Lozano-García B, Parras-Alcántara L, Brevik EC (2016) Impact of topographic aspect and vegetation (native and reforested areas) on soil organic carbon and nitrogen budgets in Mediterranean natural areas. Science of the Total Environment 544: 963–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.022
Mandal UK, Warrington DN, Bhardwaj AK, et al. (2008) Evaluating impact of irrigation water quality on a calcareous clay soil using principal component analysis. Geoderma 144: 189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.11.014
Maynard DG, Kalra YP, Crumbaugh JA (2008). Nitrate and exchangeable ammonium nitrogen. Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis (Second Edition). Boca Raton, Fl, USA: CRC Press. pp 71–73.
McClain ME, Boyer EW, Dent CL, et al. (2003) Biogeochemical hot spots and hot moments at the interface of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 6(4): 301–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-003-0161-9
Mishra U, Lal R, Slater B, et al. (2009) Predicting soil organic carbon stock using profile depth distribution functions and ordinary kriging. Soil Science Society of America Journal 73(2): 614. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2007.0410
Morse JL, Werner SF, Gillin CP, et al. (2014) Searching for biogeochemical hot spots in three dimensions: Soil C and N cycling in hydropedologic settings in a northern hardwood forest. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 119(8): 1596–1607. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013jg002589
Molodovskaya M, Singurindy O, Richards BK, et al. (2012) Temporal variability of nitrous oxide from fertilized croplands: hot moment analysis. Soil Science Society of America Journal 76(5): 1728. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2012.0039
Nielsen DR, Hopmans JW, Kutílek M, et al. (1997) A brief review of soil water, solute transport and regionalized variable analysis. Scientia Agricola 54: 89–115. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90161997000300012
Palta MM, Ehrenfeld JG, Groffman PM (2014) “Hotspots” and “Hot Moments” of denitrification in Urban Brownfield wetlands. Ecosystems 17(7): 1121–1137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-014-9778-0
Ping CL, Jastrow JD, Jorgenson MT, et al. (2015) Permafrost soils and carbon cycling. Soil 1(1): 147–171. https://doi.org/10.5194/soil-1-147-2015
Sajedi T (2010) The effects of excessive moisture on soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization and forest productivity. Ph. D. Dissertation, the University of British Columbia, Vancouver. pp 82–84.
Schütt M, Borken W, Spott O, et al. (2014) Temperature sensitivity of C and N mineralization in temperate forest soils at low temperatures. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 69: 320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.11.014
Schwanghart W, Jarmer T (2011) Linking spatial patterns of soil organic carbon to topography — A case study from south-eastern Spain. Geomorphology 126: 252–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.11.008
Singer MB, Harrison LR, Donovan PM, et al. (2016) Hydrologic indicators of hot spots and hot moments of mercury methylation potential along river corridors. Science of the Total Environment 568: 697–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.005
Ska D, Zapata F, Awonaike KO (1995) Measurement of biological N2 fixation in field-grown Robinia pseudoacacia L. Soil Biology & Biochemistry 27(4/5): 415–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(95)98612-r
Sulebak JR, Tallaksen LM, Erichsen B (2000) Estimation of areal soil moisture by use of terrain data. Geografiska Annaler 82(1): 89–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0435-3676.2000.00009.x
Sørensen J (2010) Nitrogen distribution and potential nitrate leaching in a combined production system of energy crops and free range pigs. Master Master, Aarhus University.
Tarboton DG, Bras RL, Rodriguez-Iturbe I (1991) On the extraction of channel networks from digital elevation data. Hydrological Processes 5(1): 81–100. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.3360050107
Vernimmen RRE, Verhoef HA, Verstraten JM, et al. (2007) Nitrogen mineralization, nitrification and denitrification potential in contrasting lowland rain forest types in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Soil Biology & Biochemistry 39(12): 2992–3003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2007.06.005
Walter C, McBratney AB, Douaoui A, et al. (2001) Spatial prediction of topsoil salinity in the Chelif Valley, Algeria, using local ordinary kriging with local variograms versus whole-area variogram. Austranlian Journal of Soil Research 39: 259–272. https://doi.org/10.1071/sr99114
Wang J, Fu BJ, Qiu Y, et al. (2001) Soil nutrients in relation to land use and landscape position in the semi-arid small catchment on the Loess Plateau in China. Journal of Arid Environments 48(4): 537–550. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2000.0763
Wang WY, Ma YG, Xu J, et al. (2012) The uptake diversity of soil nitrogen nutrients by main plant species in kobresia humilis alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese Science: Earth Science 55(10): 1688–1695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-012-4461-9
Wang YQ, Shao MG, Liu ZP, et al. (2012) Investigation of factors controlling the regional-scale distribution of dried soil layers under forestland on the Loess Plateau, China. Surveys in Geophysics 33(2): 311–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-011-9154-y
Wang YQ, Zhang XC, Huang CQ (2009) Spatial variability of soil total nitrogen and soil total phosphorus under different land uses in a small watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 150(1–2): 141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.01.021
Wanshnong RK, Thakuria D, Sangma CB, et al. (2013) Influence of hill slope on biological pools of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in acidic alfisols of citrus orchard. Catena 111: 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2013.07.009
Wei XR, Shao MG, Fu XL, et al. (2009) Distribution of soil organic C, N and P in three adjacent land use patterns in the northern Loess Plateau, China. Biogeochemistry 96(1–3): 149–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-009-9350-8
Wiesmeier M, Hübner R, Barthold F, et al. (2013) Amount, distribution and driving factors of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in cropland and grassland soils of southeast Germany (Bavaria). Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 176: 39–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2013.05.012
WRB IWG (2006). World reference base for soil resources 2006. 2nd edition. Rome: FAO. pp 74–75.
Xiong ZQ, Li SC, Yao L, et al. (2015) Topography and land use effects on spatial variability of soil denitrification and related soil properties in riparian wetlands. Ecological Engineering 83: 437–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.04.094
Yang XL, Zhu B, Li YL (2013) Spatial and temporal patterns of soil nitrogen distribution under different land uses in a watershed in the hilly area of purple soil, China. Journal of Mountain Science 10(3): 410–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-013-2712-7
Yang Y, Dou YX, Liu D, et al. (2017) Spatial pattern and heterogeneity of soil moisture along a transect in a small catchment on the Loess Plateau. Journal of Hydrology 550: 466–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.05.026
Yimer F, Ledin S, Abdelkadir A (2006) Soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks as affected by topographic aspect and vegetation in the Bale Mountains, Ethiopia. Geoderma 135: 335–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.01.005
Zhang L (2009) Study on population characteristics and ecological adaptability of Artemisia scarorum Ledeb. in junger loess hill-gully region. Master Thesis, Inner Mongolia University, Inner Mongolia. (In Chinese)
Zhang SR, Xia CL, Li T, et al. (2016) Spatial variability of soil nitrogen in a hilly valley: Multiscale patterns and affecting factors. Science of the Total Environment 563–564: 10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.111
Zheng H, Lin H, Zhou WJ, et al. (2019) Revegetation has increased ecosystem water-use efficiency during 2000–2014 in the Chinese Loess Plateau: Evidence from satellite data. Ecological Indicators 102: 507–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.02.049
Zhu HH, Wu JS, Guo SL, et al. (2014) Land use and topographic position control soil organic C and N accumulation in eroded hilly watershed of the Loess Plateau. Catena 120: 64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.04.007
Zhang R Wienhold BJ (2002) The effect of soil moisture on mineral nitrogen, soil electrical conductivity, and pH. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems 63(2–3): 251–254. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021115227884
Zhu Q, Castellano MJ, Yang GS (2018) Coupling soil water processes and the nitrogen cycle across spatial scales: Potentials, bottlenecks and solutions. Earth-Science Reviews 187: 248–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.10.005
Zhu Q, Lin HS (2009) Comparing ordinary kriging and regression kriging for soil properties in contrasting landscapes. Pedosphere 20: 594–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(10)60049-5
Zhu Q, Schmidt JP, Bryant RB (2012) Hot moments and hot spots of nutrient losses from a mixed land use watershed. Journal of Hydrology 414–415: 393–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.11.011
Acknowledgment
This study was financially supported by the National key research and development program (2017YFD0800502), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41573067, 41790444, 41471189, 31700414).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Yl., Jin, Z., Lin, H. et al. Spatial variation and soil nitrogen potential hotspots in a mixed land cover catchment on the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 16, 1353–1366 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5175-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-018-5175-z