Abstract
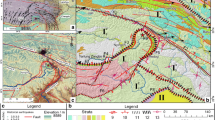
On August 8, 2017, a Ms 7.0 earthquake occurred 5 km to the west of Jiuzhaigou National Park, causing 25 deaths and injuring 525. The objective of this study was to explore the seismogenic fault of the earthquake and tectonic dynamics of the source rupture. Field investigations, radon activity tests, remote sensing interpretations, and geophysical data analyses were carried out immediately after the earthquake. The Jiuzhaigou earthquake occurred at the intersection of the northern margin of the Minshan uplift belt and the south part of the Wenxian–Maqin fault in the south margin of the West Qinling geosyncline. There are two surface rupture zones trending northwest (NW), which are ground coseismic ruptures caused by concealed earthquake faults. The rupture on the southwest is the structure triggering the earthquake, along the Jiuzhaitiantang–Epicenter–Wuhuahai. The other one on the northeast (Shangsizhai–Zhongcha–Bimang) is a reactivation and extension of the secondary fault trending NW. The source rupture of this earthquake is a strike-slip shear fracture associated with the fault plane trending NW 331° and steeply dipping 75°, which is continuously expanding at both ends. The tectonic dynamics process of the source rupture is that the “Jiuzhaigou protrusion” is left-lateral sheared along the seismogenic fault in the NW direction. Finally, the Maqin fault and the arc fault system at the top of the “Wenxian protrusion” will be gradually broken through sometime in far future, as well as earthquaketriggered landslides will be further occurred along the narrow corridor between the seismogenic faults. The research results revealed the basic geological data and tectonic dynamic mechanism in this earthquake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
China Earthquake Administration (2017) Comprehensive Atlas of Jiuzhaigou Ms 7.0 Earthquake in Aba Prefecture, Sichuan Province. https://doi.org/www.csi.ac.cn/manage/eqDown/05LargeEQ/201708082119M7.0/zonghe.html (Accessed on 11 August 2017)
China Earthquake Networks Center (2017) China Earthquake Catalog. https://doi.org/www.csndmc.ac.cn/newweb/(Accessed on 20 August 2017)
Daryono MR, Tohari A (2016) Surface Rupture and Geotechnical Features of The July 2, 2013 Tanah Gayo Earthquake. Indonesian Journal on Geoscience, 3 (2): 95–105. https://doi.org/10.17014/ijog.3.2.95-105
Drolet JP, Martel R, Poulin P, et al. (2013) An approach to define potential radon emission level maps using indoorradon concentration measurements and radiogeochemical data positive proportion relationships. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 124: 57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2013.04.006
Drolet, JP, Martel, R. (2016) Distance to faults as a proxy for radon gas concentration in dwellings. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 152: 8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2015.10.023
Fairhurst C (1964) Measurement of in–situ rock stresses. with particular reference to hydraulic fracturing. Rock Mech.; (United States), 2.
Guo H, Jiang WL, Xie XS (2017) Multiple faulting events revealed by trench analysis of the seismogenic structure of the 1976 Ms 7.1 Luanxian earthquake, Tangshan Region, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 147: 424–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.06.004
Hua W, Chen ZL, Li ZX, et al. (2009) Seismic triggering and the aftershock distribution of the Wenchuan M 8.0 Earthquake. Earthquake 29(1):33–39. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-3274.2009.01.005
Hu JH, Fu LY, Sun WJ (2017) A study of the Coulomb stress and seismicity rate changes induced by the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, SW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 135: 303–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.12.048
Jiang LW, Wang ST, Wang YS, et al. (2005) Active tectonic system and its control of seismic activity in the east part of the northwest fault block of Sichuan, China. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technoloy Edition) 32(4): 340–344. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2005.04.002
Kirby E, Whipple KX, Burchfiel BC, et al. (2000) Neotectonics of the Min Shan, China: implications for mechanisms driving Quaternary deformation along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau. GSA Bulletin 112(3): 375–393. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(2000)112<375:NOTMSC>2.0.CO;2
Lin AM, Sano M, Yan B (2015) Co–seismic surface ruptures produced by the 2014 Mw 6.2 Nagano earthquake, along the Itoigawa–Shizuoka tectonic line, central Japan. Tectonophysics 656: 142–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2015.06.018
Lin AM (2017) Structural features and seismotectonic implications of coseismic surface ruptures produced by the 2016 Mw 7.1 Kumamoto earthquake. Journal of Seismology 21(5): 1079–1100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-017-9653-5
Li YS, Huang RQ (2008) Engineering geological assessments of reconstruction sites for cities and towns destroyed by Wenchuan earthquake. Journal of Engineering Geology 16 (6): 764–773. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.06.006
Mohammad R Ghassemi (2016) Surface ruptures of the Iranian earthquakes 1900–2014: Insights for earthquake fault rupture hazards and empirical relationships. Earth–Science Reviews 156: 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.03.001
Pan JW, Li HB, Si JL, et al. (2014) Rupture process of the Wenchuan earthquake (Mw 7.9) from surface ruptures and fault striations characteristics. Tectonophysics 619–620: 13–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2013.06.028
Wang YS (2002) Application of radon measurement to the study of regional tectonic stability. Mountain Research 20(4):505–508. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.2002.04.021
Wang YS, Huang RQ, Luo YH, et al. (2011) The genetic mechanism of Wenchuan Earthquake. Journal of Mountain Science 8(2): 336–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-011-2096-5
Wu CH, Cui P, Li YS, et al. (2018) Seismogenic fault and topography control on the spatial patterns of landslides triggered by the 2017 Jiuzhaigou earthquake. Journal of Mountain Science 15(4): 793–807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4761-9
Xie ZJ, Zheng Y, Liu CL, et al. (2017) An integrated analysis of source parameters, seismogenic structure, and seismic hazards related to the 2014 Ms 6.3 Kangding earthquake, China. Tectonophysics 712–713: 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2017.04.030
Yalım HA, Sandıkcıoglu A, Ertugrul O, et al. (2012) Determination of the relationship between radon anomalies and earthquakes in well waters on the Aksehir–Simav Fault System in Afyonkarahisar province, Turkey. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity 110: 7–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2012.01.015
Yi GX, Long F, Liang MJ, et al. (2017) Focal mechanism solutions and seismogenic structure of the 8 August 2017 M 7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake and its aftershocks, northern Sichuan. Chinese Journal of Geophysics 60(10):4083–4097. (In Chinese) https://doi.org/10.6038/cjg20171033
Zhu SB, Miao M (2015) How Did the 2013 Lushan Earthquake (Ms = 7.0) Trigger its Aftershocks? Insights from Static Coulomb Stress Change Calculations. Pure & Applied Geophysic 172(10): 2481–2494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-015-1064-3
Zhang ZY, Wang ST, Wang LS, et al. (2016) Analysis principle of engineering geology. Beijing, China. Geological Publishing House. pp 78–80. (In Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the Open Research Fund from the Key Laboratory of Mountain Hazards and Earth Surface Process (Chinese Academy of Sciences) (Grant No. KLMHESP-17-06), the Independent Research Fund from the State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection (Chengdu University of Technology) (Grant No. 40100-00002219). Deep appreciation goes to LIU Kai and Dr TANG Jie for their suggestion and assistance, as well as LetPub (www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript. We thank anonymous referees and editors for their constructive comments on an earlier version of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, Sj., Wu, Ch., Li, Ys. et al. Source tectonic dynamics features of Jiuzhaigou Ms 7.0 earthquake in Sichuan Province, China. J. Mt. Sci. 15, 2266–2275 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4703-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4703-6