Abstract
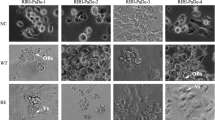
A new cell line, MSU-TnT4 (TnT4), was established from Trichoplusia ni embryos for use with baculovirus expression vectors and evaluated for its potential for membrane protein production. To evaluate membrane protein synthesis, recombinant baculoviruses were constructed to express the human neurotensin receptor 1 as an enhanced green fluorescent protein (GFP) fusion. TnT4 cells had a doubling time of 21 h and expressed the membrane-GFP fusion protein at approximately twice the level as Sf21 cells from the p10 promoter, as evaluated by GFP intensity. Expression of secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) was similar to that of Sf21 cells. Expression of membrane-GFP fusion proteins in recombinant baculoviruses provides a rapid method for evaluating the potential of new cell lines for the production of membrane proteins using a baculovirus expression vector system (BEVS).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akermoun M.; Koglin M.; Zvalova-Iooss D.; Folschweiller N.; Dowell S. J.; Gearing K. L. Characterization of 16 human G protein-coupled receptors expressed in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Protein Expr. Purif. 44: 65–74; 2005.
Becker G. W.; Miller J. R.; Kovacevic S.; Ellis R. M.; Louis A. I.; Small J. S.; Stark D. H.; Roberts E. F.; Wyrick T. K.; Hoskins J.; Chiou X. G.; Sharp J. D.; McClure D. B.; Riggin R. M.; Kramer R. M. Characterization by electrospray mass-spectrometry of human Ca2+-sensitive cytosolic phospholipase A2 produced in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Bio-Technol. 12: 69–74; 1994.
Chai H.; AlRubeai M.; Chua K. L.; Oh S. K. W.; Yap M. G. S. Insect cell line dependent gene expression of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-beta. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 18: 126–132; 1996.
Chen C. J.; Thiem S. M. Differential infectivity of two Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus mutants on three permissive cell lines is the result of lef-7 deletion. Virology 227: 88–95; 1997.
Clem R. J.; Fechheimer M.; Miller L. K. Prevention of apoptosis by a baculovirus gene during infection of insect cells. Science 254: 1388–1390; 1991.
Cullen B. R.; Malim M. H. Secreted placental alkaline-phosphatase as a eukaryotic reporter gene. Methods Enzymol. 216: 362–368; 1992.
Davis T. R.; Trotter K. M.; Granados R. R.; Wood H. A. Baculovirus expression of alkaline-,phosphatase as a reporter gene for evaluation of production, glycosylation and secretion. Bio-Technol. 10: 1148–1150; 1992.
Davis T. R.; Wickham T. J.; McKenna K. A.; Granados R. R.; Shuler M. L.; Wood H. A. Comparative recombinant protein-production of 8 insect-cell lines. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 29A: 388–390; 1993.
Gaw Z. -Y.; Liu N. T.; Zia T. U. Tissue culture methods for cultivation of virus grasserie. Acta Virol. 3Suppl.: 55–60; 1959.
Grace T. Establishment of four strains of cells from insect tissues grown in vitro. Nature (London) 195: 788–789; 1962.
Granados R. R.; Li G. X.; Derksen A. C. G.; McKenna K. A. A new insect-cell line from Trichoplusia ni (BTI-TN-5B1-4) Susceptible to Trichoplusia ni single enveloped nuclear polyhedrosis-virus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 64: 260–266; 1994.
Grisshammer R.; Tate C. G. Overexpression of integral membrane-proteins for structural studies. Q. Rev. Biophys. 28: 315–422; 1995.
Grunewald S.; Haase W.; Reilander H.; Michel H. Glycosylation, palmitoylation, and localization of the human D-2S receptor in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Biochemistry 35: 15149–15161; 1996.
Hink W. F. A serum-free medium for the culture of insect cells and production of recombinant proteins. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 27: 397–401; 1991.
Hollister J.; Grabenhorst E.; Nimtz M.; Conradt H.; Jarvis D. L. Engineering the protein N-glycosylation pathway in insect cells for production of biantennary, complex N-glycans. Biochemistry 41: 15093–15104; 2002.
Kuchler R. J. Biochemical methods in cell culture and virology. Dowden, Hutchinson & Ross, Stroudsburg; 1977.
Lu A.; Miller L. K. Species-specific effects of the hcf-1 gene on baculovirus virulence. J. Virol. 70: 5123–5130; 1996.
Lynn D. E. Development and characterization of insect cell lines. Cytotechnology 20: 3–11; 1996.
Lynn D. E. Novel techniques to establish new insect cell lines. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol., Anim. 37: 319–321; 2001.
Massotte D. G protein-coupled receptor overexpression with the baculovirus-insect cell system: A tool for structural and functional studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Biomembr. 1610: 77–89; 2003.
McCusker E. C.; Bane S. E.; O'Malley M. A.; Robinson A. S. Heterologous GPCR expression: A bottleneck to obtaining crystal structures. Biotechnol. Prog. 23: 540–547; 2007.
McIntosh A. H.; Grasela J. J.; Matteri R. L. Identification of insect cell lines by DNA amplification fingerprinting (DAF). Insect Mol. Biol. 5: 187–195; 1996.
McKenna K. A.; Hong H. Z.; vanNunen E.; Granados R. R. Establishment of new Trichoplusia ni cell lines in serum-free medium for baculovirus and recombinant protein production. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 71: 82–90; 1998.
Ng G. Y. K.; George S. R.; Zastawny R. L.; Caron M.; Bouvier M.; Dennis M.; Odowd B. F. Human serotonin 1B receptor expression in Sf9 cells—Phosphorylation, palmitoylation, and adenylyl-cyclase inhibition. Biochemistry 32: 11727–11733; 1993.
Ng G. Y. K.; Odowd B. F.; Caron M.; Dennis M.; Brann M. R.; George S. R. Phosphorylation and palmitoylation of the human D2L dopamine-receptor in Sf9 cells. J. Neurochem. 63: 1589–1595; 1994.
O'Reilly, D. R.; Miller, L. K.; Luckow, V. Baculovirus expression vectors. A laboratory manual. New York: Freeman; 1992.
Ogonah O. W.; Freedman R. B.; Jenkins N.; Patel K.; Rooney B. C. Isolation and characterization of an insect cell line able to perform complex N-linked glycosylation on recombinant proteins. Bio-Technol. 14: 197–202; 1996.
Palomares L. A.; Joosten C. E.; Hughes P. R.; Granados R. R.; Shuler M. L. Novel insect cell line capable of complex N-glycosylation and sialylation of recombinant proteins. Biotechnol. Prog. 19: 185–192; 2003.
Sarramegna V.; Talmont R.; Demange P.; Milon A. Heterologous expression of G-protein-coupled receptors: Comparison of expression systems from the standpoint of large-scale production and purification. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 60: 1529–1546; 2003.
Smith G. E.; Ju G.; Ericson B. L.; Moschera J.; Lahm H. W.; Chizzonite R.; Summers M. D. Modification and secretion of human interleukin-2 produced in insect cells by a baculovirus expression vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 82: 8404–8408; 1985.
Vaughn J. L.; Goodwin R. H.; Tompkins G. J.; McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.: Plant 13: 213–217; 1977.
Weyer U.; Knight S.; Possee R. D. Analysis of very late gene-expression by Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus and the further development of multiple expression vectors. J. Gen. Virol. 71: 1525–1534; 1990.
Wickham T. J.; Davis T.; Granados R. R.; Shuler M. L.; Wood H. A. Screening of insect cell-lines for the production of recombinant proteins and infectious virus in the baculovirus expression system. Biotechnol. Prog. 8: 391–396; 1992.
Zavodzky P.; Cseh S. Production of multidomain complement glycoproteins in insect cells. Cytotechnology 20: 279–288; 1996.
Zhao Y.; Sane D. C. Expression of a recombinant baculovirus for vitronectin in insect cells—Purification, characterization of posttranslational modifications and functional-studies of the recombinant protein. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 304: 434–442; 1993.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Michigan State University Grant REF03-016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Manzan, M.A., Peplinski, H.M. et al. A new Trichoplusia ni cell line for membrane protein expression using a baculovirus expression vector system. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 44, 214–223 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-008-9095-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-008-9095-z