Abstract
Purpose
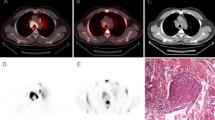
This study aimed to assess the imaging features and natural course of hilar and mediastinal sarcoid-like reaction on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT after the treatment of malignancies.
Methods
Sixteen patients with the appearance of sarcoid-like reaction seen on 18F-FDG-PET/CT after treatment were included. Hilar and mediastinal lymph node metastases were pathologically or clinically ruled out. Posttreatment 18F-FDG-PET/CT imaging features were assessed.
Results
The maximum standardized uptake values of sarcoid-like reaction were 3.8–13.6 (mean 6.8). FDG uptake of hilar nodes was symmetrical in 12 (75%) patients and asymmetrical in 4 (25%). The time interval between the initiation of therapy and appearance of sarcoid-like reaction was 9–86 months (median 27.1 months). Among 14 patients who underwent further follow-up using 18F-FDG-PET/CT, sarcoid-like reaction regressed in 11 (79%) patients and did not regress in 3 (21%) patients. The time interval between the appearance of sarcoid-like reaction and its regression was 3–80 months (median, 8.5 months).
Conclusion
After the treatment of malignancies, benign sarcoid-like reaction was rarely observed during follow-up. Although sarcoid-like reaction appeared a long time after the treatment of malignancies, it frequently and spontaneously regressed in a relatively short period of time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sacks EL, Donaldson SS, Gordon J, Dorfman RF. Epithelioid granulomas associated with Hodgkin’s disease: clinical correlations in 55 previously untreated patients. Cancer. 1978;41(2):562–7.
Hunsaker AR, Munden RF, Pugatch RD, Mentzer SJ. Sarcoidlike reaction in patients with malignancy. Radiology. 1996;200(1):255–61.
Gooneratne L, Nagi W, Lim Z, Ho AY, Devereux S, Pagliuca A, et al. Sarcoidosis and haematological malignancies: is there an association? Br J Haematol. 2008;141(2):260–2.
Chowdhury FU, Sheerin F, Bradley KM, Gleeson FV. Sarcoid-like reaction to malignancy on whole-body integrated (18)F-FDG PET/CT: prevalence and disease pattern. Clin Radiol. 2009;64(7):675–81.
Inoue K, Goto R, Shimomura H, Fukuda H. FDG-PET/CT of sarcoidosis and sarcoid reactions following antineoplastic treatment. Springerplus. 2013;2(1):113.
Blank N, Lorenz HM, Ho AD, Witzens-Harig M. Sarcoidosis and the occurrence of malignant diseases. Rheumatol Int. 2014;34(10):1433–9.
London J, Grados A, Ferme C, Charmillon A, Maurier F, Deau B, et al. Sarcoidosis occurring after lymphoma: report of 14 patients and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2014;93(21):e121.
Grados A, Ebbo M, Bernit E, Veit V, Mazodier K, Jean R, et al. Sarcoidosis occurring after solid cancer: a nonfortuitous association: report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(28):e928.
Lau RK, Takasugi JE, David Godwin J, Pipavath SN. Sarcoid-like reaction-computed tomography features in 12 patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2015;39(2):143–8.
Arish N, Kuint R, Sapir E, Levy L, Abutbul A, Fridlender Z, et al. Characteristics of sarcoidosis in patients with previous malignancy: causality or coincidence? Respiration. 2017;93(4):247–52.
Brincker H, Wilbek E. The incidence of malignant tumours in patients with respiratory sarcoidosis. Br J Cancer. 1974;29(3):247–51.
Ji J, Shu X, Li X, Sundquist K, Sundquist J, Hemminki K. Cancer risk in hospitalized sarcoidosis patients: a follow-up study in Sweden. Ann Oncol. 2009;20(6):1121–6.
Askling J, Grunewald J, Eklund A, Hillerdal G, Ekbom A. Increased risk for cancer following sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160(5 Pt 1):1668–72.
Piekarski E, Benali K, Rouzet F. Nuclear imaging in sarcoidosis. Semin Nucl Med. 2018;48(3):246–60.
Keijsers RG, van den Heuvel DA, Grutters JC. Imaging the inflammatory activity of sarcoidosis. Eur Respir J. 2013;41(3):743–51.
Mostard RL, van Kroonenburgh MJ, Drent M. The role of the PET scan in the management of sarcoidosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2013;19(5):538–44.
Sobic-Saranovic D, Grozdic I, Videnovic-Ivanov J, Vucinic-Mihailovic V, Artiko V, Saranovic D, et al. The utility of 18F-FDG PET/CT for diagnosis and adjustment of therapy in patients with active chronic sarcoidosis. J Nucl Med. 2012;53(10):1543–9.
Brincker H. Sarcoid reactions in malignant tumours. Cancer Treat Rev. 1986;13(3):147–56.
Umezu H, Chida M, Inoue T, Araki O, Tamura M, Tatewaki M, et al. Sarcoidosis development during induction chemotherapy for lung cancer mimicked progressive disease. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;58(8):434–7.
Maeda J, Ohta M, Hirabayashi H, Matsuda H. False positive accumulation in 18F fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography scan due to sarcoid reaction following induction chemotherapy for lung cancer. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;53(4):196–8.
Skipworth RJ, Stewart GD, Dejong CH, Preston T, Fearon KC. Pathophysiology of cancer cachexia: much more than host-tumour interaction? Clin Nutr. 2007;26(6):667–76.
Funding
The authors declare that there is no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
The authors declare that they preserve ethical standards.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaneko, Y., Kato, H. & Matsuo, M. Hilar and mediastinal sarcoid-like reaction after the treatment of malignant tumors: imaging features and natural course on 18F-FDG-PET/CT. Jpn J Radiol 37, 88–94 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-018-0786-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-018-0786-4