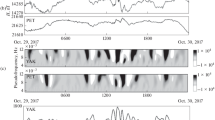
Abstract
The present study analyzes the efficiency of local intermittency measure based on wavelet transforms in identifying solar flare effects on magnetograms. If we observe the flare-time features in geomagnetic components, most often, disturbances associated with other solar phenomena will enhance or mask the solar flare signatures. Similarly, diurnal and high-latitude geomagnetic variabilities will suppress solar flare effects on magnetograms. The measurements of amplitudes taken directly from temporal variations of weak geomagnetic components have certain limitations regarding the identification of the proper base and peak values from which the deviation due to solar flare has to be measured. In such situations, local intermittency measure based on cross-wavelet analysis can be employed which could remarkably identify the flare effects, even if the signatures are weak or masked by other disturbance effects. The present study shows that local intermittency measure based on wavelet analysis could act as an alternate quantification technique for analyzing solar flare effects on geomagnetic activity.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruno R, Bavassano B, Pietropaolo E, Carbone V, Veltri P (1999) Effects of intermittency on interplanetary velocity and magnetic field fluctuations anisotropy. Geophys Res Lett 26(20):3185–3188
Carrington RC (1859) Description of a singular appearance seen in the Sun on September 1. Mon Not R Astron Soc 20:13–15
Consolini G, De Michelis P (2005) Local intermittency measure analysis of AE index: the directly driven and unloading component. Geophys Res Lett 32:1–4
De Michelis P, Tozzi R (2005) A Local Intermittency Measure (LIM) approach to the detection of geomagnetic jerks. Earth Planet Sci Lett 235:261–272
Dmitriev AV, Yeh HC (2008) Geomagnetic signatures of sudden ionospheric disturbances during extreme solar radiation events. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 70:1971–1984
Farge M (1992) Wavelet transforms and their applications to turbulence. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 24:395
Farge M, Holschneider M, Colonna JF (1990) Wavelet analysis of coherent structures in two-dimensional turbulent flows in Topological Fluid Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Giménez de Castro G, Simões PJA, Raulin JP, Guimarães OM (2016) Analysis of intermittency in submillimeter radio and hard X-Ray data during the impulsive phase of a solar flare. Sol Phys 291:2003–2016
Hodgson R (1860) On a curious appearance seen in the Sun. Mon Not R Soc 20:15–16
Kovács P, Carbone V, Vörös Z (2001) Wavelet-based filtering of intermittent events from geomagnetic time-series. Planet Space Sci 49:1219–1231
Liu JY, Chiu CS, Lin CH (1996) The solar flare radiation responsible for sudden frequency deviation and geomagnetic fluctuation. J Geophys Res 101:10855–10862
Mallat S (1998) A wavelet tour of signal processing. Academic Press, New York
Meignen S, Oberlin T, McLaughlin S (2012) Multicomponent signal denoising with synchrosqueezing. In: 2012 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP 2012), pp 660–663
Meneveau C (1991) Analysis of turbulence in the orthonormal wavelet representation. J Fluid Mech 232:469–520
Meyer Y (1992) Wavelets and operators. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Meza A, Van Zele MA, Rovira M (2009) Solar flare effect on the geomagnetic field and ionosphere. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 71:1322–1332
Nagata T (1966) Solar flare effect on the geomagnetic field. J Geomagn Geoelectr 18:197–219
Ohshio M, Fukushima N, Nagata T (1967) Solar flare effects on geomagnetic field. Rep Ionos Space Res Jpn 21:77–114
Okeke FN, Okpala KC (2005) Geomagnetic solar flare effect in H, Y, and Z fields in the Northern Hemisphere. NJSR 1:39–99
Rastogi RG (1962) Longitudinal variation in the equatorial electrojet. J Atmos Terr Phys 24:1031–1040
Rastogi RG (2001) Electromagnetic induction due to solar flares at equatorial stations. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 63:599–604
Rastogi RG, Chandra H, Yumoto K (2013) Unique examples of solar flare effects in geomagnetic H field during partial counter electrojet along CPMN longitude sector. Earth Planets Space 65:1027–1040
Richmond AD, Venkateswaran SV (1971) Geomagnetic crochets and associated ionospheric current systems. Radio Sci 6:139–164
Tandberg-Hanssen E, Emslie AG (1988) The physics of solar flares. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ugonabo OJ, Okeke FN, Ugwu BI (2016) Solar flare effects (SFE) on geomagnetic fields across latitudes. Int J Phys Sci 11:112–120
Van Sabben D (1961) Ionospheric current systems of ten IGY-solar flare effects. J Atmos Terr Phys 22:32–42
Venugopal V, Roux SG, Foufoula-Georgiou E, Arneodo A (2006) Revisiting multifractality of high-resolution temporal rainfall using a wavelet-based formalism. Water Resour Res 42(6):W06D14
Volland H, Taubenheim J (1958) On the ionospheric current system of the geomagnetic solar flare effect (SFE). J Atmos Terr Phys 12:258–265
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) for providing GOES X-ray flux archived at the NOAA National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC) (http://www.swpc.noaa.gov/products/goes-x-ray-flux). The authors are also thankful to INTERMAGNET for providing 1-min data of geomagnetic components (www.intermagnet.org). One of the authors SG acknowledges a Junior Research Fellowship (Ac.EVI(4)/17465/JRF/2017) from the University of Kerala, Trivandrum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gopinath, S., Prince, P.R. Investigations into solar flare effects using wavelet-based local intermittency measure. Acta Geophys. 67, 687–701 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-019-00257-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-019-00257-7