Summary
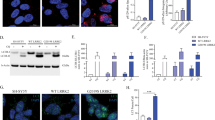
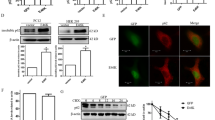
The G2019S mutation of the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) is the most common genetic cause of Parkinson’s disease (PD). However, the molecular mechanisms of LRRK2 mutation contributing to the onset and progression of PD have not been fully illustrated. We generated HEK293 cells stably transfected with α-synuclein and investigated the effect of LRRK2 G2019S mutation on the degradation of α-synuclein. The lysosomal activity was assessed by the protein degradation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and ribonuclease A. It was found that α-synuclein was mainly degraded in lysosomes. LRRK2 G2019S inhibited the degradation of α-synuclein, and promoted its aggregation. LRRK2 G2019S also decreased the activities of lysosomal enzymes including cathepsin B and cathepsin L. Furthermore, the inhibitory effect of LRRK2 G2019S on lysosomal functions did not depend on its kinase activity. These findings indicated that the inhibitory effect of LRRK2 G2019S on α-synuclein degradation could underlie the pathogenesis of aberrant α-synuclein aggregation in PD with LRRK2 mutation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozansoy M, Basak AN. The central theme of Parkinson’s disease: alpha-synuclein. Mol Neurobiol, 2013,47(2):460–465
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, et al. Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science, 2012,338(6109):949–953
Kachergus J, Mata IF, Hulihan M, et al. Identification of a novel LRRK2 mutation linked to autosomal dominant parkinsonism: evidence of a common founder across European populations. Am J Hum Genet, 2005,76(4):672–680
Lesage S, Brice A. Parkinson’s disease: from monogenic forms to genetic susceptibility factors. Hum Mol Genet, 2009, 18(R1):R48–59
Sepulveda B, Mesias R, Li X, et al. Short-and longterm effects of LRRK2 on axon and dendrite growth. PLoS One, 2013,8(4):e61986
Wider C, Dickson DW, Wszolek ZK. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 gene-associated disease: redefining genotype-phenotype correlation. Neurodegener Dis, 2010, 7(1-3):175–179
Yao C, El Khoury R, Wang W, et al. LRRK2-mediated neurodegeneration and dysfunction of dopaminergic neurons in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis, 2010,40(1):73–81
Lin X, Parisiadou L, Gu XL, et al. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 regulates the progression of neuropathology induced by Parkinson’s-disease-related mutant alphasynuclein. Neuron, 2009,64(6):807–827
Novello S, Arcuri L, Dovero S, et al. G2019S LRRK2 mutation facilitates alpha-synuclein neuropathology in aged mice. Neurobiol Dis, 2018,120:21–33
McGlinchey RP, Lee JC. Cysteine cathepsins are essential in lysosomal degradation of alpha-synuclein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2015,112(30):9322–9327
West AB, Moore DJ, Biskup S, et al. Parkinson’s disease-associated mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 augment kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005,102(46):16842–16847
Blake RA, Broome MA, Liu X, et al. SU6656, a selective src family kinase inhibitor, used to probe growth factor signaling. Mol Cell Biol, 2000,20(23):9018–9027
Tofaris GK. Lysosome-dependent pathways as a unifying theme in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord, 2012,27(11):1364–1369
Osellame LD, Duchen MR. Defective quality control mechanisms and accumulation of damaged mitochondria link Gaucher and Parkinson diseases. Autophagy, 2013,9(10):1633–1635
Kyratzi E, Pavlaki M, Kontostavlaki D, et al. Differential effects of Parkin and its mutants on protein aggregation, the ubiquitin-proteasome system, and neuronal cell death in human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurochem, 2007,102(4):1292–1303
Gong B, Leznik E. The role of ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 in neurodegenerative disorders. Drug News Perspect, 2007,20(6):365–370
Bennett MC, Bishop JF, Leng Y, et al. Degradation of alpha-synuclein by proteasome. J Biol Chem, 1999,274(48):33855–33858
Rideout HJ, Larsen KE, Sulzer D, et al. Proteasomal inhibition leads to formation of ubiquitin/alphasynuclein-immunoreactive inclusions in PC12 cells. J Neurochem, 2001,78(4):899–908
Cuervo AM, Stefanis L, Fredenburg R, et al. Impaired degradation of mutant alpha-synuclein by chaperonemediated autophagy. Science, 2004,305(5688):1292–1295
Zimprich A, Muller-Myhsok B, Farrer M, et al. The PARK8 locus in autosomal dominant parkinsonism: confirmation of linkage and further delineation of the disease-containing interval. Am J Hum Genet, 2004,74(1):11–19
Hyun CH, Yoon CY, Lee HJ, et al. LRRK2 as a Potential Genetic Modifier of Synucleinopathies: Interlacing the Two Major Genetic Factors of Parkinson’s Disease. Exp Neurobiol, 2013,22(4):249–257
Orenstein SJ, Kuo SH, Tasset I, et al. Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy. Nat Neurosci, 2013,16(4):394–406
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 81401051, No. 81671051, and No. 81501107).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, D., Niu, Jy., Xiong, J. et al. LRRK2 G2019S Mutation Inhibits Degradation of α-Synuclein in an In Vitro Model of Parkinson’s Disease. CURR MED SCI 38, 1012–1017 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1977-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1977-z