Summary
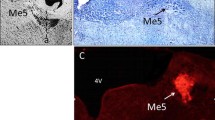
The precise anatomy of the facial nerve branches innervating rat whisker pad and the distribution of their corresponding motor neurons in facial nucleus area were investigated. The extratemporal facial nerves of 6 rats were anatomically observed under a surgical microscope, and then the nerve specimens of facial nerve branches at 7 anatomical sites were taken and examined for the axons and myelin sheath using Luxol fast blue staining. The distribution of facial motor neurons innervating the facial branches was observed in 12 rats by retrograde labelling. The distal pes, a fusing architecture of the buccal and marginal mandibular branches, was found to furcate into superior, middle and inferior branches to innervate whisker pad. Histologically, the myelin sheath of each branch was morphologically consistent, and the nerve fiber bundles of facial nerve branches became increasingly thinner and scattered, particularly after crossing the distal pes site and innervating the whisker pad. The facial motor neurons innervating the buccal and marginal mandibular branches were clearly distributed in similar regions in facial nucleus. This study confirmed the highly spatial synergy between the buccal and marginal mandibular branches innervating the whisker pad from extratemporal anatomy and distribution of facial motor neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bermejo R, Houben D, Zeigler HP. Optoelectronic monitoring of individual whisker movements in rats. J Neurosci Methods, 1998,83(2):89–96
Bermejo R, Szwed M, Friedman W, et al. One whisker whisking: unit recording during conditioned whisking in rats. Somatosens Mot Res, 2004, 21(3–4):183–187
Hadlock T, Kowaleski J, Lo D, et al. Functional assessments of the rodent facial nerve: a synkinesis model. Laryngoscope, 2008,118(10):1744–1749
Heaton JT, Kowaleski JM, Bermejo R, et al. A system for studying facial nerve function in rats through simultaneous bilateral monitoring of eyelid and whisker movements. J Neurosci Methods, 2008,171(2):197–206
Drfl J. The innervation of the mystacial region of the white mouse: a topographical study. J Anat, 1985,142:173–184
Semba K, Egger MD. The facial “motor” nerve of the rat: control of vibrissal movement and examination of motor and sensory components. J Comp Neurol, 1986,247:144–158
Yetiser S, Kahraman E, Satar B, et al. Anatomy of the Extratemporal Facial Nerve in Rats. Mediterr J Otol, 2005,1:117–121
Skouras E, Merkel D, Grosheva M, et al. Manual stimulation, but not acute electrical stimulation prior to reconstructive surgery, improves functional recovery after facial nerve injury in rats. Restor Neurol Neurosci, 2009,27(3):237–251
Henstrom D, Hadlock T, Lindsay R, et al. The convergence of facial nerve branches providing whisker pad motor supply in rats: implications for facial reanimation study. Muscle Nerve, 2012,45(5):692–697
Chen P, Knox CJ, Yao L, et al. The effects of venous ensheathment on facial nerve repair in the rat. Laryngoscope, 2017,127(7):1558–1564
Chen P, Song J, Luo LH, et al. Abnormal motor reflexes and dormant facial motor neurons in rats with facialfacial anastomosis. J Int Med Res, 2009,37(3):705–716
Chen P, Wang P, Chen G, et al. Study on remodeling of astrocytes in facial neuclus after peripheral injury. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2005,25(6):726–728
Martin MR, Lodge D. Morphology of the facial nucleus of the rat. Brain, 1977,123(1):1–12
Weinberg JS, Kleiss IJ, Knox CJ, et al. The Dilator Naris Muscle as a Reporter of Facial Nerve Regeneration in a Rat Model. Ann Plast Surg, 2016,76(1):94–98
Seitz M, Grosheva M, Skouras E, et al. Poor functional recovery and muscle polyinnervation after facial nerve injury in fibroblast growth factor-2-/-mice can be improved by manual stimulation of denervated vibrissal muscles. Neuroscience, 2011,182(1):241–247
Yamada H, Hato N, Murakami S, et al. Facial synkinesis after experimental compression of the facial nerve comparing intratemporal and extratemporal lesions. Laryngoscope, 2010,120(5):1022–1027
Hinrichsen CF, Watson CD. The facial nucleus of the rat: representation of facial muscles revealed by retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. Anat Rec, 1984,209(3):407–415
Ashwell KW. The adult mouse facial nerve nucleus: Morphology and musculotopic organization. J Anat, 1982,135(3):531–538
Choi D, Li D, Raisman G. Fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracers that label the rat facial nucleus: a comparison of Fast Blue, Fluoro-ruby, Fluoroemerald, Fluoro-Gold and DiI. J Neurosci Methods, 2002,117(2):167–172
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Project of Health and Family Planning Commission of Hubei Province (No. WJ2017M179).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Ll., Zhang, E., Li, Cl. et al. Dual Convergence of Facial Nerve Branches Innervating Whisker Pad in Rats. CURR MED SCI 38, 982–988 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1973-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-018-1973-3