Summary
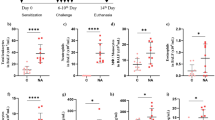
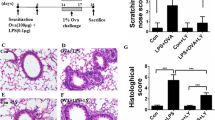
The present study aimed to examine the effect of interleukin (IL)-4 on neutrophil chemotaxis in airway inflammation in asthmatic rats and the possible mechanism. Male Wistar rats were intranasally instilled with recombinant rat (rr) IL-4 (rrIL-4) at different doses [2, 4 or 8 μg/animal, dissolved in 200 μL normal saline (NS)] or rrIL-4 at 4 μg/animal (dissolved in 200 μL NS). NS (200 μL) and LPS (6 mg/kg/animal, dissolved in 200 μL NS) were intranasally given respectively in the negative and positive control groups. Moreover, the asthmatic lung inflammation was induced in rats which were then intranasally treated with rrIL-4 (4 μg/animal) or LPS (6 mg/kg/animal). The normal rats treated with different doses of rrIL-4 and those asthmatic rats were sacrificed 6 h later. And animals instilled with rrIL-4 at 4 μg were sacrificed 6, 12 or 24 h later. The bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and lungs were harvested for detection of leukocyte counts by Wright-Giemsa staining and lung histopathology by haematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining. The levels of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC)-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 in BALF were determined by ELISA. Real-time PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression of CINCs (CINC-1, CINC-2α, CINC-2β, CINC-3) and ICAM-1 in lung tissues. The results showed that the intranasal instillation of IL-4 did not induce a recruitment of neutrophils in BALF in rats. However, IL-4 could increase the CINC-1 level in BALF in a dose-dependent manner at 6 h. But the mRNA expression levels of CINC-1, CINC-2α, CINC-2β, CINC-3 were not significantly increased in lungs of IL-4-treated rats relative to NS negative control group. Moreover, IL-4 was found to augment the mRNA expression of ICAM-1 in lungs and the ICAM-1 level in BALF at 6 h. However, the increase in CINC-1 and ICAM-1 levels in BALF of IL-4-treated asthmatic rats was not significantly different from that in untreated asthmatic rats. These findings indicate that IL-4 does not directly recruit neutrophils in the rat lungs, but it may contribute to airway neutrophilia through up-regulation of CINC-1 and ICAM-1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kon OM, Kay AB. T cells and chronic asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 1999,118(2–4):133–135
Kay AB. T lymphocytes and their products in atopic allergy and asthma. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol, 1991,94(1–4):189–193
Taube C, Dakhama A, Gelfand EW. Insights into the pathogenesis of asthma utilizing murine models. Int Arch Allerg Immun, 2004,135(2):173–186
Chatila TA. Interleukin-4 receptor signaling pathways in asthma pathogenesis. Trends Mol Med, 2004,10(10):493–499
Sur S, Crotty TB, Kephart GM, et al. Sudden-onset fatal asthma. A distinct entity with few eosinophils and relatively more neutrophils in the airway submucosa? Am Rev Respir Dis, 1993,148(3):713–719
Norzila MZ, Fakes K, Henry RL, et al. Interleukin-8 secretion and neutrophil recruitment accompanies induced sputum eosinophil activation in children with acute asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2000,161(3 Pt 1):769–774
Fahy JV, Kim KW, Liu J, et al. Prominent neutrophilic inflammation in sputum from subjects with asthma exacerbation. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 1995,95(4):843–852
Lamblin C, Gosset P, Tillie-Leblond I, et al. Bronchial neutrophilia in patients with noninfectious status asthmaticus. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 1998,157(2):394–402
Turner MO, Hussack P, Sears MR, et al. Exacerbations of asthma without sputum eosinophilia. Thorax, 1995,50(10):1057–1061
Mukaida N, Harada A, Matsushima K. Interleukin-8 (IL-8) and monocyte chemotactic and activating factor (MCAF/MCP-1), chemokines essentially involved in inflammatory and immune reactions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 1998,9(1):9–23
Wagner JG, Roth RA. Neutrophil migration mechanisms, with an emphasis on the pulmonary vasculature. Pharmacol Rev, 2000,52(3):349–374
Brat DJ, Bellail AC, Van Meir EG. The role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol, 2005,7(2):122–133
Li A, Dubey S, Varney ML, et al. IL-8 directly enhanced endothelial cell survival, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinases production and regulated angiogenesis. J Immunol, 2003,170(6):3369–3376
Lee KS, Jin SM, Kim HJ, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor regulates inflammatory cell migration by reducing ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression in a murine model of toluene diisocyanate-induced asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2003,111(6):1278–1284
Gueders MM, Balbin M, Rocks N, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 deficiency promotes granulocytic allergen-induced airway inflammation. J Immunol, 2005,175(4):2589–2597
Ohbayashi H. Matrix metalloproteinases in lung diseases. Curr Protein Pept Sci, 2002,3(4):409–421
Suzuki R, Miyazaki Y, Takagi K, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of asthma and COPD: Implications for therapy. Treat Respir Med, 2004,3(1):17–27
Nishina K. Expression of CINC-2 is related to the state of differentiation of alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2005,33(5):505–512
Shibata F, Kato H, Konishi K, et al. Differential changes in the concentrations of cytokine induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC)-1 and CINC-2 in exudate during rat lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Cytokine, 1996,8(3):222–226
Shibata F. Identification of a common receptor for three types of rat cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractants (CINCs). Cytokine, 2000,12(9):1368–1373
Green CE, Pearson DN, Camphausen RT, et al. Shear-dependent capping of L-selectin and P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 by E-selectin signals activation of high-avidity beta2-integrin on neutrophils. J Immunol, 2004,172(12):7780–7790
McEver RP, Zhu C. A catch to integrin activation. Nat Immunol, 2007,8(10):1035–1037
Chan SC, Shum DK, Tipoe GL, et al. Upregulation of ICAM-1 expression in bronchial epithelial cells by airway secretions in bronchiectasis. Respir Med, 2008,102(2):287–298
Striz I, Mio T, Adachi Y, et al. IL-4 induces ICAM-1 expression in human bronchial epithelial cells and potentiates TNF-alpha. Am J Physiol, 1999,277(1 Pt 1):L58–L64
Huang H, Lavoie-Lamoureux A, Moran K, et al. IL-4 stimulates the expression of CXCL-8, E-selectin, VEGF, and inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA by equine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2007,292(5):L1147–L1154
Yang DF, Huang H, Guan S, et al. Interleukin(IL)-4 promotion of CXCL-8 gene transcription is mediated by ERK1/2 pathway in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Mol Immunol, 2011,48(15–16):1784–1792
Zhang C, Ge CL, Guo RX, et al. Effect of IL-4 on altered expression of complement activation regulators in rat pancreatic cells during severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol, 2005,11(43):6770–6774
Ratthé C, Ennaciri J, Garcês Gonçalves DM, et al. Interleukin (IL)-4 induces leukocyte infiltration in vivo by an indirect mechanism. Mediators Inflamm, 2009,2009:1–10
Kang JL, Lee HW, Lee HS, et al. Genistein prevents nuclear factor-kappa B activation and acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2001,164(12):2206–2212
Rabb HA, Olivenstein R, Issekutz TB, et al. The role of the leukocyte adhesion molecules VLA-4, LFA-1, and MAC-1 in allergic airway responses in the rat. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 1994,149(5):1186–1191
Livak K Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods, 2001,25(4):402–408
Niiro H, Otsuka T, Izuhara K, et al. Regulation by interleukin-10 and interleukin-4 of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human neutrophils. Blood, 1997,89(5):1621–1628
Marie C, Pitton C, Fitting C, et al. IL-10 and IL-4 synergize with TNF-alpha to induce IL-1ra production by human neutrophils. Cytokine, 1996,8(2):147–151
Colotta F, Re F, Muzio M, et al. Interleukin-1 type II receptor: A decoy target for IL-1 that is regulated by IL-4. Science, 1993,261(5120):472–475
Masinovsky B, Urdal D, Gallatin WM. IL-4 acts synergistically with IL-1 beta to promote lymphocyte adhesion to microvascular endothelium by induction of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. J Immunol, 1990,145(9):2886–2895
Dubois GR, Bruijnzeel PL IL-4-induced migration of eosinophils in allergic inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1994,725:268–273
Hiester AA, Metcalf DR, Campbell PA. Interleukin-4 is chemotactic for mouse macrophages. Cell Immunol, 1992,139(1):72–80
Clinchy B, Elenstrom C, Severinson E, et al. T and B cell collaboration: Induction of motility in small, resting B cells by interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol, 1991,21(6):1445–1451
Boey H, Rosenbaum R, Castracane J, et al. Interleukin-4 is a neutrophil activator. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 1989,83(5):978–984
Lavoie-Lamoureux A, Moran K, Beauchamp G, et al. IL-4 activates equine neutrophils and induces a mixed inflammatory cytokine expression profile with enhanced neutrophil chemotactic mediator release ex vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2010,299(4):L472–L482
Mulligan MS, Jones ML, Vaporciyan AA, et al. Protective effects of IL-4 and IL-10 against immune complex-induced lung injury. J Immunol, 1993,151(10):5666–5674
Perretti M, Szabo C, Thiemermann C. Effect of inter leukin-4 and interleukin-10 on leucocyte migration and nitric oxide production in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol, 1995,116(4):2251–2257
Piela-Smith TH, Broketa G, Hand A, et al. Regulation of ICAM-1 expression and function in human dermal fibroblasts by IL-4. J Immunol, 1992,148(5):1375–1381
Obiri NI, Tandon N, Puri RK. Up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) on human renal cell carcinoma cells by interleukin-4. Int J Cancer, 1995,61(5):635–642
Valent P, Bevec D, Maurer D, et al. Interleukin 4 promotes expression of mast cell ICAM-1 antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1991,88(8):3339–3342
Chinen LT, Cipriano IM, de Oliveira RS, et al. Recombinant interleukin-4-treated macrophages, epithelioid cell surrogates, harbor and arrest mycobacterium avium multiplication in vitro. Microbes Infect, 2006,8(4):965–973
Berger RB, Blackwell NM, Lass JH, et al. IL-4 and IL-13 regulation of ICAM-1 expression and eosinophil recruitment in onchocerca volvulus keratitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2002,43(9):2992–2997
Spoelstra FM, Postma DS, Hovenga H, et al. Interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 differentially regulate ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 expression on human lung fibroblasts. Eur Respir J, 1999,14(4):759–766
Vignola AM, Bonsignore G, Siena L, et al. ICAM-1 and alpha3beta1 expression by bronchial epithelial cells and their in vitro modulation by inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators. Allergy, 2000,55(10):931–939
Jatakanon A, Uasuf C, Maziak W, et al. Neutrophilic inflammation in severe persistent asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 1999,160(5 Pt 1):1532–1539
Yousefi S, Hemmann S, Weber M, et al. IL-8 is expressed by human peripheral blood eosinophils. Evidence for increased secretion in asthma. J Immunol, 1995,154(10):5481–5490
Shannon J, Ernst P, Yamauchi Y, et al. Differences in airway cytokine profile in severe asthma compared to moderate asthma. Chest, 2008,133(2):420–426
Zerfaoui M, Naura AS, Errami Y, et al. Effects of PARP-1 deficiency on airway inflammatory cell recruitment in response to LPS or TNF: Differential effects on CXCR2 ligands and duffy antigen receptor for chemokines. J Leukoc Biol, 2009,86(6):1385–1392
Gjelstrup LC, Boesen T, Kragstrup TW, et al. Shedding of large functionally active CD11/CD18 integrin complexes from leukocyte membranes during synovial inflammation distinguishes three types of arthritis through differential epitope exposure. J Immunol, 2010,185(7):4154–4168
Manicone AM. Role of the pulmonary epithelium and inflammatory signals in acute lung injury. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2009,5(1):63–75
Nathan C. Neutrophils and immunity: Challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol, 2006,6(3):173–182
Yamasawa H, Ishii Y, Kitamura S. Cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Inflammation, 1999, 23(3):263–274
Haddadel B, McCluskie K, Birrell MA, et al. Differential effects of ebselen on neutrophil recruitment, chemokine, and inflammatory mediator expression in a rat model of lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation. J Immunol, 2002,169(2):974–982
Zhao M, Brown DM, Maccallum J, et al. Effect of nippostrongylus brasiliensis L3ES on inflammatory mediator gene transcription in lipopolysaccharide lung inflammation. Parasite Immunol, 2009,31(1):50–56
Mafra de Lima F, Villaverde AB, Salgado MA, et al. Low intensity laser therapy (LILT) in vivo acts on the neutrophils recruitment and chemokines/cytokines levels in a model of acute pulmonary inflammation induced by aerosol of lipopolysaccharide from escherichia coli in rat. J Photochem Photobiol B, 2010,101(3):271–278
Martins JO, Zanoni FL, Martins DO, et al. Insulin regulates cytokines and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene expression through nuclear factor-kappa B activation in LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. Shock, 2009,31(4):404–409
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30770945).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Yl., Huang, H., Zeng, Dx. et al. Interleukin (IL)-4 induces production of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractants (CINCs) and intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 in lungs of asthmatic rats. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 33, 470–478 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1144-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1144-5