Abstract
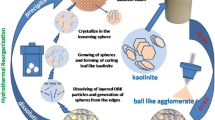
Low-cost porous calcined dolomite microspheres were prepared by simple spray drying and subsequent calcination. Effects of calcination temperature on phase evolution and adsorption properties of MB were investigated systematically. Results showed that microspheres treated at 400 °C kept mainly calcium carbonate (CaMg (CO3)) phase with some small pores, showing better removal efficiency for MB. With the dosage of 20 g/L under the starting concentration of 100 mg/L, the removal efficiency of the microspheres reached 95.6%. The adsorption kinetics data followed the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, and the isotherm data fit the Langmuir isotherm model. The low-cost microsphere could be applied as a promising absorbent for dyes in wastewater filtration and adsorption treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martínez-Huitle C A, Brillas E. Decontamination of Wastewaters Containing Synthetic Organic Dyes by Electrochemical Methods: a General Review[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2009, 87(3–4): 105–145
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R et al. Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Low-cost Adsorbents: a Review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 177(1–3): 70–80
Oller I, Malato S, Sánchez-Pérez J A. Combination of Advanced Oxidation Processes and Biological Treatments for Wastewater Decontamination-a Review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409(20): 4 141–4 166
Pant D, Adholeya A. Biological Approaches for Treatment of Distillery Wastewater: a Review[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2007, 98(12): 2 321–2 334
Mohan D, Singh K P, Singh V K. Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Aqueous Solution Using Low-cost Activated Carbons Derived from Agricultural Waste Materials and Activated Carbon Fabric Cloth[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2005, 44(4): 1 027–1 042
Singh K P, Mohan D, Sinha S, et al. Color Removal from Wastewater Using Low-cost Activated Carbon Derived from Agricultural Waste Material[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2003, 42(9): 1 965–1 976
Foo K Y, Hameed B H. An Overview of Landfill Leachate Treatment via Activated Carbon Adsorption Process[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 171(1): 54–60
Bessa L P, Terra N M, Cardoso V L, et al. Macro-porous Dolomite Hollow Fibers Sintered at Different Temperatures Toward Widened Applications[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43(18): 16 283–16 291
Zheng R, Gao H, Guan J, et al. Characteristics of Cationic Red X-GRL Adsorption by Diatomite tailings[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2017, 32(5): 1 038–1 047
Yagub M T, Sen T K, Afroze S, et al. Dye and Its Removal from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption: A Review[J]. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2014, 209(7): 172
Ekholm P, Kallio K, Turtola E, et al. Adsorption of Cu2+ and Pb2+ Ion on Dolomite Powder.[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 167(1): 1 044–1 049
Ghaemi A, Torab-Mostaedi M, Ghannadi-Maragheh M. Characterizations of Strontium(II) and Barium(II) Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions Using Dolomite Powder[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 190(1–3): 916–921
Walker G M, Hansen L, Hanna J A, et al. Kinetics of a Reactive Dye Adsorption onto Dolomitic Sorbents[J]. Water Research, 2003, 37(9): 2 081–2 089
Boucif F, Marouf-Khelifa K, Batonneau-Gener I, et al. Preparation, Characterisation of Thermally Treated Algerian Dolomite Powders and Application to Azo-dye Adsorption[J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 201(3): 277–282
Yin Y, Lu Y, Gates B, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Mesoscopic Hollow Spheres of Ceramic Materials with Functionalized Interior Surfaces[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2001, 13(4): 1 146–1 148
Cheow W S, Li S, Hadinoto K. Spray Drying Formulation of Hollow Spherical Aggregates of Silica Nanoparticles by Experimental Design[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2010, 88(5–6): 673–685
Katona B, Szebényi G, Orbulov I N. Fatigue Properties of Ceramic Hollow Sphere Filled Aluminium Matrix Syntactic Foams[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2017, 679: 350–357
Song X, Gao L. Fabrication of Hollow Hybrid Microspheres Coated with Silica/Titania via Sol- Gel Process and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activities[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(23): 8 180–8 187
Yu F, Zhang J, Yang Y, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Mesoporous LiFePO4/C Microsphere by Spray Drying Assisted Template Method[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 189(1): 794–797
Stunda-Zujeva A, Irbe Z, Berzina-Cimdina L. Controlling the Morphology of Ceramic and Composite Powders Obtained via Spray Drying-A Review[J]. Ceramics International, 2017, 43: 11 543–11 551
Pal M, Wan L, Zhu Y, et al. Scalable Synthesis of Mesoporous Titania Microspheres via Spray-drying Method[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 479: 150–159
Tao H, Xiong L, Zhu S, et al. Porous Si/C/reduced Graphene Oxide Microspheres by Spray Drying as Anode for Li-ion Batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2017, 797: 16–22
Jiao Y, Lu Y P, Xiao G Y, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Hollow Hydroxyapatite Microspheres by the Centrifugal Spray Drying Method[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 217: 581–584
Qi F, Xu X, Xu J, et al. A Novel Way to Prepare Hollow Sphere Ceramics[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2014, 97(10): 3 341–3 347
Wang A, Lu Y, Zhu R, et al. Effect of Process Parameters on the Performance of Spray Dried Hydroxyapatite Microspheres[J]. Powder Technology, 2009, 191(1–2): 1–6
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, et al. Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Low-cost Adsorbents: a Review[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 177(1–3): 70–80
Yang J, Cai K, Xi X, et al. Process and Device for the Preparation of Hollow Microspheres Comprising Centrifugal Atomization[P]. U.S. Patent 8 845 936, 2 014-9–2 030
Qu Y N, Xu J, Su Z G, et al. Lightweight and High-strength Glass Foams Prepared by a Novel Green Spheres Hollowing Technique[J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(2): 2 370–2 377
Cao X Q, Vassen R, Schwartz S, et al. Spray-drying of Ceramics for Plasma-spray Coating[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2000, 20(14–15): 2 433–2 439
Lukasiewicz S J. Spray-drying Ceramic Powders[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1989, 72(4): 617–624
Messing G L, Zhang S C, Jayanthi G V. Ceramic Powder Synthesis by Spray Pyrolysis[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1993, 76(11): 2 707–2 726
Ruan S, Liu J, Yang E H, et al. Performance and Microstructure of Calcined Dolomite and Reactive Magnesia-Based Concrete Samples[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(12): 04 017 236
Wang H, Liu H, Xie J, et al. An insight into the Carbonation of Calcined Clayey Dolomite and Its Performance to Remove Cd (II)[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2017, 150: 63–70
Albadarin A B, Mangwandi C, Al-Muhtaseb A H, et al. Kinetic and Thermodynamics of Chromium Ions Adsorption onto Low-cost Dolomite Adsorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 179(1): 193–202
Vimonses V, Lei S, Jin B, et al. Adsorption of Congo Red by Three Australian Kaolins[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2009, 43(3–4): 465–472
Ziane S, Bessaha F, Marouf-Khelifa K, et al. Single and Binary Adsorption of Reactive Black 5 and Congo Red on Modified Dolomite: Performance and Mechanism[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018, 249: 1 245–1 253
Ma N, Deng Y, Liu W, et al. A One-step Synthesis of Hollow Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica Spheres with Radially Oriented Mesochannels [J]. Chemical Communications, 2016, 52(17): 3 544–3 547
Liu W, Ma N, Li S, et al. A One-step Method for Pore Expansion and Enlargement of Hollow Cavity of Hollow Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica Spheres[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2016: 1–11
Li LH, Xiao J, Liu P, et al. Super Adsorption Capability from Amorphousization of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Dye Removal[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015; 5: 9 028
Hassan A F, Elhadidy H. Production of Activated Carbons from Waste Carpets and Its Application in Methylene Blue Adsorption: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2017, 5(1): 955–963
Li Q, Li Y, Ma X, et al. Filtration and Adsorption Properties of Porous Calcium Alginate Membrane for Methylene Blue Removal from Water[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 316: 623–630
Hu Y, Quan C, Guo M, et al. Preparation of Fe3O4-octadecyltrichlorosilane for Removal of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue: Influence of pH and Ionic Strength on Competitive Adsorption[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2017, 32(6): 1 413–1 419
Xu N, Liu Z, Dong Y, et al. Controllable Synthesis of Mesoporous Alumina with Large Surface Area for High and Fast Fluoride Removal[J]. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(14): 15 253–15 260
Wang S, Ma Q, Zhu Z H. Characteristics of Coal Fly Ash and Adsorption Application[J]. Fuel, 2008, 87(15–16): 3 469–3 473
Ali I. New Generation Adsorbents for Water Treatment[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(10): 5 073–5 091
Gupta V K, Suhas, Ali I, et al. Removal of Rhodamine B, Fast Green, and Methylene Blue from Wastewater Using Red Mud, an Aluminum Industry Waste[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2004, 43(7): 1 740–1 747
Gürses A, Doğar Ç, Yalçın M, et al. The Adsorption Kinetics of the Cationic Dye, Methylene Blue, onto Clay[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 131(1–3): 217–228
Tan I A W, Ahmad A L, Hameed B H. Adsorption of Basic Dye Using Activated Carbon Prepared from Oil Palm Shell: Batch and Fixed Bed Studies[J]. Desalination, 2008, 225(1–3): 13–28
Fu Y, Viraraghavan T. Removal of a Dye from an Aqueous Solution by the Fungus Aspergillus Niger[J]. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 2000, 35(1): 95–111
Kannan N, Sundaram M M. Kinetics and Mechanism of Removal of Methylene Blue by Adsorption on Various Carbons-a Comparative Study[J]. Dyes and Pigments, 2001, 51(1): 25–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51702184 and 51572140) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2017M610085)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, S., Wang, Q., Liu, J. et al. Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorption Properties of Low-cost Porous Calcined Dolomite Microspheres for Removal of Dyes. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 34, 507–515 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2080-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-019-2080-4