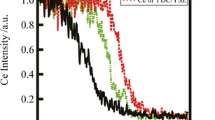
Abstract
A new anode-supported ceria/bismuth oxide bilayer electrolyte solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) was developed. Yittria-ceria double-doped bismuth oxide (Bi0.75Y0.25)1.86Ce0.14O3 ± δ, (YCSB) which showed stable ionic conductivity across the temperature range of 650–500 °C was used as both the second electrolyte layer and as the oxygen ion conductor phase in the cathode. For a cell with a ~ 20 μm 10% gadolinium-doped ceria (GDC) layer and a ~ 12–13 μm YCSB layer, open circuit voltage (OCV) and maximum power density (MPD) of the cell at 650 °C reached 0.833 V and 760 mW/cm2, respectively. OCV stability of this bilayer was measured for 50 h at 625 and 600 °C (100 h in total), and exceptional stability of OCV with zero degradation was observed. In comparison, the cell with 10GDC/erbium-stabilized bismuth oxide (ESB) bilayer electrolyte showed a very rapid degradation of OCV at 600 °C (average hourly degradation rate of − 0.55%/h). In addition to the exceptional OCV stability, this new bilayer electrolyte exhibited no ohmic area-specific resistance (ASR) degradation at 600 and 625 °C. In contrast, the ohmic ASR of the cell with 10GDC/ESB bilayer electrolyte at 600 °C increased by five times over the first 50 h of operation mainly due to the conductivity decay of ESB. The rate of non-ohmic ASR degradation was also decreased by replacing the ESB with YCSB in the cathode structure.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Courtin E, Boy P, Piquero T, Vulliet J, Poirot N, Laberty-Robert C (2012) A composite sol–gel process to prepare a YSZ electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 206:77–83
Haile SM (2003) Fuel cell materials and components☆☆☆The Golden Jubilee Issue—selected topics in materials science and engineering: past, present and future, edited by S. Suresh. Acta Mater 51:5981–6000
Will J, Mitterdorfer A, Kleinlogel C, Perednis D, Gauckler L (2000) Fabrication of thin electrolytes for second-generation solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 131:79–96
Minh NQ (1993) Ceramic Fuel Cells. J Am Ceram Soc 76:563–588
Steele BC, Heinzel A (2001) Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature 414:345–352
Singh P, Minh NQ (2004) Solid oxide fuel cells: technology status. Int J Appl Ceram Technol 1(1):5–15
Wachsman ED, Lee KT (2011) Lowering the temperature of solid oxide fuel cells. Science (New York, NY) 334:935–939
Tsai T, Perry E, Barnett S (1997) Low-temperature solid-oxide fuel cells utilizing thin bilayer electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 144:L130–L132
Wachsman ED (2009) Development of a Lower Temperature SOFC. ECS Trans 25(2):783–788
Park JY, Yoon H, Wachsman ED (2005) Fabrication and characterization of high-conductivity bilayer electrolytes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J Am Ceram Soc 88:2402–2408
Park J-Y, Wachsman ED (2005) Lower temperature electrolytic reduction of CO[sub 2] to O[sub 2] and CO with high-conductivity solid oxide bilayer electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 152:A1654–A1659
Eguchi K, Setoguchi T, Inoue T, Arai H (1992) Electrical properties of ceria-based oxides and their application to solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 52:165–172
Zha S, Xia C, Meng G (2003) Effect of Gd (Sm) doping on properties of ceria electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 115:44–48
Omar S, Wachsman ED, Nino JC (2007) Higher ionic conductive ceria-based electrolytes for solid oxide fuel cells. Appl Phys Lett 91(14):144106
Bishop SR, Stefanik TS, Tuller HL (2011) Electrical conductivity and defect equilibria of Pr0.1Ce0.9O2−δ. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:10165–10173
Yahiro H, Baba Y, Eguchi K, Arai H (1988) High temperature fuel cell with ceria-yttria solid electrolyte. J Electrochem Soc 135:2077–2080
Zhang X, Robertson M, Decès-Petit C, Xie Y, Hui R, Yick S, Styles E, Roller J, Kesler O, Maric R, Ghosh D (2006) NiO–YSZ cermets supported low temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 161:301–307
Hui S, Yang D, Wang Z, Yick S, Decès-Petit C, Qu W, Tuck A, Maric R, Ghosh D (2007) Metal-supported solid oxide fuel cell operated at 400–600°C. J Power Sources 167:336–339
Yamaguchi T, Shimizu S, Suzuki T, Fujishiro Y, Awano M (2008) Demonstration of the rapid start-up operation of cathode-supported sofcs using a microtubular LSM support. J Electrochem Soc 155:B1141–B1144
Yamaguchi T, Shimizu S, Suzuki T, Fujishiro Y, Awano M (2008) Evaluation of micro LSM-supported GDC/ScSZ bilayer electrolyte with LSM–GDC activation layer for intermediate temperature-SOFCs. J Electrochem Soc 155:B423–B426
Yamaguchi T, Shimizu S, Suzuki T, Fujishiro Y, Awano M (2009) Effect of Anode Composition on the Performances of Cathode Supported Micro Channel SOFCs. ECS Trans 25(2):939–943
Wang Z, Huang X, Lv Z, Zhang Y, Wei B, Zhu X, Wang Z, Liu Z (2015) Preparation and performance of solid oxide fuel cells with YSZ/SDC bilayer electrolyte. Ceram Int 41:4410–4415
Zhang X, Gazzarri J, Robertson M, Decès-Petit C, Kesler O (2008) Stability study of cermet-supported solid oxide fuel cells with bi-layered electrolyte. J Power Sources 185:1049–1055
Seok C, Moon J, Park M, Hong J, Kim H, Son J-W, Lee J-H, Kim B-K, Lee H-W, Yoon KJ (2016) Low-temperature co-sintering technique for the fabrication of multi-layer functional ceramics for solid oxide fuel cells. J Eur Ceram Soc 36:1417–1425
Yang D, Zhang X, Nikumb S, Decès-Petit C, Hui R, Maric R, Ghosh D (2007) Low temperature solid oxide fuel cells with pulsed laser deposited bi-layer electrolyte. J Power Sources 164:182–188
Koval’chuk AN, et al (2018) Single SOFC with Supporting Ni-YSZ Anode, Bilayer YSZ/GDC Film Electrolyte, and La 2 NiO 4+ δ Cathode. Russ J Electrochem 54(6):541–546
Jee Y, Cho GY, An J, Kim H-R, Son J-W, Lee J-H, Prinz FB, Lee MH, Cha SW (2014) High performance bi-layered electrolytes via atomic layer deposition for solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 253:114–122
Yoo Y (2006) Fabrication and characterization of thin film electrolytes deposited by RF magnetron sputtering for low temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 160:202–206
Myung D-H, Hong J, Yoon K, Kim B-K, Lee H-W, Lee J-H, Son J-W (2012) The effect of an ultra-thin zirconia blocking layer on the performance of a 1-μm-thick gadolinia-doped ceria electrolyte solid-oxide fuel cell. J Power Sources 206:91–96
Oh EO, Whang CM, Lee YR, Park SY, Prasad DH, Yoon KJ, Son JW, Lee JH, Lee HW (2012) Extremely thin bilayer electrolyte for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) fabricated by chemical solution deposition (CSD). Adv Mater 24:3373–3377
Qian J, Tao Z, Xiao J, Jiang G, Liu W (2013) Performance improvement of ceria-based solid oxide fuel cells with yttria-stabilized zirconia as an electronic blocking layer by pulsed laser deposition. Int J Hydrog Energy 38:2407–2412
Lee Y, Park YM, Choi GM (2014) Micro-solid oxide fuel cell supported on a porous metallic Ni/stainless-steel bi-layer. J Power Sources 249:79–83
Tsoga A, Gupta A, Naoumidis A, Nikolopoulos P (2000) Gadolinia-doped ceria and yttria stabilized zirconia interfaces: regarding their application for SOFC technology. Acta Mater 48:4709–4714
Gao Z, Kennouche D, Barnett SA (2014) Reduced-temperature firing of solid oxide fuel cells with zirconia/ceria bi-layer electrolytes. J Power Sources 260:259–263
Mukai T, Tsukui S, Yoshida K, Yamaguchi S, Hatayama R, Adachi M, Ishibashi H, Kakehi Y, Satoh K, Kusaka T (2013) Fabrication of Y2O3-doped zirconia/gadolinia-doped ceria bilayer electrolyte thin film SOFC cells of SOFCs by single-pulsed laser deposition processing. J Fuel Cell Science Technol 10:061006
Jordan N, Assenmacher W, Uhlenbruck S, Haanappel VAC, Buchkremer HP, Stöver D, Mader W (2008) Solid state ionics 16: proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Solid State Ionics (SSI-16), Part I, 179: 919–923
Fonseca FC, Uhlenbruck S, Nedéléc R, Buchkremer HP (2010) Properties of bias-assisted sputtered gadolinia-doped ceria interlayers for solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 195:1599–1604
Oh E-O, Whang C-M, Lee Y-R, Park S-Y, Prasad DH, Yoon KJ, Kim B-K, Son J-W, Lee J-H, Lee H-W (2014) Fabrication of thin-film gadolinia-doped ceria (GDC) interdiffusion barrier layers for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells (IT-SOFCs) by chemical solution deposition (CSD). Ceram Int 40:8135–8142
Park T, Lee YH, Cho GY, Ji S, Park J, Chang I, Cha SW (2015) The 7th International Conference on Technological Advances of Thin Films & Surface Coatings (ThinFilms2014), 584 120–124
Yu W, Cho GY, Hong S, Lee Y, Kim YB, An J, Cha SW (2016) PEALD YSZ-based bilayer electrolyte for thin film-solid oxide fuel cells. Nanotechnology 27:415402
Noh H-S, Hong J, Kim H, Yoon KJ, Kim B-K, Lee H-W, Lee J-H, Son J-W (2016) Scale-up of thin-film deposition-based solid oxide fuel cell by sputtering, a commercially viable thin-film technology. J Electrochem Soc 163:F613–F617
Schlupp MVF, Evans A, Martynczuk J, Prestat M (2014) Micro-solid oxide fuel cell membranes prepared by aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition. Adv Energy Mater 4(5):1301383
Yang S-H, Choi H-W (2014) Fabrication of YSZ/GDC bilayer electrolyte thin film for solid oxide fuel cells. Trans Electr Electron Mater 15:189–192
An J, Kim Y-B, Park J, Gür TM, Prinz FB (2013) Three-dimensional nanostructured bilayer solid oxide fuel cell with 1.3 W/cm2 at 450 °C. Nano Lett 13:4551–4555
Tsai T, Barnett SA (1998) Effect of mixed-conducting interfacial layers on solid oxide fuel cell anode performance. J Electrochem Soc 145:1696–1701
Jiang Y, Virkar AV (2003) Fuel composition and diluent effect on gas transport and performance of anode-supported SOFCs. J Electrochem Soc 150:A942–A951
Ji S, Lee YH, Park T, Cho GY, Noh S, Lee Y, Kim M, Ha S, J An, Cha SW (2015) Selected papers from 16th International Conference on Thin Films, October 13-16, 2014, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 591, Part B: 250–254
Martinez-Amesti A, Larranaga A, Rodriguez-Martinez LM, Aguayo AT, Pizarro JL, Nó ML, Laresgoiti A, Arriortua MI (2009) J Electrochem Soc 156:B856eB861
Jiang N, Wachsman ED, Jung S-H (2002) A higher conductivity Bi2O3-based electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 150:347–353
Wachsman ED, Jayaweera P, Jiang N, Lowe DM, Pound BG (1997) Stable high conductivity ceria/bismuth oxide bilayered electrolytes. J Electrochem Soc 144:233–236
Jiang N, Wachsman ED (1999) Structural stability and conductivity of phase‐stabilized cubic bismuth oxides. J Am Ceram Soc 82(11):3057–3064
Wachsman ED, Boyapati S, Kaufman MJ, Jiang N (2000) Modeling of ordered structures of phase‐stabilized cubic bismuth oxides. J Am Ceram Soc 83(8):1964–1968
Park J-Y, Wachsman ED (2006) Stable and high conductivity ceria/bismuth oxide bilayer electrolytes for lower temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Ionics 12:15–20
Wachsman ED (2002) Functionally gradient bilayer oxide membranes and electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 152:657–662
Zhang L, Xia C, Zhao F, Chen F (2010) Thin film ceria–bismuth bilayer electrolytes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells with La0.85Sr0.15MnO3−δ–Y0.25Bi0.75O1.5 cathodes. Mater Res Bull 45:603–608
Ahn JS, Camaratta MA, Pergolesi D, Lee KT, Yoon H, Lee BW, Jung DW, Traversa E, Wachsman ED (2010) Development of high performance ceria/bismuth oxide bilayered electrolyte SOFCs for lower temperature operation. J Electrochem Soc 157:B376–B382
Lee KT, Jung DW, Camaratta MA, Yoon HS, Ahn JS, Wachsman ED (2012) Gd0.1Ce0.9O1.95/Er0.4Bi1.6O3 bilayered electrolytes fabricated by a simple colloidal route using nano-sized Er0.4Bi1.6O3 powders for high performance low temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 205:122–128
Zhang L, Li L, Zhao F, Chen F, Xia C (2011) Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9/Y0.25Bi0.75O1.5 bilayered electrolytes for low-temperature SOFCs with Ag-Y0.25Bi0.75O1.5 composite cathodes. Solid State Ionics 192:557–560
Hou J, Bi L, Qian J, Zhu Z, Zhang J, Liu W (2015) High performance ceria–bismuth bilayer electrolyte low temperature solid oxide fuel cells (LT-SOFCs) fabricated by combining co-pressing with drop-coating. J Mater Chem A 3:10219–10224
Leng Y, Chan S (2006) Anode-supported SOFCs with Y2O3-doped Bi2O3 / Gd2O3-doped CeO2 composite electrolyte film. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 9:A56–A59
Ahn JS, Pergolesi D, Camaratta MA, Yoon H, Lee BW, Lee KT, Jung DW, Traversa E, Wachsman ED (2009) High-performance bilayered electrolyte intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochem Commun 11:1504–1507
Lee KT, Jung DW, Yoon HS, Lidie AA, Camaratta MA, Wachsman ED (2012) Interfacial modification of La0.80Sr0.20MnO3−δ–Er0.4Bi0.6O3 cathodes for high performance lower temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 220:324–330
Hou J, Liu F, Gong Z, Wu Y, Liu W (2015) Different ceria-based materials Gd0.1Ce0.9O2−δ and Sm0.075Nd0.075Ce0.85O2−δ for ceria–bismuth bilayer electrolyte high performance low temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 299:32–39
Hou J, Bi L, Qian J, Gong Z, Zhu Z, Liu W (2016) A novel composite cathode Er 0.4 Bi 1.6 O 3 –Pr 0.5 Ba 0.5 MnO 3−δ for ceria-bismuth bilayer electrolyte high performance low temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J Power Sources 301:306–311
Sanna S, Esposito V, Andreasen JW, Hjelm J, Zhang W, Kasama T, Simonsen SB, Christensen M, Linderoth S, Pryds N (2015) Enhancement of the chemical stability in confined δ-Bi 2 O 3. Nat Mater 14(5):500
Lee JG, Park MG, Yoon HH, Shul YG (2013) Application of GDC-YDB bilayer and LSM-YDB cathode for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J Electroceram 31:231–237
Ruth AL, Lee KT, Clites M, Wachsman ED (2014) Synthesis and characterization of double-doped bismuth oxide electrolytes for lower temperature SOFC application. ECS Trans 64:135–141
Boyapati S, Wachsman ED, Chakoumakos BC (2001) Neutron diffraction study of occupancy and positional order of oxygen ions in phase stabilized cubic bismuth oxides. Solid State Ionics 138:293–304
Boyapati S, Wachsman ED, Jiang N (2001) Effect of oxygen sublattice ordering on interstitial transport mechanism and conductivity activation energies in phase-stabilized cubic bismuth oxides. Solid State Ionics 140:149–160
Huang K, Feng M, Goodenough JB (1996) Bi2O3_Y2O3_CeO2 solid solution oxide-ion electrolyte. Solid State Ionics 89:17–24
Zhang C, Huang K (2017) A new composite cathode for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells with zirconia-based electrolytes. J Power Sources 342:419–426
Jaiswal A, Wachsman ED (2005) Bismuth-ruthenate-based cathodes for IT-SOFCs. J Electrochem Soc 152:A787–A790
Jaiswal A, Hu C-T, Wachsman ED (2007) Bismuth ruthenate-stabilized bismuth oxide composite cathodes for IT-SOFC. J Electrochem Soc 154:B1088–B1094
Jaiswal A, Pesaran A, Omar S, Wachsman ED (2017) Ceria/bismuth oxide bilayer electrolyte based low-temperature SOFCs with stable electrochemical performance. ECS Trans 78:361–370
Yang T, Zhao H, Fang M, Świerczek K, Wang J, Du Z (2019) A new family of Cu-doped lanthanum silicate apatites as electrolyte materials for SOFCs: Synthesis, structural and electrical properties. J Eur Ceram Soc 39(2-3):424–431
Fop S, Skakle JM, McLaughlin AC, Connor PA, Irvine JT, Smith RI, Wildman EJ (2016) Oxide ion conductivity in the hexagonal perovskite derivative Ba3MoNbO8.5. J Am Chem Soc 138:16764–16769
Funding
The authors wish to thank the funding support for this work from the Department of Energy under ARPA-E contract no. DE-AR0000494.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pesaran, A., Jaiswal, A., Ren, Y. et al. Development of a new ceria/yttria-ceria double-doped bismuth oxide bilayer electrolyte low-temperature SOFC with higher stability. Ionics 25, 3153–3164 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02838-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-019-02838-4