Abstract
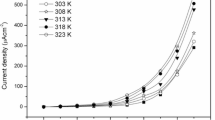
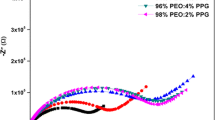
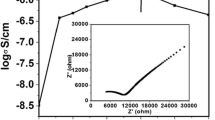
A novel polyethylene oxide (PEO)–based sodium conducting thin nanocomposite polymer electrolyte (NPE) is prepared using solution casting technique. The concentration of the salt has been varied and for EO:Na of 40:1, the room temperature electrical conductivity is found to be increased by two orders of magnitude relative to the pure PEO (σ298 K = 2.8 × 10−9 S cm−1). Ionic conductivity and thermal behavior of PEO40NaC12H25SO4 complex have been investigated with different levels of loading of nano-sized MgO powder whereas the complexation has been confirmed by X-ray diffraction and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic analyses. Structural, thermal, and morphology results have also clearly demonstrated the reduction of crystallinity of the composite polymer electrolyte by the addition of fine MgO nanoparticles. The nanocomposite polymer electrolyte while employed in the fabrication of electrochemical cell has yielded an open-circuit voltage (OCV) of 2.35 V and short-circuit current (SCC) of 412 μA. On incorporation of MgO nanoparticles, it was observed that there is a further enhancement in the conductivity. The room temperature ionic conductivity of PEO–NaC12H25SO4–MgO is relatively high and stable, indicating that it is a promising electrolyte for several thin solid-state energy devices.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fenton DE, Parker JM, Wright PV (1973) Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly(ethylene oxide). Polymer 14:589
Xi J, Qiu X, Li J, Tang X, Zhu W, Chen L (2006) PVDF–PEO blends based microporous polymer electrolyte: effect of PEO on pore configurations and ionic conductivity. J Power Sources 157:501–506
Prosini PP, Fujieda T, Passerini S (2000) Enhanced performance of lithium polymer batteries using a V2O5–PEG composite cathode. Electrochem Commun 2:44–47
De Paoli MA, Casalbore-Miceli G, Girotto EM, Gazotti WA (1999) All polymeric solid state electrochromic devices. Electrochim Acta 44:2983–2991
Ni’mah YL, Cheng MY, Cheng JH, Rick J, Hwang BJ (2015) Solid-state polymer nanocomposite electrolyte of TiO2/PEO/NaClO4 for sodium ion batteries. J Power Sources 278:375–381
Ram Kumar S, Aparna Y (2016) Synthesis and characterization of PEO complexed with NaClO4 soluble base salt and Nb2O5 nano-filler. Int J Eng Res Sci 2:16–24
Hashmi SA, Kumar A, Maurya KK, Chandra S (1990) Proton-conducting polymer electrolyte. I. The polyethylene oxide+ NH4ClO4 system. J Phys D Appl Phys 23:1307–1314
Mohamad AA, Mohamad NS, Yahya MZA, Othman R, Ramesh S, Alias Y, Aroof AK (2003) Ionic conductivity studies of poly(vinyl alcohol) alkaline solid polymer electrolyte and its use in nickel–zinc cells. Solid State Ionics 156:171–177
Parveen A, Anilkumar KR, Patil SD, Roy AS (2013) PEO|SnCl2|PANI composites: as an electrolyte in solid-state battery. Ionics 19:91–97
Xu J, Xiong Q, Liang G, Shen X, Zou H, Xu W (2009) Ion-polymer interactions in SmCl3(H2O)6 doped poly(ethylene oxide) electrolytes. J Macromol Sci Part B 48:856–866
Li Z, Su G, Wang X, Gao D (2005) Micro-porous P(VDF-HFP)-based polymer electrolyte filled with Al2O3 nanoparticles. Solid State Ionics 176:1903–1908
Noor SAM, Ahmad A, Talib IA, Rahman MYA (2010) Morphology, chemical interaction, and conductivity of a PEO-ENR50 based on solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics 16:161–170
Chatterjee S, Salaün F, Campagne C (2014) The influence of 1-butanol and trisodium citrate ion on morphology and chemical properties of chitosan-based microcapsules during rigidification by alkali treatment. Mar Drugs 12:5801–5816
Rathika R, Padmaraj O, Suthanthiraraj SA (2018) Electrical conductivity and dielectric relaxation behaviour of PEO/PVdF-based solid polymer blend electrolytes for zinc battery applications. Ionics 24:243–255
Anantha PS, Hariharan K (2005) Physical and ionic transport studies on poly(ethylene oxide)–NaNO3 polymer electrolyte system. Solid State Ionics 176:155–162
Suthanthiraraj SA, Sheeba DJ (2005) Formation of polyethylene oxide-based composite polymer electrolytes blended with Al2O3 nanoparticles. Indian J Phys 79:807–813
Funding
This study received financial assistance from University Grants Commission (F. No. 4-4/2015-16) (MRP/UGC-SERO), Hyderabad; DST-FIST; and UCG-CPE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheeba, D.J., BR, S. Characteristic studies on PEO-based thin nanocomposite polymer electrolytes. Ionics 25, 2627–2631 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2799-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2799-5