Abstract
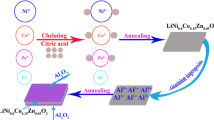
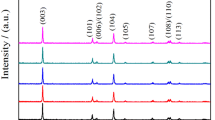
The application of LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 as a high-voltage cathode material for lithium-ion batteries is limited by its poor cycle performance. Therefore, we attempt to improve the cyclability of this material at high voltage by using a doping method and propose a detailed mechanism for the effect of the doping amount on the structure and electrochemical performance. In this work, LiNi0.5-zAlzMn0.5O2 (z = 0.00, 0.03, 0.05, 0.08) electrodes were prepared via a simple co-precipitation followed by a solid-state method. X-ray diffraction and Rietveld refinement revealed that a suitable amount of Al doping into LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 can stabilize the structure and lower the Li/Ni cation mixing, but an excessive doping would lead to Al-ion doping in the lithium layer, which can block lithium diffusion and affect the rate property. Specifically, LiNi0.47Al0.03Mn0.5O2 shows a much higher capacity retention compared to LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 both at 25 °C (78.5 vs. 68.8% at 0.2 C) and 60 °C (70.8 vs. 69.0% at 0.2 C). Moreover, Al-doping can retard the voltage drop during the discharge-charge state, with the discharge voltage for LiNi0.5-zAlzMn0.5O2 (z = 0.00, 0.03, 0.05, 0.08) decreasing slowly with increasing Al content.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thackeray MM, Kang S-H, Johnson CS, Vaughey JT, Benedek R, Hackney SA (2007) Li2MnO3-stabilized LiMO2 (M = Mn, Ni, co) electrodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Mater Chem 17(30):3112–3125
Armstrong AR, Holzapfel M, Novak P, Johnson CS, Kang S-H, Thackeray MM, Bruce PG (2006) Demonstrating oxygen loss and associated structural reorganization in the lithium battery cathode LiNi0.2Li0.2Mn0.6O2. J Am Chem Soc 128(26):8694–8698
Ohzuku T, Ueda A, Nagayama M, Iwakoshi Y, Komori H (1993) COMPARATIVE-STUDY OF LICOO2, LINI1/2CO1/2O2 AND LINIO2 FOR 4-VOLT SECONDARY LITHIUM CELLS. Electrochim Acta 38(9):1159–1167
Kong JZ, Ren C, Jiang YX, Zhou F, Yu C, Tang WP, Li H, Ye SY, Li JX (2016) Li-ion-conductive Li2TiO3-coated li Li0.2Mn0.51Ni0.19Co0.1O2 for high-performance cathode material in lithium-ion battery. J Solid State Electrochem 20(5):1435–1443
Kim JK, Manthiram A (1997) A manganese oxyiodide cathode for rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 390(6657):265–267
Armstrong AR, Bruce PG (1996) Synthesis of layered LiMnO2 as an electrode for rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 381(6582):499–500
Alessandrini F, Conte M, Passerini S, Prosini PP (2001) Overview of ENEA's projects on lithium batteries. J Power Sources 97-8:768–771
Brandt K (1995) PRACTICAL BATTERIES BASED ON THE SWING SYSTEM. J Power Sources 54(1):151–154
Huang HT, Bruce PG (1994) A 4V lithium manganese oxide cathode for rocking-chair lithium-ion cells. J Electrochem Soc 141(9):L106–L107
Shpak AY, Swamy SKK, Dittmer J, Vlasenko NY, Globa NI, Andriiko AA (2016) Formation of stable phases of the li-Mn-co oxide system at 800 a degrees C under ambient oxygen pressure. J Solid State Electrochem 20(1):87–94
Ganesh KS, Reddy BP, Kumar PJ, Jayanthbabu K, Rosaiah P, Hussain OM (2015) Microstructural and electrochemical properties of LiTi (y) co (1-y) O-2 film cathodes prepared by RF sputtering. J Solid State Electrochem 19(12):3621–3627
Li J, Wan L, Cao C (2016) A high-rate and long cycling life cathode for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries: hollow LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 nano/micro hierarchical microspheres. Electrochim Acta 191:974–979
Liu YM, Cao F, Chen BL, Zhao XZ, Suib SL, Chan HLW, Yuan JK (2012) High performance of LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 positive electrode boosted by ordered three-dimensional nanostructures. J Power Sources 206:230–235
Liu Y, Chen B, Cao F, Zhao X, Yuan J (2011) Synthesis of nanoarchitectured LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 spheres for high-performance rechargeable lithium-ion batteries via an in situ conversion route. J Mater Chem 21(28):10437
Mizuno F, Hayashi A, Tadanaga K (2003) All-solid-state lithium secondary batteries using a layer-structured LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 cathode material. J Power Sources 124(1):170–173
Labrini M, Saadoune I, Scheiba F, Almaggoussi A, Elhaskouri J, Amoros P, Ehrenberg H, Brotz J (2013) Magnetic and structural approach for understanding the electrochemical behavior of LiNi0.33Co0.33Mn0.33O2 positive electrode material. Electrochim Acta 111:567–574
Singh G, Thomas R, Kumar A, Katiyar RS (2012) Electrochemical behavior of Cr- doped composite Li2MnO3-LiMn0.5Ni0.5O2 cathode materials. J Electrochem Soc 159(4):A410
Zhao E, Chen M, Chen D, Xiao X, Hu Z (2015) A versatile coating strategy to highly improve the electrochemical properties of layered oxide LiMO(2) (M = Ni0.5Mn0.5 and Ni1/3Mn1/3Co1/3). ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(49):27096–27105
Peng C, Jin J, Chen GZ (2007) A comparative study on electrochemical co-deposition and capacitance of composite films of conducting polymers and carbon nanotubes. Electrochim Acta 53(2):525–537
Svegl F, Orel B, Grabec-Svegl I, Kaucic V (2000) Characterization of spinel Co3O4 and li-doped Co3O4 thin film electrocatalysts prepared by the sol-gel route. Electrochim Acta 45(25–26):4359–4371
Zhang X, Jiang WJ, Mauger A, Qilu GF, Julien CM (2010) Minimization of the cation mixing in Li1-x(NMC)(1-x)O-2 as cathode material. J Power Sources 195(5):1292–1301
Reale P, Privitera D, Panero S, Scrosati B (2007) An investigation on the effect of li+/Ni2+ cation mixing on electrochemical performances and analysis of the electron conductivity properties of LiCo0.33Mn0.33M0.33O2. Solid State Ionics 178(23–24):1390–1397
Okamoto K, Shizuka K, Akai T, Tamaki Y, Okahara K, Nomura M (2006) X-ray absorption fine structure study on layered LiMO2 (M = Ni, Mn, co) cathode materials. J Electrochem Soc 153(6):A1120–A1127
Zhao EY, Chen MM, Hu ZB, Xiao XL, Chen DF (2016) Layered/layered Homostyructure ion conductor coating strategy for high performance Lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 208:64–70
Dou SM, Wang WL, Li HJ, Xin XD (2011) Synthesis and electrochemical performance of LiNi0.475Mn0.475Al0.05O2 as cathode material for lithium-ion battery from Ni-Mn-Al-O precursor. J Solid State Electrochem 15(4):747–751
Yang G, Zhao E, Chen M, Cheng Y, Xue L, Hu Z, Xiao X, Li F (2017) Mg doping improving the cycle stability of LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 at high voltage. J Solid State Electrochem
Kang SH, Kim J, Stoll ME, Abraham D, Sun YK, Amine K (2002) Layered li(Ni0.5-xMn0.5-xM '(2x))O-2 (M ' = co, Al, Ti; x = 0, 0.025) cathode materials for li-ion rechargeable batteries. J Power Sources 112(1):41–48
Pan CJ, Lee YJ, Ammundsen B, Grey CP (2002) Li-6 MAS NMR studies of the local structure and electrochemical properties of Cr-doped lithium manganese and lithium cobalt oxide cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Chem Mater 14(5):2289–2299
Myung ST, Komaba S, Hosoya K, Hirosaki N, Miura Y, Kumagai N (2005) Synthesis of LiNi0.5Mn0.5-xTixO2 by an emulsion drying method and effect of Ti on structure and electrochemical properties. Chem Mater 17(9):2427–2435
Chen M, Zhao E, Chen D, Wu M, Han S, Huang Q, Yang L, Xiao X, Hu Z (2017) Decreasing li/Ni disorder and improving the electrochemical performances of Ni-rich LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 by ca doping. Inorg Chem 56(14):8355–8362
Wang D, Li X, Wang Z, Guo H, Xu Y, Fan Y, Ru J (2016) Role of zirconium dopant on the structure and high voltage electrochemical performances of LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 cathode materials for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 188:48–56
Hu G, Zhang M, Liang L, Peng Z, Du K, Cao Y (2016) Mg–Al–B co-substitution LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 cathode materials with improved cycling performance for lithium-ion battery under high cutoff voltage. Electrochim Acta 190:264–275
Han CJ, Eom WS, Lee SM, Cho WI, Jang H (2005) Study of the electrochemical properties of Ga-doped LiNi0.8Co0.2O2 synthesized by a sol–gel method. J Power Sources 144(1):214–219
Li F, Yang G, Jia G, Shangguan X, Zhuge Q, Bai B (2017) Improvement in the electrochemical performance of a LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 cathode material at high voltage. J Appl Electrochem
Kaneda H (2017) Improving the Cycling Performance and Thermal Stability of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Materials by Nb-doping and Surface Modification. International J Electrochem Sci :4640–4653
Wang Y, Yang Z, Qian Y, Gu L, Zhou H (2015) New insights into improving rate performance of Lithium-rich cathode material. Adv Mater 27(26):3915–3920
Chen J, Tan X, Liu H, Guo L, Zhang J, Jiang Y, Zhang J, Wang H, Feng X, Chu W (2017) Understanding the underlying mechanism of the enhanced performance of Si doped LiNi0.5Mn0.5-xSixO2 cathode material. Electrochim Acta 228:167–174
Zhang J, Gao R, Sun L, Zhang H, Hu Z, Liu X (2016) Unraveling the multiple effects of Li2ZrO3 coating on the structural and electrochemical performances of LiCoO2 as high-voltage cathode materials. Electrochim Acta 209:102–110
Yang G, Jia G, Shangguan X, Zhu Z, Peng Z, Zhuge Q, Li F, Bai B (2017) The synergistic effects of Li2SiO3-coating and Si4+−doping for LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 cathode materials on the structure and the electrochemical properties. J Electrochem Soc 164(12):A2889–A2897
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (U1507106 and U1507114), the Natural Science Foundation of Qinghai Province (2016-GX-101), the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project (Nos. 2016TP1007 and 2017TP1001), the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project (No. 2016TP1007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2235 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, G., Liu, S., Yang, G. et al. The multiple effects of Al-doping on the structure and electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 as cathode material at high voltage. Ionics 24, 3705–3715 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2553-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-018-2553-z