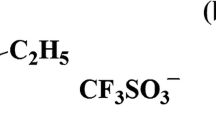Abstract
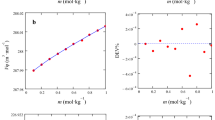
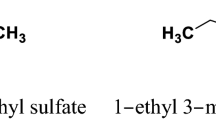
Densities, viscosities, and ionic conductivities were measured for the binary mixtures containing the ionic liquid N-butyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide and methanol over the entire range of compositions at the temperature varying from 253.15 to 318.15 K. The densities and viscosities decrease monotonously with temperature and the content of ionic liquids (ILs). Furthermore, excess isobaric expansion coefficient has been calculated from the experimental densities. The dependence of temperature on the viscosity has been fitted to the Arrhenius law with high precision. The dependence of temperature on the ionic conductivity has also been gauged by both of the Arrhenius and Vogel–Tamman–Fulcher (VTF) equations. In fact, the shape of the curves shows that the temperature dependence of the conductivity does not follow a simple Arrhenius law, but a better fitting of experimental results is achieved using the VTF model. Additionally, the effects of ILs concentration on the viscosity and the conductivity have been examined using the Walden rule, which shows that the variation of conductivity is inversely proportional to viscosity. Excess molar volumes and viscosity deviations for all mixtures are evaluated and well fitted to the Redlich–Kister polynomial expansions. Physicochemical properties show two clearly distinguished behaviors corresponding to ILs-rich and methanol-rich regions, with distinct transport and volumetric properties. The obtained results are discussed in terms of dipolar interactions and hydrogen bonding establishment between ions of ILs and the methanol molecules.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plechkova NV, Seddon KR (2008) Chem Soc Rev 37:123
Greaves TL, Drummond CJ (2008) Chem Rev 108:206
Zhang S, Lu X, Zhou Q, Li X, Zhang X, Li S (2009) Ionic Liquids: physicochemical properties. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Salminen J, Papaiconomou N, Kumar RA, Lee JM, Kerr J, Newman J, Prausnitz J (2007) Fluid Phase Equilib 261:421
Welton T (1999) Chem Rev 99:2071
Kubisa P (2004) Prog Polym Sci 29:3
Nishida T, Tashiro Y, Yamamoto M (2003) J Fluorine Chem 120:135
Alan BM, Stephen FM, Victor RK (1997) J Electrochem Soc 144:84
Wasserscheid P, Welton T (2003) Ionic Liquids in Synthesis. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Annat G, MacFarlane DR, Forsyth M (2007) J Phys Chem B 111:9018
Hofman T, Goldon A, Nevines A, Letcher TM (2008) J Chem Thermodyn 40:580
Rogers RD, Seddon KR (2003) Ionic Liquids as Green Solvents: Progress and Prospects. ACS Symposium,Washington
Van Valkenburg ME, Vaughn RL, Williams M, Wilkes JS (2005) Thermochim Acta 425:181
Abdulagatov IM, Tekin A, Safarov J, Shahverdiyev A, Hassel E (2008) J Chem Thermodyn 40:1386
Abareshi M, Goharshadi EK, Zebarjad S Mo (2009) J Mol Liq 149:66
Domanska U, Laskowska M (2009) J Solution Chem 38:779
Rilo E, Vila J, Garcia M, Varela LM, Cabeza O (2010) J Chem Eng Data 55:5156
Jin H, O'Hare B, Dong J, Arzhantsev S, Baker GA, Wishart JF, Benesi A, Maroncelli M (2008) J Phys Chem B 112:81
Geng Y, Wang T, Yu D, Peng Ch, Liu H, Hu Y (2008) Chin J Chem Eng 16:256
Kiyohara O, d'Arcy PJ, Benson GC (1978) Can J Chem 56:2803
Benson GC, Kiyohara O (1979) J Chem Thermodyn 11:1061
Tamura K, Nakamura M, Murakami S (1997) J Solution Chem 26:1199
Koel M (2008) Ionic Liquids in Chemical Analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Matsumoto H, Yanagida M, Tanimoto K, Nomura M, Kitagawa Y, Miyazaki Y (2000) Chem Lett 29:922
Cammarata L, Kazarian SG, Salter PA, Welton T (2001) J Phys Chem Chem Phys 3:5192
Olivier-Bourbigou H, Magna L (2002) J Mol Catal A 182:183
Pitner W (2008) Ionic liquids. Properties and applications. Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany http://www.merck.de/servlet/PB/menu. Accessed June 2008.
Billard I, Moutiers G, Labet A, El Azzi A, Gaillard G, Mariet C, Lutzenkirchen S (2003) Inorg Chem 42:1726
Seddon KR, Stark A, Torres M-J (2000) Pure Appl Chem 72:2275
Wang JJ, Zhu AL, Zhao Y (2005) J Solution Chem 34:585
Zafarani-Moattar MT, Shekarri H (2005) J Chem Thermodyn 37:1029
Huang JF, Chen PY, Sun IW, Wang SP (2001) Inorg Chim Acta 320:7
Powell RE, Roseveare WE, Eyring H (1941) Ind Eng Chem 33:430
Kincaid F, Eyring H, Stearn AE (1941) Chem Rev 28:301
Andrzejewska E, Podgorska-Golubska M, Stepniak I, Andrzejewski M (2009) Polymer 50:2040
Gu GY, Bouvier S, Wu C, Laura R, Rzeznik M, Abraham KM (2000) Electrochim Acta 45:3127
Yoshizawa M, Hirao M, Ito-Akita K, Ohno H (2001) J Mater Chem 11:1057
Taggougui M, Diaw M, Carré B, Willmann P, Lemordant D (2008) Electrochim Acta 53:5496
Perry RL, Jones KM, Scott WD, Liao Q, Hussey CL (1995) J Chem Eng Data 40:615
Bockris JOM, Reddy AKN (1998) Modern Electrochemistry. Plenum Press, New York
Walden P (1906) Z Phys Chem 55:207
Heintz A, Klasen D, Lehmann JK (2002) J Solution Chem 31:467
Redlich O, Kister AT (1948) Ind Eng Chem 40:345
Sibiya PN, Deenadayalu N (2008) J Chem Thermodyn 40:1041
García-Miaja G, Troncoso J, Romaní L (2008) Fluid Phase Equilib 274:59
Chagnes A, Tougui A, Carré B, Ranganathan N, Lemordant D (2004) J Solution Chem 33:245
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Dr. N. Raouafi for his helpful discussion during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 121 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarrougui, R., Dhahbi, M. & Lemordant, D. Volumetric and transport properties of N-Butyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bis(Trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide–methanol binary mixtures. Ionics 17, 343–352 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-010-0511-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-010-0511-5