Abstract
We derive new results related to the portfolio choice problem for power and logarithmic utilities. Assuming that the portfolio returns follow an approximate log-normal distribution, the closed-form expressions of the optimal portfolio weights are obtained for both utility functions. Moreover, we prove that both optimal portfolios belong to the set of mean-variance feasible portfolios and establish necessary and sufficient conditions such that they are mean-variance efficient. Furthermore, we extend the derived theoretical finding to the general class of the log-skew-normal distributions. Finally, an application to the stock market is presented and the behaviour of the optimal portfolio is discussed for different values of the relative risk aversion coefficient. It turns out that the assumption of log-normality does not seem to be a strong restriction.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
The theory of optimal portfolio choice started with the pioneering contribution of [29]. Markowitz used the variance as a measure of the risk of a portfolio return. He recommended choosing the portfolio weights in such a way that the portfolio variance is minimal for a given level of the expected portfolio return. All of these so-called efficient portfolios lie on the efficient frontier which is a parabola in the mean-variance space.
In the meantime, many further proposals for a portfolio selection have been made. A widely made approach is based on the maximization of an investor’s utility function, where the investor chooses a portfolio for which its utility reaches a maximum possible value [16, 34]. The mean-variance approach of [32] turns out to be fully consistent with the expected utility maximization (see [14]). This result is valid without any distributional assumptions imposed on the returns. Similarly, a quadratic utility provides a closed-form solution under very general conditions [5]. However, there are many other ways to choose the utility function like e.g., the power and the exponential utility function. In these cases, no closed-form solutions can be derived without information on the distribution of the return process [6].
The focus of this paper lies on the power and the logarithmic utility functions. If W denotes the wealth of the investor, then the power utility is given by \(U\left( W\right) =\frac{1}{1-\gamma }W^{1-\gamma },\ \gamma >0, \gamma \ne 1\). The logarithmic utility \(U\left( W\right) =\log W\) is obtained as a limit of the power utility if \(\gamma \) converges to one. The quantity \(\gamma \) is equal to the relative risk aversion which is constant for the power utility (CRRA). Following the classical interpretation by John W. Pratt, this means that an investor would pay the same amount of money relatively to his wealth in order to avoid the risk [8, 11]. This is a very important property and it makes this utility function quite attractive from an economic point of view.
To determine the optimal portfolio for the power utility several numerical procedures have been proposed in the literature Grauer and Hakansson [20], Cover [13]. The first-order conditions for the maximum of the expected utility are derived and a Taylor series expansion is used to transform the expected utility into a linear combination of moments [9]. However, no analytical solution is available in the literature and mostly a numerical approach is applied [8]. Yet another possibility is to make use of distributional assumptions on the predictability of the returns [3] and to combine it with a numerical procedure [10, 28].
The use of the log-normal distribution for modelling asset or portfolio returns has become popular many years ago. In Elton and Gruber [15] an efficient set theorem is derived assuming log-normally distributed portfolio returns. They present an algorithm for determining the efficient portfolio. In the paper on multi-period mean-variance analysis, Hakansson [21] describes a limiting approach for the optimal portfolio choice. Merton and Samuelson [32] discuss the log-normal approach in detail and conclude that it should be very carefully applied.
In this paper, we consider the problem of finding the optimal portfolios for power and logarithmic utilities under the assumption that the portfolio gross returns are approximately log-normally distributed. The analytical expressions of the optimal portfolio weights are obtained for both utility functions. Moreover, we state the conditions under which the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected power utility and the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected logarithmic utility are both mean-variance efficient.
The log-normal distribution used as a model for portfolio returns in this paper has several nice properties. If the portfolio gross return follows a log-normal distribution, then it is possible to determine its higher-order moments straightforwardly. Moreover, if the ratio of mean and standard deviation is large (analogue of Sharpe ratio), then the log-normal distribution is close to the normal one (analytically shown in the paper). This is, for instance, the case when the mean of the portfolio is bounded and its variance is small. Furthermore, the assumption of log-normality introduces the skewness into the model of portfolio return, a well-known feature observed in empirical data. We further extend the log-normality to a general class of log-skew-normal distributions (cf., Lin and Stoyanov [26]), which includes the log-normal model as a special case. The main advantage of the considered general model is that it allows to capture both negative and positive skewness in asset return data, while the log-normal distribution possess a positive skewness only.
In applications, the asset returns \(r_j\) vary in most cases in a range up to \(\pm 15\%\). Thus the corresponding gross returns \(R_j = 1 + r_j\) take values close to 1. Consequently, the overall portfolio mean is close to one while the portfolio variance is usually small. This means that in such a case it behaves like a normal distribution. Moreover, assuming a log-normally distributed portfolio return, its continuously compounded rate of return appears to be normally distributed and vice versa. It is also notable that the normality assumption is often used in a literature, i.e. to model the asset return path, VaR process with normally distributed error terms is taken [5, 6, 8,9,10].
The rest of the paper is structured as follows. In Sects. 2 and 3 the optimization problem is described and the assumptions used in the paper are presented and discussed. Our main findings are given in Sect. 4. In Theorem 1 we derive an explicit formula for the weights of the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility and discuss its properties. In particular, we derived the conditions under which this portfolio is mean-variance efficient in Theorem 2 and show that it converges to the portfolio with the maximum Sharpe ratio when the relative risk aversion converges to infinity. In Sect. 4.2, the analytical results for the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected logarithmic utility are present: the closed-form expression of its weights is provided in Theorem 3, while its mean-variance efficiency is proved in Theorem 4. In Sect. 4.3 we extend the theoretical results to the general family of the log-skew-normal distribution. In Sect. 5 the results of an empirical study are shown. Here we study portfolios based on stocks contained in the German stock market index. We check whether the log-normality assumption on the wealth is fulfilled and whether the conditions imposed in Theorem 1 are fulfilled. It turns out that these assumptions are reasonable and that they are mostly satisfied for the portfolios in our study. Moreover, we compare the portfolio with optimal weights with other portfolio strategies and show the dominance of the new approach.
2 Motivation of the log-normal approximation
Let us define two random variables \(X\sim N(\mu ,\sigma ^2)\) and \(Y\sim \ln N(\ln \mu ,\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2})\). It is easy to see that the first two moments of the discussed distributions coincide if \(\sigma /\mu \) is small, i.e., \(E(Y)=e^{\ln \mu +\frac{\sigma ^2}{2\mu ^2}}\approx \mu \) and \(Var(Y)=e^{2\ln \mu +\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}}(e^{\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}}-1)\approx \sigma ^2\) as \(\sigma /\mu \rightarrow 0\). Indeed, next we show that if \(\sigma /\mu \rightarrow 0\) and \(\mu >0\) then the distribution of Y approaches to the distribution of X.
In order to find the accuracy of the approximation we consider the difference of both distribution functions, namely
Lemma 1
(Log-normal approximation) Let \(\mu >0\) then for \(\Psi (x)\) defined in (1) holds
Thus, difference between normal and log-normal distribution functions approaches zero quite fast as \(\sigma /\mu \rightarrow 0\). So, the smaller \(\sigma /\mu \) the better approximation we receive.
Taking into account that the maximization problem deals with a portfolio gross return, it is well-known that in practice asset returns are close to zero, so one expects to have a portfolio gross return fluctuating around one. Consequently, considering the asset returns to be normally distributed with a mean nearby zero and a small variance we obtain normally distributed gross portfolio returns with a mean around one and a small variance. Meanwhile, the power utility is defined on a nonnegative domain, thus, it is natural to assume that the expected portfolio gross return is positive and the portfolio standard deviation is small. That is why, as it was shown, log-normal distribution can be a good proxy for the normally distributed portfolio returns.
As an illustrative example Fig. 1 describes an identical behaviour of density functions of normal and log-normal distributions for several combinations of \(\mu \) and \(\sigma \).
3 Portfolio selection using a utility function
In this section, we give some notations and basic assumptions used in the paper and discuss the portfolio selection problem for a power utility function.
Suppose that a portfolio consists of k risky assets. Let \(r_i\) denote the relative price change of the ith asset within one period, also known in the literature as the simple one-period return on the ith asset (see e.g., [35]). Let \(\varvec{r} = (r_1,\dots ,r_k)^\prime \) be the vector of (simple) returns. The quantity \(\omega _i\) stands for the relative amount of money invested into the ith asset. Then it holds for the vector of the portfolio weights \(\varvec{\omega }=\left( {\omega }_{1},\omega _{2},\dots ,{\omega }_{k}\right) ^\prime \) that \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \mathbf {1}=1\), where \(\mathbf {1}\) is a vector of ones. The portfolio return at the end of the period is equal to \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \varvec{r}\). If \(W_0\) denotes the wealth of the investor at the beginning of the period, then the wealth at the end of the period is given by
where \(\varvec{R}=\varvec{r}+\mathbf {1}\). The mean vector of \(\varvec{R}\) and its covariance matrix are denoted by \(E(\varvec{R})=\varvec{\varvec{\mu }}\) and \(Var(\varvec{R})=\varvec{\varvec{\Sigma }}\) where \(\varvec{\varvec{\Sigma }}\) is assumed to be positive definite.
Many procedures have been proposed in literature how to construct an optimal portfolio, i.e., how to choose the optimal portfolio weights. [29] developed the mean-variance principle for portfolio selection. The idea is to choose the portfolio weights such that the portfolio variance is minimal for a given value of the portfolio return. Another attempt is based on utility functions. It is described in detail by, e.g., [14]. The optimal weights are obtained by maximizing the expected utility \(U\left( \cdot \right) \) of the wealth W at the end of the investment period and it is given by
There are many possibilities for the choice of a utility function \(U(\cdot )\) (see [34]). In the case of the quadratic utility the solution of (3) is mean-variance efficient, i.e., it coincides with Markowitz’s optimization problem under some conditions (see [4]). Other utility functions considered in the literature are the HARA, the CARA, and the SAHARA utilities (see e.g., [12, 34]).
In this paper we deal with the optimal portfolio choice problem under the power utility function expressed as
It is the only utility function with constant relative risk aversion (cf. [34]) equal to \(\gamma \). The logarithmic utility is a limiting case of the power utility when \(\gamma \) converges to 1 and it is given by
Both the power utility function and the logarithmic utility function are widely applied in practice.
In order to calculate the expected utility, it is necessary to have a statement on the distribution of the portfolio return. There have been many proposals in the literature on how to model the return of stocks. [1] proposed to use the normal distribution for asset returns while [17] and [33] suggested the use of stable distributions. An overview on various proposals can be found in, e.g., Jondeau et al. [23].
Here we choose a slightly different way. In light of the discussion in Sect. 2 we assume that the portfolio return of the investor at the end of the investment period can be well approximated by a log-normal distribution, which is characterized by two parameters \(\alpha \in I\!\!R\) and \(\beta > 0\). We briefly write \(Z \sim \ln \mathcal {N}\left( \alpha ,\beta ^2\right) \) to denote that a random variable Z is log-normally distributed. It holds that \(Z \sim \ln \mathcal {N}\left( \alpha ,\beta ^2\right) \) if and only if \(\ln \, Z \sim \mathcal {N}\left( \alpha ,\beta ^2\right) \) with the density given by
and 0 otherwise. This distribution has a nice property that its moments can be easily derived by
The log-normal distribution has been applied in finance by several authors (see e.g., [25, 31]). If the portfolio return is assumed to be log-normally distributed, then its continuously compounded rate of return is normally distributed and vice versa. Moreover, doing so it is implicitly assumed that the investor’s wealth is positive.
4 Closed-form solutions of optimal portfolio choice problems
In this section, we present the analytical expressions of the optimal portfolio weights obtained for both the power utility and the logarithmic utility. Under the assumption that the portfolio gross return \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \varvec{R}\) at the end of the investment period is approximately log-normally distributed, namely \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \varvec{R}\sim \ln \mathcal {N}\left( \alpha ,\beta ^2\right) \), we get (see Lemma 2 in the Appendix) that
where
are the expected return and the variance of the portfolio with the weights \(\varvec{\omega }\). Now we are ready to formulate our main assumption, which justifies a good log-normal approximation.
Assumption 1
\(\mathbf {(A1)}\) For any \(\varvec{\omega }\) it holds \(\lim \limits _{k\rightarrow \infty }\frac{\sqrt{V}}{X}\rightarrow 0\).
For example, if the portfolio gross return is bounded and the asset universe is large then it is easy to check that many classical portfolios, like global minimum variance portfolio and equally weighted portfolio satisfy Assumption \(\mathbf {(A1)}\) if the covariance matrix of the asset returns \(\varvec{\Sigma }\) is well behaved for increasing dimension k (its largest eigenvalue is uniformly bounded in k). Thus, one can expect that the log-normal approximation works better in case of large dimensional portfolios.
In the following we also use of the set of efficient constants, i.e. of three quantities which uniquely determine the location of the efficient frontier, the set of optimal portfolios obtained as solutions of Markowitz’s optimization problem, in the mean-variance space. They are given by [7]
with
Here, \(R_{GMV}\) denotes the expected portfolio return of a global minimum variance (GMV) portfolio (the portfolio with the smallest variane), \(V_{GMV}\) stands for its variance, and s represents the slope parameter of the efficient frontier which is the upper part of the parabola given by
The whole parabola is known in the literature as a feasible set of optimal portfolios.
4.1 Analytical solution for the power utility
In Theorem 1 we present the closed-form solution of the optimal portfolio choice problem for the power utility function, i.e. the solution of (3) with \(U(\cdot )\) given in (4).
Theorem 1
Assume that \(\mathbf {(A1)}\) holds. If
then the solution of the optimization problem (3) with the power utility function \(U(\cdot )\) from (4) is given by
with
Moreover, if \(\gamma =\gamma _{min}\) then \(\mathcal {D}=0\) and (13) simplifies to
The proof of Theorem 1 is given in the appendix.
Remark 1
Theorem 1 reveals one very important fact: the solution for the power utility function not always exists. Indeed, to guarantee the existence we need to have \(\gamma \ge \gamma _{min}\), which implies that there exists a minimum level of risk aversion \(\gamma _{min}>0\) so that for all \(\gamma \ge \gamma _{min}\) the solution of the optimization problem (3) with the power utility function exists and is unique. Going through the proof of Theorem 1 one can justify that this condition is equivalent to a more technical one, i.e., \(\mathcal {D}\ge 0\) for all \(\gamma >0\).
The expected return of the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility is X, while its variance is equal to \(V=Y-X^2\). Moreover, the maximum value of the optimization problem (3) is given by
It is remarkable that the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected power utility function is located for any relative risk aversion coefficient \(\gamma \) on the set of feasible portfolios, i.e., on the parabola (10). This result is formulated as Corollary 1 with the proof provided in the Appendix.
Corollary 1
Under the assumptions of Theorem 1, it holds that
where
are the weights of the global minimum variance portfolio; \(R_{GMV}\) and s are given in (8) and (9); X is the expected return of the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility as provided in (13).
The expression of optimal portfolio weights (17) coincides with the formula for weights obtained as a solution of Markowitz’s portfolio selection problem. Moreover, the results of Corollary 1 are used to derive conditions on the relative risk aversion coefficient \(\gamma \) which ensure that the obtained portfolio (17) lies in the upper part of the parabola (10) and, hence, the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility function is mean-variance efficient. This finding is summarized in Theorem 2 with the proof moved to the Appendix.
Theorem 2
Under the conditions of Theorem 1, the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected power utility function is mean-variance efficient if and only if
The result of Theorem 2 provides the rigorous mathematical proof of Markowitz’s conjecture that the mean-variance analysis provides a very good proxy to the utility optimization problem with the power utility in the sense that it sophistically approximates its solution (see e.g., [24, 30]). This result is also in-line with the finding of [19]. In the case of the power utility function, Corollary 1 shows that both approaches lead to the same set of optimal portfolios, while Theorem 2 makes one step further and presents the conditions under which the mean-variance efficiency holds for the optimal portfolios obtained by maximizing the expected power utility.
It is remarkable that the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected power utility will never coincide with the global minimum variance portfolio (GMV). This observation follows from the fact that if \(X=R_{GMV}\), then from Theorem 1 we get
what is not possible since \(Y=E\left[ (\varvec{\omega }^\prime \varvec{R})^2\right] \ge 0\).
The further interesting property of the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected power utility is formulated in Corollary 2. Here, we prove that it converges to the optimal portfolio that maximizes the Sharpe ratio, another popular portfolio in the financial literature when \(\gamma \rightarrow \infty \).
Corollary 2
Suppose that the assumptions of Theorem 2 are satisfied.
If \(\gamma \) tends to infinity, then the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility converges to the Sharpe ratio portfolio with the weights:
Remark 2
Note that the Sharpe ratio portfolio presented in (20) is slightly different from a classical one because the mean vector \(\varvec{\mu }\) is not equal to expected value of the asset returns \(\text {E}(\mathbf {r})\) but to \(\text {E}(\mathbf {R})=\text {E}(\mathbf {r})+\mathbf {1}\). This implies a very interesting fact that although the expected power utility portfolio can not be exactly equal to the GMV portfolio they are very close to each other in some situations. Indeed, if \(\text {E}(\mathbf {r})\) is close to zero then the weights presented in (20) are close to the GMV portfolio from (18). This is natural because the GMV portfolio plays the role of the least risky portfolio in the mean-variance framework.
Next, Corollary 3 proves that the expected return of the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected power utility function is not smaller than the expected return of the Sharpe ratio portfolio.
Corollary 3
Suppose that the assumptions of Theorem 2 are satisfied and \(R_{GMV}> 0\). Then the expected return of the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility is larger than or equal to the expected return of the Sharpe ratio portfolio, i.e.
The other interesting statement is related to the coefficient of relative risk aversion. It is natural to conclude that if \(\gamma \) increases (what means the less risky investor) we can expect the decrease of the variance of the portfolio return. So as the result we present described fact in a Corollary 4. Besides, we have also received that the expected portfolio return decreases as well.
Corollary 4
Suppose that the assumptions of Theorem 2 are satisfied and \(R_{GMV}> 0\). Then the expected return and the variance of the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility are decreasing functions of \(\gamma \).
4.2 Analytical solution for the logarithmic utility
In Theorem 3 we present the closed-form solution of the optimization problem (3) for the logarithmic utility given in (5). The proof of the theorem is given in the Appendix.
Theorem 3
Assume that \(\mathbf {(A1)}\) holds. If
where \(\gamma _{min}\) is defined in (11), then the solution of the optimization problem (3) with the logarithmic utility function \(U(\cdot )\) as in (5) is given by
with
The expected return of the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected logarithmic utility is X and its variance is given by \(V=Y-X^2\). Using the results of Theorem 1, we also obtain the maximum value of the optimization problem (3) for the logarithmic utility given by
The expression of the weights obtained for the logarithmic utility function is a special case of the optimal portfolio weights derived for the power utility function corresponding to \(\gamma =1\). This finding is not surprising since the logarithmic utility function is a limiting case of the power utility function when \(\gamma \rightarrow 1\). Although the power utility cannot be defined for \(\gamma =1\) and only its limiting behaviour is considered, that is no longer the case with the formula for the weights presented in Theorem 1 which can also be computed for \(\gamma =1\) as soon as the condition (11) is fulfilled which coincides with (22) of Theorem 3.
Another important application of the results given in Theorems 1 and 3 is that the weights of the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected logarithmic utility function can also be presented in the form of Markowitz’s portfolio, similarly to the expression for the weights obtained for the power utility function and they are given by
with X as in (24), i.e. the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected logarithmic utility function also lies on parabola (10). Finally, Theorem 4 presents conditions under which this portfolio is mean-variance efficient, i.e. it lies on the upper part of the parabola.
Theorem 4
Under the conditions of Theorem 1, the optimal portfolio in the sense of maximizing the expected logarithmic utility is mean-variance efficient if and only if
4.3 Extension to the log-skew-normal distribution
In this section, we extend the previous results to a larger class of distributions, the so-called log-skew-normal distributions. The main feature of this family of distribution is the ability to model negative skewness that is usually observed in the behaviour of asset returns as well as of portfolio returns.
A random variable Z is said to have a log-skew-normal distribution denoted by \(Z \sim \ln \mathcal {SN}(\alpha ,\beta ^2,\nu ,\omega ^2)\) if and only if \(\ln Z\) has a skew-normal distribution denoted by \(\tilde{Z}=\ln Z \sim \mathcal {SN}(\alpha ,\beta ^2,\nu ,\omega ^2)\) and defined by its moment generating function given by (see González-Farías et al. [18], Lemma 1)
where \(\tilde{\nu }=\frac{\beta ^2\nu }{\sqrt{\omega ^2+\nu ^2\beta ^2}}\) and \(\Phi (.)\) denotes the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution.
This class of distribution possesses several nice properties, which appear to be very useful in modeling the stochastic behaviour of the asset returns and the portfolio returns. First, the model parameter \(\nu \) is used to model the skewness in the returns. In contrast to the log-normal distribution, the negative values of skewness, which are usually present in the return series, can be well captured by the new family of distributions by assuming \(\nu <0\). If \(\nu =0\), then the log-skew-normal distribution becomes the log-normal distribution. Furthermore, the considered class of skew-normal distributions is closed with respect to linear transformations (see González-Farías et al. [18], Theorem 1).
The application of (28) leads to
where the last equality is obtained using that \(\nu <0\) corresponding to the negative skewness and by the application of the following approximation (see [2, 22, 27])
In using that \(0.5\beta ^2-0.416\tilde{\nu }^2>0\), we get that (29) can be rewritten by
with \(\tilde{\alpha }=\alpha +0.717\tilde{\nu }\) and \(\tilde{\beta }^2=\beta ^2-2\cdot 0.416\tilde{\nu }^2\), which is the same expression as (6) obtained for the log-normal distribution.
Following the proof of Theorem 1 we get the following expression for the optimal portfolio weights that approximately optimize the power utility function under the assumption that the portfolio return follows a log-skew-normal distribution:
where \(X(\nu )\) and \(Y(\nu )\) are given in (13) and (14) with \(\varvec{\mu }(\nu )\) and \(\varvec{\Sigma }(\nu )\) instead of \(\varvec{\mu }\) and \(\varvec{\Sigma }\). Although the expression of the optimal portfolio weights obtained by maximizing the power utility function under the assumption of a log-skew-normal distribution is the same as one derived in (12) assuming a log-normal distribution, it has to be noted that the mean vector \(\varvec{\mu }(\nu )\) and the covariance matrix \(\varvec{\Sigma }(\nu )\) are model specific. Only in the special case of \(\nu =0\), the solution obtained under the log-skew-normal model will coincide with the one obtained under the log-normal distribution.
5 Empirical study
This section aims to show how the above results can be applied in practice. We will analyze in detail as well whether the demanded assumptions are fulfilled in practice or not.
Our empirical study is based on stocks listed in the German stock index (DAX). We select 17 stocks from the DAX (ADS, ALV, BAYN, BMW, CBK, DAI, DBK, DPW, DTE, HEI, IFX, LHA, LIN, SAP, SIE, TKA, VOW3) and study their behaviour during the time period from September 21, 2014 up to September 17, 2017. Our analysis is based on weekly returns. Consequently, we have 157 observations for each stock.
Based on these 17 stocks we construct portfolios by randomly sampling \(k \in \{4,...,14\}\) assets. Thus, for each k the number of different sets of assets is equal to \(\left( {\begin{array}{c}17\\ k\end{array}}\right) \). From every such set, we determine the optimal portfolios in the sense of maximizing the expected power (logarithmic) utility. The parameters \(\varvec{\mu }\) and \(\varvec{\Sigma }\) are estimated for each portfolio constellation by the sample mean vector and the sample covariance matrix. Moreover, without loss of generality, we set \(W_0 = 1\).
5.1 Validating of model assumption and conditions of theorems
The findings of Theorems 1 and 3 are obtained under certain assumptions. In the following, we analyze whether these conditions are reasonable for the underlying data set.
First, we validate the assumption of log-normally distributed portfolio returns. To test the hypothesis of log-normality, we apply the Shapiro-Wilk test to the logarithmized returns of optimal portfolios that maximize the expected power utility functions for the chosen set of assets. In Table 1 the 25% quantiles of the p-values are provided for several numbers of assets k within the portfolio and several values of the relative risk aversion coefficient \(\gamma \). We remind again that for each fixed k the number of optimal portfolios under consideration is \(\left( {\begin{array}{c}17\\ k\end{array}}\right) \). Table 1 shows that more than 75% of the p-values are always considerably larger than the possible nominal levels of the test, like 5% in our case. Consequently, in at least of 75% of all considered cases, the null hypothesis that the returns of optimal portfolios in the sense of maximizing the expected power utility are log-normally distributed cannot be rejected. For example, choosing \(k=12\) and \(\gamma = 5\) we receive that 75% of p-values are greater than 0.26. Moreover, with an increasing number of assets, the p-values are monotonically increasing as well. Hence, this gives rise to the conclusion that the log-normality assumption seems to be reasonable in many practical situations. Such a result is in line with the portfolio diversification theory, i.e. adding assets into the portfolio will reduce the portfolio variance and thus, the ratio between the portfolio mean and the portfolio variance might increases indicating a better approximation of the log-normal distribution by the normal one. This finding can also be used as a motivation for the validity of Assumption \(\mathbf {(A1)}\) in Sect. 4, namely a better approximation is present for larger portfolio size.
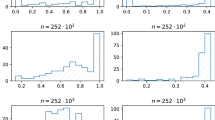
Next, we analyze whether the condition (11) of Theorem 1 is fulfilled in the considered application. Our results are summarized in Fig. 2 (above). Here the percentage of all considered cases are present for several values of the number of assets k in the portfolio and of the relative risk aversion \(\gamma \) when the condition \(\{ \gamma \ge \gamma _{min}\}\) is not fulfilled. The dashed vertical lines represent the values of \(\gamma _{min}(k)\) for every number of assets k. We observe that with decreasing k and increasing \(\gamma \) this condition is almost always satisfied and the number of inappropriate cases goes to zero. For example, the probability of having \(\gamma <\gamma _{min}\) for k assets is virtually zero if \(\gamma >\gamma _{min}(k)\) for all considered values of \(k\in \{4, 5, \ldots , 14\}\). This is in line with the theoretical findings of Theorem 1. Moreover, because \(\gamma _{min}(k)\) is always smaller than one, we can conclude due to Theorem 3 that the solution for the logarithmic portfolios exists as well. Hence, the condition (11) is realistic for both small or large portfolios and the relatively large values of the risk aversion coefficient, at the same time the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility exists with a small probability if \(\gamma \) is close to zero.
Finally, we analyze the condition for the mean-variance efficiency of the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility which is stated in Theorem 2. The results are presented in Fig. 2 (below). Here we proceed in the same way as above for Theorem 1. The second expression in (19) supplies the classical mean-variance efficiency in sense that the accumulated expected portfolio return of GMV portfolio, i.e., \(R_{GMV}=\frac{\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}\varvec{\mu }}{\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}\mathbf {1}}=\frac{\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}\text {E}(\mathbf {r})}{\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}\mathbf {1}}+1\) must be always positive. As we can observe, the related results look the same as the upper part of Fig. 2, which means that the first expression of (19) seems to be a stronger restriction than the second one for the considered data set. Finally, Pennacchi [34], p.21 points out that the empirical evidence on the size of individuals relative risk aversions indicates that this coefficient is usually larger than 1 in practical applications and, as such, the values of \(\gamma _{min}\) smaller than one in Fig. 2 show that the derived optimal portfolio strategy can be applied for all considered portfolio sizes in practice.
5.2 Location of the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility function on the efficient frontier
The other part of the empirical study presented by Fig. 3 is related to the location of the optimal portfolios. As it was shown in (13) and (14) the mean and the variance of the optimal portfolio depends on three parameters: \(\varvec{\mu }, \varvec{\Sigma }, \gamma \). The mean vector and the covariance matrix can be estimated and in our example, we consider four possible number of assets \(k\in \{4, 7, 10, 14\}\). We choose the first k assets in the alphabetic order. Then we build efficient frontier for each combination of assets where we add the location of the optimal portfolios for \(\gamma \in \{1, 2, 5\}\) and the Sharpe ratio portfolio. Like it was proved in Corollary 4 we receive the decrease of the variance and the mean with the increase of a risk aversion coefficient and optimal portfolio tends to the Sharpe ratio portfolio as it was shown in Corollary 2. Also, we receive the increase of both mean and variance of portfolio returns with a larger amount of assets in the portfolio.
5.3 A comparison of several portfolio strategies
Finally, we compare the power utilities of several portfolio strategies with each other. We examine the naive portfolio with equal weights, the Sharpe ratio portfolio, and the optimal portfolio derived in Theorem 1. Note that the GMV portfolio was excluded from the study because it was too close to the Sharpe ratio portfolio for a considered data set (see, Remark 2). In Fig. 4 the empirical distribution functions of the power utility obtained for each of the considered methods are given for the portfolios consisting of \(k=9\) assets and for various values of \(\gamma \). The figure shows that the best results are obtained for the strategy derived in Theorem 1 as expected. Besides, as another visualisation of Corollary 2 result we have that the utility of the Sharpe ratio portfolio nearly coincides with the derived one in Theorem 1 as the coefficient of a relative risk aversion increases. Finally, very bad performance of the equally-weighted (naive) portfolio is observed.
References
Bachelier, L.: Théorie de la spéculation. Gauthier-Villars, Paris (1900)
Bailey, B.: Alternatives to hastings’ approximation to the inverse of the normal cumulative distribution function. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Applied Statistics) 30(3), 275–276 (1981)
Barberis, N.: Investing for the long run when returns are predictable. J. Finance 55(1), 225–264 (2000)
Bodnar, T., Parolya, N., Schmid, W.: On the equivalence of quadratic optimization problems commonly used in portfolio theory. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 229(3), 637–644 (2013)
Bodnar, T., Parolya, N., Schmid, W.: A closed-form solution of the multi-period portfolio choice problem for a quadratic utility function. Ann. Oper. Res. 229(1), 121–158 (2015a)
Bodnar, T., Parolya, N., Schmid, W.: On the exact solution of the multi-period portfolio choice problem for an exponential utility under return predictability. Eur J. Oper. Res. 246(2), 528–542 (2015b)
Bodnar, T., Schmid, W.: Econometrical analysis of the sample efficient frontier. Eur. J. finance 15(3), 317–335 (2009)
Brandt, M.: Portfolio choice problems. Handb. Financ. Econom. 1, 269–336 (2009)
Brandt, M.W., Goyal, A., Santa-Clara, P., Stroud, J.R.: A simulation approach to dynamic portfolio choice with an application to learning about return predictability. Rev. Financ. Stud. 18(3), 831–873 (2005)
Brandt, M.W., Santa-Clara, P.: Dynamic portfolio selection by augmenting the asset space. J. Finance 61(5), 2187–2217 (2006)
Campbell, J.Y., Viceira, L.M.: Strategic Asset Allocation: Portfolio Choice for Long-Term Investors. Clarendon Lectures in Economic. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2002)
Chen, A., Pelsser, A., Vellekoop, M.: Modeling non-monotone risk aversion using sahara utility functions. J. Econ. Theory 146(5), 2075–2092 (2011)
Cover, T.M.: Universal portfolios. Math. finance 1(1), 1–29 (1991)
Dybvig, P.H., Ingersoll, J.E.: Mean-variance theory in complete markets. J. Bus. 55, 233–251 (1982)
Elton, E.J., Gruber, M.J.: Portfolio theory when investment relatives are lognormally distributed. J. Finance 29(4), 1265–1273 (1974)
Elton, E.J., Gruber, M.J., Brown, S.J., Goetzmann, W.N.: Modern Portfolio Theory and Investment Analysis. John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey (2009)
Fama, E.F.: Portfolio analysis in a stable paretian market. Manag. sci. 11(3), 404–419 (1965)
González-Farías, G., Domínguez-Molina, A., Gupta, A.K.: Additive properties of skew normal random vectors. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 126(2), 521–534 (2004)
Grauer, R.R.: Normality, solvency, and portfolio choice. J. Financ. Quant. Anal. 21(3), 265–278 (1986)
Grauer, R.R., Hakansson, N.H.: Gains from international diversification: 1968–85 returns on portfolios of stocks and bonds. J. Finance 42(3), 721–739 (1987)
Hakansson, N.H.: Multi-period mean-variance analysis: toward a general theory of portfolio choice. J. Finance 26(4), 857–884 (1971)
Hamaker, H.C.: Approximating the cumulative normal distribution and its inverse. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Applied Statistics) 27(1), 76–77 (1978)
Jondeau, E., Poon, S.-H., Rockinger, M.: Financial Modeling Under Non-Gaussian Aistributions. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin (2007)
Levy, H., Markowitz, H.M.: Approximating expected utility by a function of mean and variance. Am. Econ. Rev. 69(3), 308–317 (1979)
Limpert, E., Stahel, W.A., Abbt, M.: Log-normal distributions across the sciences: keys and clues. BioScience 51(5), 341–352 (2001)
Lin, G.D., Stoyanov, J.: The logarithmic skew-normal distributions are moment-indeterminate. J. Appl. Probab. 46(3), 909–916 (2009)
Lin, J.-T.: Approximating the normal tail probability and its inverse for use on a pocket calculator. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C (Applied Statistics) 38(1), 69–70 (1989)
Lynch, A.W., Tan, S.: Multiple risky assets, transaction costs, and return predictability: allocation rules and implications for u.s. investors. J. Financ. Quant. Anal. 45(4), 1015–1053 (2010)
Markowitz, H.: Portfolio selection. J. finance 7(1), 77–91 (1952)
Markowitz, H.: Mean-variance approximations to expected utility. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 234(2), 346–355 (2014)
McDonald, J.B.: Probability distributions for financial models. In: Statistical Methods in Finance, Handbook of Statistics, vol. 14, pp. 427 – 461. Elsevier (1996)
Merton, R.C., Samuelson, P.A.: Fallacy of the log-normal approximation to optimal portfolio decision-making over many periods. J. Financ. Econ. 1(1), 67–94 (1974)
Mittnik, S., Rachev, S.T.: Modeling asset returns with alternative stable distributions. Econom. Rev. 12(3), 261–330 (1993)
Pennacchi, G.G.: Theory of Asset Pricing. Pearson/Addison-Wesley, Boston (2008)
Ruppert, D.: Statistics and Data Analysis for Financial Engineering, vol. 13. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Ulrich Horst, the Associate Editor and two anonymous Reviewers for their helpful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
6 Appendix
6 Appendix
Proof of Lemma 1
It is easy to see that \(\Psi (\mu )=0\) and the point \(\mu \) is its minimum. Indeed, let us consider a point different from \(\mu \) and define it as \(x_0=a\mu \), \(a>0\), \(a\ne 1\). Then it holds
Now we consider the upper bound of \(\Psi (x)\)
or
Denoting \(y=\ln \frac{x}{\mu }\) we find
One can see that the equation (34) has three roots (plotting is helpful in this case): the one is greater than zero, the second one is less than zero and already examined \(y=0\). It is also notable that as soon as \(\Psi (\cdot )\) is a continuously differentiable function and \(\Psi (x)\rightarrow 0\ \text {for}\ x\rightarrow \pm \infty \), non zero extrema points are local and global maxima.
For \(y<0\) the expression \((e^y-1)^2\) is smaller than \(\left( \frac{y}{y-1}\right) ^2\) and if \(y<-2\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}\) holds that \(y^2+2\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}y>\left( y+2\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}\right) ^2\), consequently, the solution belongs to the interval \(\left( 1-\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}-\sqrt{\frac{\sigma ^4}{\mu ^4}+1},-2\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}\right) \) which can be derived plugging left hand side of (34) equal to zero and solving the equation \(\left( \frac{y}{y-1}\right) ^2=\left( y+2\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}\right) ^2\) for a negative root.
In case of \(y>0\) it holds that \((e^y-1)^2>\left( \left( 1+\frac{y}{2}\right) ^2-1\right) ^2\) and \(y^2+2\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}y<\left( y+\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}\right) ^2\) and one can derive that the other extrema locates between zero and \(2\frac{\sigma }{\mu }\). As the result we have two intervals for extrema points
\(l_1=\left( e^{1-\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}-\sqrt{\frac{\sigma ^4}{\mu ^4}+1}},e^{-2\frac{\sigma ^2}{\mu ^2}}\right) \) and \(l_2=\left( 1,e^{2\frac{\sigma }{\mu }}\right) \), so \(\Psi (x)\) can be bounded as follows.
Now taking the limit \(\sigma /\mu \rightarrow 0\) we get
where the last equality folows from the fact that \(e^{x}=1+x+O(x^2)\) as \(x\rightarrow 0\). \(\square \)
Lemma 2
Assume that the portfolio return \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \varvec{R}\) at the end of the investment period is log-normally distributed, i.e. \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \varvec{R}\sim \ln \, N(\alpha , \beta ^2)\). Let
Then
Proof of Lemma 2
In using (6), we get
Substituting (36) into (37) and solving these two equations with respect to \(\alpha \) and \(\beta ^2\) leads to the statement of the lemma. \(\square \)
Proof of Theorem 1
For the power utility function, we get that
In order to maximize the expected utility we need to find the maximum of the expression in the exponent of (38) for \(\gamma <1\) or its minimum for \(\gamma >1\) under the side condition \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \varvec{1} = 1\). In both cases the method of Lagrange multipliers is used with the Lagrange function given by
Partial derivation leads to
Let
Then, the multiplication of (40) by \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \) leads to \(\lambda = {\gamma -1}\). Furthermore, multiplying (40) by \({\varvec{\mu }} ^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}/{\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}\mathbf {1}}\) and \(\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}/{\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}\mathbf {1}}\) and using the following equalities
with \(R_{GMV}\), \(V_{GMV}\), and s as in (8), we get
Next, we multiply (43) by \(R_{GMV}\), multiply (44) by \(R_{GMV}^2+s V_{GMV}\), and subtract the first equation from the second one to get
and, consequently,
Substituting (46) to (44) leads to
or equivalently to
The roots of the quadratic equation (47) are given by
where
Finally, from (46) and (48), we get
Moreover, equation (48) shows that the quadratic equation has a solution if and only if \(\mathcal {D}\ge 0\) which is equivalent to (11). Indeed, taking the derivative of \(\mathcal {D}(\gamma )\) with respect to \(\gamma \) and setting it equal to zero one gets
with the solution \(\gamma ^*=\frac{2(1+s)(R^2_{GMV}+sV_{GMV})}{R^2_{GMV}}-2=2s\left( 1+(1+s)\frac{V_{GMV}}{R^2_{GMV}}\right) \). One can easily check that \(\mathcal {D}(\gamma ^*)\) is negative, thus, \(\gamma ^*\) can not be the minimum possible value of \(\gamma \) which guarantees the existence of the solution of (47). On the other side, the second derivative of \(\mathcal {D}(\gamma )\) is positive, which indicates that \(\gamma ^*\) is the global minimum point of the parabola \(\mathcal {D}(\gamma )\). Now from \(\mathcal {D}(0)<0\) follows that the smallest possible value of \(\gamma >0\) should be the positive solution of equation \(\mathcal {D}(\gamma )=0\), which is exactly \(\gamma _{min}\) presented in (11).
Further, inserting two solutions of X and Y into (40), we get two equations for the possible optimal portfolio weights. Since the method of Lagrange multipliers only provides a necessary condition for the optimality in constrained problems we have to analyze the critical points in more detail to check whether a maximum or a minimum is present. We consider the right side of (38) for \((X_+,Y_+)\) and \((X_-,Y_-)\) and prove for all \(\gamma \ge \gamma _{min}\) and \(\gamma \ne 1\) that
and, thus, the maximum is attained at \((X_-,Y_-)\).
In the case of \(\gamma >1\), (50) is equivalent to
or
Similarly, for \(0<\gamma <1\) we get
which coincides with (51).
Consequently, in order to prove (50), it is sufficient to show (51) for \(\gamma >\gamma _{min}\) such that \(\gamma \ne 1\). Or, equivalently, we have to show that for all \(\gamma >\gamma _{min}\) the following inequality holds
First, we prove that the derivative of the function on the left side of (52) with respect to \(\gamma \) is positive. It holds that
Now we calculate \(\frac{\partial }{\partial \gamma }\left( \frac{X_+}{X_-}\right) \) and \(\frac{\partial }{\partial \gamma }\left( \frac{Y_+}{Y_-}\right) \). It holds
where second last equality follows from \((1+s)(R^2_{GMV}+sV_{GMV})=\frac{(\gamma +2)^2R^2_{GMV}-\mathcal {D}}{4(1+\gamma )}\). In order to proceed to the derivative of \(\frac{Y_+}{Y_-}\) we first note that
Thus, taking the derivative of \(\frac{Y_+}{Y_-}\) leads to
Thus, we only need to calculate \(\frac{\partial }{\partial \gamma }\left( \frac{\gamma R_{GMV}+\sqrt{\mathcal {D}}}{\gamma R_{GMV}-\sqrt{\mathcal {D}}}\right) \). It holds
which immediately implies that
Putting all together it follows that for \(\gamma > \gamma _{min}\)
Thus, the function on the left side in (52) is monotonically increasing function of \(\gamma \) and, thus, attains its minimum value at \(\gamma =\gamma _{min}\). So, calculating the value of function in (52) at point \(\gamma =\gamma _{min}\) we get
because when \(\gamma =\gamma _{min}\) it holds \(\mathcal {D}=0\). Hence, the inequality (52) holds for all \(\gamma >\gamma _{min}\) and, thus, the maximum is attained at \(\left( X_{-},Y_{-}\right) \)\(\square \)
Proof of Corollary 1
It holds that
where in using (46) we get
and
where the third line follows from (47).
Hence,
\(\square \)
Proof of Theorem 2
First part, i.e., \(\gamma \ge \gamma _{min}\), follows obviously from the condition (11). For the second one using (15) we first observe that
Next, in order to prove the second inequality in (19), we only have to find in which case
Inserting X from (13) in the above equation (55) we get
So, because of (54) we have \((\gamma -2s)^2R^2_{GMV}\ge \mathcal {D}\) and together with \(\gamma \ge \gamma _{min}>2s\) and (56) it implies that (55) is satisfied \(\iff \)\(R_{GMV}>0\). \(\square \)
Proof of Corollary 2
For the proof of the corollary, we only have to compute the following limit
Now, the application of Corollary 1 leads to
\(\square \)
Proof of Corollary 3
Using (14) and (47), the variance of the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility is given by
which is non-negative if and only if
\(\square \)
Proof of Corollary 4
Using (10) the variance of the optimal portfolio that maximizes the expected power utility is given by
Next, we show that a partial derivative of X with respect to \(\gamma \) is negative what brings the decrease of X and V by \(\gamma \).
\(\square \)
Proof of Theorem 3
For the logarithmic utility function it holds with Lemma 2 that
In order to maximize the expected logarithmic utility (57) under the constrain \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \mathbf {1}=1\), the method of Lagrange multipliers is used with the Lagrange function given by
Partial derivation yields
The multiplication of (59) by \(\varvec{\omega }^\prime \) leads to \(\lambda = -1\). Using the definition of X and Y from (42) and multiplying (59) by \({\varvec{\mu }} ^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}/{\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}\mathbf {1}}\) and \(\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}/{\mathbf {1}^\prime \varvec{\Sigma }^{-1}\mathbf {1}}\), we get
The system of equations (61) and (62) is a partial case of (43) and (44) given in the proof of Theorem 1 which corresponds to \(\gamma =1\). Hence, its solution is given by
where
Finally, for \(\mathcal {D}> 0\) or, equivalently, for \(\gamma _{min}\le 1\) we get that
Hence, \((X_{-},Y_{-})\) maximizes the expected logarithmic utility. \(\square \)
Proof of Theorem 4
The proof of Theorem 4 follows from the proof of Theorem 2 with \(\gamma =1\).
\(\square \)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Bodnar, T., Ivasiuk, D., Parolya, N. et al. Mean-variance efficiency of optimal power and logarithmic utility portfolios. Math Finan Econ 14, 675–698 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11579-020-00270-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11579-020-00270-1
Keywords
- Optimal portfolio selection
- Power utility
- Log-normal distribution
- Mean-variance analysis
- Logarithmic utility