Abstract
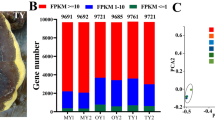
Taiwanofungus camphoratus is a widely used medicinal macrofungus unique to Taiwan, China, and it produces a diverse set of bioactive compounds. In this study, we resequenced the genome and transcriptome of artificially cultivated Taiwanofungus camphoratus and obtained its 29.7-Mb genome. Our aim was to elucidate the possible reasons for its medicinal value and its environmental adaptation from the genomic and evolutionary perspective. Compounds of triterpenoid family are highly abundant in Taiwanofungus camphoratus, and we identified 25 candidate genes that participated in the secondary metabolism leading to these valuable products. We observed fewer genes relating to the CAZymes family in Taiwanofungus camphoratus than in Ganoderma lucidum and Postia placenta, and these genes are considered beneficial for survival. Transcriptome sequencing revealed a large number of differentially expressed genes at various growth stages of Taiwanofungus camphoratus. Our data will be useful for studying the environmental adaptation of Taiwanofungus camphoratus and for developing a strategy to increase the production of its useful secondary metabolites.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Samarrai T, Schmid J (2000) A simple method for extraction of fungal genomic DNA. Lett Appl Microbiol 30:53–56
Amadou C et al (2008) Genome sequence of the β-rhizobium Cupriavidus taiwanensis and comparative genomics of rhizobia. Genome Res 18:1472–1483. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.076448.108
Anders S, Huber W (2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2010-11-10-r106
Andrew PJ, Mayer B (1999) Enzymatic function of nitric oxide synthases. Cardiovasc Res 43:521–531
Burge SW et al (2012) Rfam 11.0: 10 years of RNA families. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D226–D232
Cai TB, Lu D, Tang X, Zhang Y, Landerholm M, Wang PG (2005) New glycosidase activated nitric oxide donors: glycose and 3-morphorlinosydnonimine conjugates. J Org Chem 70:3518–3524. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo050010o
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V, Henrissat B (2009) The carbohydrate-active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D233–D238
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552
Chaisson MJ, Pevzner PA (2008) Short read fragment assembly of bacterial genomes. Genome Res 18:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.7088808
Chang T, Chou W (1995) Antrodia cinnamomea sp. nov. on Cinnamomum kanehirai in Taiwan. Mycol Res 99:756–758
Chang C-J et al (2015) Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Nat Commun 6:7489. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8489
Chen C-C et al (2006) Neuroprotective Diterpenes from the fruiting body of Antrodia camphorata. J Nat Prod 69:689–691
Chen Y-J, Cheng P-C, Lin C-N, Liao H-F, Chen Y-Y, Chen C-C, Lee K-M (2008) Polysaccharides from Antrodia camphorata mycelia extracts possess immunomodulatory activity and inhibits infection of Schistosoma mansoni. Int Immunopharmacol 8:458–467
Chen S et al (2012) Genome sequence of the model medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. Nat Commun 3:913. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1923
Chen Y-T, Hong P-F, Wen L, Lin C-T (2014) Molecular cloning and characterization of a thioredoxin from Taiwanofungus camphorata. Bot Stud 55(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40529-014-0077-z
Conesa A, Götz S (2008) Blast2GO: a comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int J Plant Genomics 2008:619832
Consortium GO (2004) The gene ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D258–D261
Darling AC, Mau B, Blattner FR, Perna NT (2004) Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res 14:1394–1403. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.2289704
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2011) ProtTest 3: fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 27:1164–1165
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Finn RD et al (2013) Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D222–D230
Fischer S et al (2011) Using OrthoMCL to assign proteins to OrthoMCL-DB groups or to cluster proteomes into new Ortholog groups. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics:6.12 11–16.12. 19. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi0612s35
Fujiwara Y, Takeya M, Komohara Y (2014) A novel strategy for inducing the antitumor effects of triterpenoid compounds: blocking the protumoral functions of tumor-associated macrophages via STAT3 inhibition. Biomed Res Int 2014:348539
Gao Q et al (2011) Genome sequencing and comparative transcriptomics of the model entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and M. acridum. PLoS Genet 7:e1001264
Geethangili M, Tzeng Y-M (2011) Review of pharmacological effects of Antrodia camphorata and its bioactive compounds. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2011:212641
Guindon S, Dufayard J-F, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W, Gascuel O (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst Biol 59:307–321
Haas BJ et al (2008) Automated eukaryotic gene structure annotation using EVidenceModeler and the program to assemble spliced alignments. Genome Biol 9:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2008-9-1-r7.
Hahn MW, De Bie T, Stajich JE, Nguyen C, Cristianini N (2005) Estimating the tempo and mode of gene family evolution from comparative genomic data. Genome Res 15:1153–1160. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.3567505
Han L-T, Li J, Huang F, Yu S-G, Fang N-B (2009) Triterpenoid saponins from Anemone flaccida induce apoptosis activity in HeLa cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res 11:122–127
Harris MA et al (2004) The gene ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D258–D261. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh036
Hattori M, Sheu C-C (2006) Compounds from Antrodia camphorata having anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor activity. US Patents
Huang C-Y, Chen Y-T, Wen L, Sheu D-C, Lin C-T (2014) A peroxiredoxin cDNA from Taiwanofungus camphorata: role of Cys31 in dimerization. Mol Biol Rep 41:155–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2848-0
Huber W et al (2015) Orchestrating high-throughput genomic analysis with Bioconductor. Nat Methods 12:115–121. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3252
Jones MG (2007) The first filamentous fungal genome sequences: aspergillus leads the way for essential everyday resources or dusty museum specimens? Microbiology 153:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.2006/001479-0.
Jones P et al (2014) InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30:1236–1240
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27.
Kapitonov VV, Jurka J (2008) A universal classification of eukaryotic transposable elements implemented in Repbase. Nat Rev Genet 9:411–412. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2165-c1
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Stærfeldt H-H, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm160.
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2009-10-3-r25.
Lee C-L et al (2011) First total synthesis of antrocamphin a and its analogs as anti-inflammatory and anti-platelet aggregation agents. Org Biomol Chem 9:70–73
Lee K-H et al (2012) Recent progress of research on medicinal mushrooms, foods, and other herbal products used in traditional Chinese medicine. J Tradit Complement Med 2:1–12
Li H et al (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079
Li R et al (2010) De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequencing. Genome Res 20:265–272
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:955–964
Lu M-YJ et al (2014) Genomic and transcriptomic analyses of the medicinal fungus Antrodia cinnamomea for its metabolite biosynthesis and sexual development. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111:4743–4752. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1417570111
Martinez D et al (2009) Genome, transcriptome, and secretome analysis of wood decay fungus Postia placenta supports unique mechanisms of lignocellulose conversion. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:1954–1959. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0809575106
Meldrum BS (2000) Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the brain: review of physiology and pathology. J Nutr 130:1007S–1015S
Moriya Y, Itoh M, Okuda S, Yoshizawa AC, Kanehisa M (2007) KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W182–W185
Ortiz-Santana B, Lindner DL, Miettinen O, Justo A, Hibbett DS (2013) A phylogenetic overview of the antrodia clade (Basidiomycota, Polyporales). Mycologia 105:1391–1411
Parra G, Bradnam K, Korf I (2007) CEGMA: a pipeline to accurately annotate core genes in eukaryotic genomes. Bioinformatics 23:1061–1067
Powell S et al (2012) eggNOG v3. 0: orthologous groups covering 1133 organisms at 41 different taxonomic ranges. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D284–D289
Rosenheim O, Webster TA (1928) The specificity of ergosterol as parent substance of vitamin D. Biochem J 22:762
Sanodiya BS, Thakur GS, Baghel RK, Prasad G, Bisen P (2009) Ganoderma lucidum: a potent pharmacological macrofungus. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 10:717–742
Stanke M, Morgenstern B (2005) AUGUSTUS: a web server for gene prediction in eukaryotes that allows user-defined constraints. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W465–W467
Suyama M, Torrents D, Bork P (2006) PAL2NAL: robust conversion of protein sequence alignments into the corresponding codon alignments. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W609–W612
Tatusov RL et al (2003) The COG database: an updated version includes eukaryotes. BMC Bioinformatics 4:1
Tempel S (2012) Using and understanding RepeatMasker. Mobile Genetic Elements. 859:29–51. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-603-6_2
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25:1105–1111
Trapnell C et al (2010) Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat Biotechnol 28:511–515. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1621
Tsai T-C et al (2015) Anti-inflammatory effects of Antrodia camphorata, a herbal medicine, in a mouse skin ischemia model. J Ethnopharmacol 159:113–121
Wu S-H et al (2004) Taiwanofungus, a polypore new genus. Fungal Sci 19:109–116
Yang Z (2007) PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol 24:1586–1591
Yeh C-T et al (2009) Cytotoxic triterpenes from Antrodia camphorata and their mode of action in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett 285:73–79
Yu Z-H, Wu S-H, Wang D-M, Chen C-T (2010) Phylogenetic relationships of Antrodia species and related taxa based on analyses of nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Bot Stud 51:1586–1591
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (grant No. 31572384) and the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (grant No. 2011AA100901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: Marco Thines
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Guan, R., Shi, Y. et al. Comparative genome and transcriptome analysis reveal the medicinal basis and environmental adaptation of artificially cultivated Taiwanofungus camphoratus. Mycol Progress 17, 871–883 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-018-1391-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-018-1391-8