Abstract
Background
Patients in the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) intermediate-risk group have heterogeneous prognoses and thus may benefit from improved risk stratification.
Objective
The aim of this study was to analyze inflammatory parameters such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as prognostic markers for IMDC intermediate-risk patients.
Methods
Patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (n = 71) with IMDC intermediate risk who received tyrosine kinase inhibitors as first-line therapy were included in this retrospective study. Multivariate Cox regression analyses were performed to identify prognostic factors for overall survival (OS).
Results
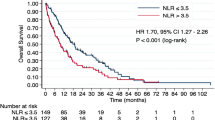
As first-line systemic therapy, 46 (65%), 19 (27%), and 6 (8%) patients received sunitinib, sorafenib, and pazopanib, respectively. An IMDC prognostic score of 1 and 2 were observed in 34 (48%) and 37 (52%) patients, respectively. Mean CRP level was 1.06 mg/dL, and mean NLR was 3.0. Multivariate Cox regression revealed several factors significantly associated with poor OS, including NLR ≥ 3 (vs NLR < 3; hazard ratio [HR] 2.57; p = 0.0228), CRP level ≥ 1 mg/dL (vs CRP < 1 mg/dL; HR 2.89; p = 0.0279), and two or more metastatic organs (vs one organ; HR 3.77; p = 0.0008). Using these risk factors, patients were stratified into the following three risk categories: F0 (no prognostic factors; n = 20), in which the median OS (mOS) was not achieved; F1 (1 prognostic factor; n = 31), in which the mOS was 31 months; and F2–3 (2 or 3 prognostic factors; n = 20) in which the mOS was 13 months (log-rank p < 0.0001).
Conclusion
CRP, NLR, and the number of metastatic organs were independent prognostic factors in IMDC intermediate-risk patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Motzer RJ, Rini BI, McDermott DF, et al. Nivolumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase ii trial. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(13):1430–7.
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(14):1277–90.
Powles T, Albiges L, Staehler M, et al. Updated European Association of Urology guidelines recommendations for the treatment of first-line metastatic clear cell renal cancer. Eur Urol. 2018;73(3):311–5.
Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, et al. Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1816714.
Motzer RJ, Penkov K, Haanen J, et al. Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1816047.
Takamatsu K, Mizuno R, Omura M, et al. Prognostic value of baseline serum c-reactive protein level in intermediate-risk group patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma treated by first-line vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018;16(4):e927–33.
Sella A, Michaelson MD, Matczak E, Simantov R, Lin X, Figlin RA. Heterogeneity of patients with intermediate-prognosis metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15(2):291.e291–299.e291.
Semeniuk Wojtaś A, Lubas A, Stec R, Syryło T, Niemczyk S, Szczylik C. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and C-reactive protein as new and simple prognostic factors in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018;16(3):e685–93.
Sobin LH, Compton CC. TNM seventh edition: what’s new, what’s changed: communication from the International Union Against Cancer and the American Joint Committee on Cancer. Cancer. 2010;116(22):5336–9.
Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C. Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1982;6(7):655–63.
Moch H, Cubilla AL, Humphrey PA, Reuter VE, Ulbright TM. The 2016 WHO classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs-part A: renal, penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol. 2016;70(1):93–105.
Heng DY, Xie W, Regan MM, et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: results from a large, multicenter study. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(34):5794–9.
Bilen MA, Martini DJ, Liu Y, et al. The prognostic and predictive impact of inflammatory biomarkers in patients who have advanced-stage cancer treated with immunotherapy. Cancer. 2019;125(1):127–34.
Sacdalan DB, Lucero JA. Prognostic utility of baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: a review and meta-analysis. Oncotargets Ther. 2018;11:955–65.
Zahoor H, Barata PC, Jia X, et al. Patterns, predictors and subsequent outcomes of disease progression in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients treated with nivolumab. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):107.
Bilen MA, Dutcher GMA, Liu Y, et al. Association between pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and outcome of patients with metastatic renal-cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018;16(3):e563–75.
Lalani A-KA, Xie W, Martini DJ, et al. Change in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in response to immune checkpoint blockade for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):5.
Rini BI, Hutson TE, Figlin RA, et al. Sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: clinical outcome according to International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium risk group. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018;16(4):298–304.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms Nobuko Hata for her secretarial work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No external funding was used in the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Toshio Takagi, Hironori Fukuda, Tsunenori Kondo, Hiroki Ishihara, Kazuhiko Yoshida, Hirohito Kobayashi, Junpei Iizuka, Masayoshi Okumi, Hideki Ishida, and Kazunari Tanabe declare that they have no conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takagi, T., Fukuda, H., Kondo, T. et al. Prognostic Markers for Refined Stratification of IMDC Intermediate-Risk Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Therapy. Targ Oncol 14, 179–186 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-019-00634-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-019-00634-8