Abstract
Apoptosis proteins are related to many diseases. Obtaining the subcellular localization information of apoptosis proteins is helpful to understand the mechanism of diseases and to develop new drugs. At present, the researchers mainly focus on the primary protein sequences, so there is still room for improvement in the prediction accuracy of the subcellular localization of apoptosis proteins. In this paper, a new method named ERT-ECT-PSSM-IS is proposed to predict apoptosis proteins based on the position-specific scoring matrix (PSSM). First, the local and global features of different directions are extracted by evolutionary row transformation (ERT) and cross-covariance of evolutionary column transformation (ECT) based on PSSM (ERT-ECT-PSSM). Second, an improved isometric mapping algorithm (I-SMA) is used to eliminate redundant features. Finally, we adopt a support vector machine (SVM) to classify our results, and the prediction accuracy is evaluated by jackknife cross-validation tests. The experimental results show that the proposed method not only extracts more abundant feature expression but also has better predictive performance and robustness for the subcellular localization of apoptosis proteins in ZD98, ZW225, and CL317 databases.

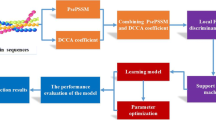
Framework of the proposed prediction model

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhou GP, Doctor K (2003) Subcellular location prediction of apoptosis proteins, Proteins Struct. Funct Genet 50(1):44–48
Chen YL, Li QZ (2007) Prediction of the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins. J Theor Biol 245(4):775–783
Kuo HH, Ahmad R, Lee GQ, Gao C, Chen HR, Ouyang Z, Szucs MJ, Kim D, Tsibris A, Chun TW, Battivelli E, Verdin E, Rosenberg ES, Carr SA, Yu XG, Lichterfeld M (2018) Anti-apoptosis protein BIRC5 maintains survival of HIV-1-infected CD4 + T cells. Immunity 48(6):1183–1194
Pohl SO, Aqositino M, Dhamarajan A et al (2018) Crosstalk between cellular redox state and the anti-apoptosis protein Bcl-2. Antioxid Redox Signal 29(13):1215–1236
Hasan MA, Ahmad S, Molla MK (2017) Protein subcellular localization prediction using multiple kernel learning based support vector machine. Mol BioSyst 13(4):785–795
Shu BS, Jia JW, Zhang JJ, Sethuraman V, Yi X, Zhong G (2018) DnaJ homolog subfamily a member1 (DnaJ1) is a newly discovered anti-apoptosis protein regulated by azadirachtin in Sf9 cells. BMC Genomics 19(1):413–424
Lumbroso D, Soboh S, Avi M et al (2018) Macrophage-derived protein s facilitates apoptosis polymorphonuclear cell clearance by resolution phase macrophages and supports their reprogramming. Front Immunol 9(358):1–10
Arpital B, Sarmishtha R, Supriyo C et al (2018) Evaluating the antimicrobial, apoptosis, and cancer cell gene delivery properties of protein-capped gold nanoparticles synthesized from the edible mycorrhizal fungus tricholoma crassum. Nanoscale Res Lett 13(1):154–170
Zhou H, Yang Y, Shen HB (2016) Hum-mPLoc 3.0: prediction enhancement of human protein subcellular localization through modeling the hidden correlations of gene ontology and functional domain features. Bioinformatics 33(6):843–853
Almagro AJ, Aonderby CK, Sonderby SK et al (2017) DeepLoc: prediction of protein subcellular localization using deep learning. Bioinformatics 33(21):3387–3395
Khan AA, Khan ZK, Kalam MA et al (2018) Inter-kingdom prediction certainty evaluation of protein subcellular localization tools: microbial pathogenesis approach for deciphering host microbe interaction. Brief Bioinform 19(1):12–22
Lópezbegines S, Planabonamaisó A, Méndez A (2018) Molecular determinants of guanylate cyclase activating protein subcellular distribution in photoreceptor cells of the retina. Sci Rep 8(1):2903–2915
Zhang SL, Duan X (2017) Prediction of protein subcellular localization with oversampling approach and Chou’s general PseAAC. J Theor Biol 437(2017):239–250
Qiu JD, Luo SH, Huang JH, Sun XY, Liang RP (2010) Predicting subcellular location of apoptosis proteins based on wavelet transform and support vector machine. Amino Acids 38(4):1201–1208
Paliwal K, Heffernan R, Hanson J et al (2018) Sixty-five years of the long march in protein secondary structure prediction: the final stretch? Brief Bioinform 3(19):482–494
Wang T, Yun JH, Xie Y et al (2017) Finding RNA-protein interaction sites using HMMs. Methods Mol Biol 1552:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6753-7_13
Mandal M, Mukhopadhyay A, Maulik U (2015) Prediction of protein subcellular localization by incorporating multiobjective PSO-based feature subset selection into the general form of Chou’s PseAAC. Med Biol Eng Comput 53(4):331–344
Xiang QL, Liao B, Li X, Xu H, Chen J, Shi Z, Dai Q, Yao Y (2017) Subcellular localization prediction of apoptosis proteins based on evolutionary information and support vector machine[J]. Artif Intell Med 78(2017):41–46
Wang X, Li H, Wang R, Zhang Q, Zhang W, Gan Y (2017) MultiP-Apo: a multilabel predictor for identifying subcellular locations of apoptosis proteins. Comput Intell Neurosci 2017:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9183796
Tan YT, Rosdi BA (2015) FPGA-based hardware accelerator for the prediction of protein secondary class via fuzzy k-nearest neighbors with lempel–ziv complexity-based distance measure. Neurocomputing 148(148):409–419
Xia B, Zhagn H, Li QM et al (2015) PETs: a stable and accurate predictor of protein-protein interacting sites based on extremely-randomized trees. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience 14(8):882–893
Cardon LR, Stormo GD (1992) Expectation maximization algorithm for identifying protein-binding sites with variable lengths from unaligned DNA fragments. J Mol Biol 223(1):159–170
Jia JH, Liu Z, Xiao X, Liu B, Chou KC (2016) iPPBS-Opt: a sequence-based ensemble classifier for identifying protein-protein binding sites by optimizing imbalanced training datasets. Molecules 21(1):95–114
Liang YY, Zhang SS (2018) Prediction of apoptosis protein’s subcellular localization by fusing two different descriptors based on evolutionary information. Acta Biotheor 66(1):61–78
Yu B, Li S, Qiu WY et al (2017) Accurate prediction of subcellular location of apoptosis proteins combining Chou’s PseAAC and PsePSSM based on wavelet denoising. Oncotarget 8(64):107640–107665
Ying LC, Qian ZL (2007) Prediction of apoptosis protein subcellular location using improved hybrid approach and pseudo-amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 248(2):377–381
Zhang ZH, Wang ZH, Zhang ZR, Wang YX (2006) A novel method for apoptosis protein subcellular localization prediction combining encoding based on grouped weight and support vector machine. FEBS Lett 580(26):6169–6174
Wang G, Dunbrack RL (2003) PISCES: a protein sequence culling server. Bioinformatics 19(12):1589–1591
Liang YY, Zhang SL (2018) Identify gram-negative bacterial secreted protein types by incorporating different modes of PSSM into Chou’s general PseAAC via Kullback-Leibler divergence. J Theor Biol 454(7):22–29
Liu B, Wang SY, Dong QW, Li S, Liu X (2016) Identification of DNA-binding proteins by combining auto-cross covariance transformation and ensemble learning. IEEE Trans NanoBiosci 15(4):328–334
Liu B, Xu J, Fan S, Xu R, Zhou J, Wang X (2015) PseDNA-pro: DNA-binding protein identification by combining Chou’s PseAAC and physicochemical distance transformation. Mol Inform 34(1):8–17
Harsh S, Gaurav R, Sunil L et al (2016) A. Protein fold recognition using genetic algorithm optimized voting scheme and profile bigram. J Softw 11(8):756–767
Chen PF, Zhao RZ, Peng B et al (2017) Method for the dimension reduction of rotor fault data sets by using ISOMAP and LLE. J Vibr Shock 36(6):45–50 and 156
Yang XL, Yang W, Song H, Huang P (2018) Polarimetric SAR image classification using geodesic distances and composite kernels. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 11(5):1606–1614
Huang R, Zhang GP, Chen JL (2018) Semi-supervised discriminant Isomap with application to visualization, image retrieval and classification. Int J Mach Learn Cybern:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0809-6
Zobia SH, Erika RE, Reyer Z (2018) Classification of micro-calcification in mammograms using scalable linear fisher discriminant analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 56(8):1475–1485
Backenroth D, He ZH, Kiryluk K, Boeva V, Pethukova L, Khurana E, Christiano A, Buxbaum JD, Ionita-Laza I (2018) FUN-LDA: a latent dirichlet allocation model for predicting tissue-specific functional effects of noncoding variation: methods and applications. Am J Hum Genet 102(5):920–942
Bhat PC, Prosper HB, Sekmen S, Stewart C (2018) Optimizing event selection with the random grid search. Comput Phys Commun 228(2018):245–257
Chou KC, Zhang CT (1995) Prediction of protein structural classes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 30(4):275–349
Chou KC, Shen HB (2008) Cell-PLoc: a package of Web servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat Protoc 3(2):153–162
Chen YL, Li QZ (2004) Prediction of the subcellular location of apoptosis proteins using the algorithm of measure of diversity. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Neimongol 35(4):413–417
Huang J, Shi F, Zhou HB (2005) Support vector machine for predicting apoptosis proteins types by incorporating protein instability index. Bioinformatiocs 3(3):121–123
Bulashevska A, Eils R (2006) Predicting protein subcellular locations using hierarchical ensemble of bayesian classifiers based on markov chains. Bmc Bioinformatics 7(1):298–311
Qiu JD, Luo SH, Huang JH, Sun XY, Liang RP (2010) Predicting subcellular location of apoptosis proteins based on wavelet transform and support vector machine. Amino Acids 38(4):1201–1208
Zhang L, Liu B, Li DC et al (2009) A novel representation for apoptosis protein subcellular localization prediction using support vector machine. J Theor Biol 259(2):361–365
Liu TG, Zheng XQ, Wang CH, Wang J (2010) Prediction of subcellular location of apoptosis proteins using pseudo amino acid composition: an approach from auto covariance transformation. Protein Pept Lett 17(10):1263–1269
Yu XQ, Zheng XQ, Liu YG et al (2012) Predicting subcellular location of apoptosis proteins with pseudo amino acid composition: approach from amino acid substitution matrix and auto covariance transformation. Amino Acids 42(5):1619–1625
Gu Q, Ding YS, Jiang XY, Zhang TL (2010) Prediction of subcellular location apoptosis proteins with ensemble classifier and feature selection. Amino Acids 38(4):975–983
Liang YY, Liu SY, Zhang SL (2016) Geary autocorrelation and DCCA coefficient: application to predict apoptosis protein subcellular localization via PSSM. PHYSICA A 467(2017):296–306
Zhang SL, Liang YY (2018) Predicting apoptosis protein subcellular localization by integrating auto-cross correlation and PSSM into Chou’s PseAAC. J Theor Biol 457(2018):163–169
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their careful works and valuable suggestions for this study. This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 61463052, 61365001), and the 10th Research Innovation Project of Yunnan University of China (no. 2018Z081), and Yunnan Province University Key Laboratory Construction Plan Funding, China (no. 2019Y0003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruan, X., Zhou, D., Nie, R. et al. Prediction of apoptosis protein subcellular location based on position-specific scoring matrix and isometric mapping algorithm. Med Biol Eng Comput 57, 2553–2565 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-02045-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-02045-3