Abstract
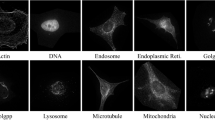
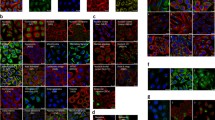
The development of computer technology now allows the quick and efficient automatic fluorescence microscopy generation of a large number of images of proteins in specific subcellular compartments using fluorescence microscopy. Digital image processing and pattern recognition technology can easily classify these images, identify the subcellular location of proteins, and subsequently carry out related work such as analysis and investigation of protein function. Here, based on a fluorescence microscopy 2D image dataset of HeLa cells, the CapsNet network model was used to classify ten types of images of proteins in different subcellular compartments. Capsules in the CapsNet network model were trained to capture the possibility of certain features and variants rather than to capture the characteristics of a specific variant. The capsule at the same level predicted the instantiation parameters of the higher level capsule through the transformation matrix, and the higher level capsule became active when multiple dynamic routing forecasts were consistent. Experiments show that using the CapsNet network model to classify 2D HeLa datasets can achieve higher accuracy.

ᅟ








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boland MV, Murphy RF (2001) A neural network classifier capable of recognizing the patterns of all major subcellular structures in fluorescence microscope images of HeLa cells. Bioinformatics 17(12):1213–1223
Huang K, Murphy RF (2004) Boosting accuracy of automated classification of fluorescence microscope images for location proteomics. BMC Bioinformatics 5:78
Chen X (2006) Automated interpretation of subcellular patterns in fluorescence microscope images for location proteomics. Cytometry 69(7):631–640
Nanni L, Lumini A, Brahnam S (2010) Local binary patterns variants as texture descriptors for medical image analysis. Artif Intell Med 49(2):117–125
Godinez WJ, Hossain I, Lazic SE (2017) A multi-scale convolutional neural network for Phenotyping high-content cellular images. Bioimage Imform 33(13):2010–2019
Pärnamaa T, Parts L (2017) Accurate classification of protein subcellular localization from high throughput microscopy images using deep learning. G3 7(5):1385–1392
Tahir M (2018) Pattern analysis of protein images from fluorescence microscopy using gray level co-occurrence matrix. J King Saud Univ Sci 30(1):29–40
Sabour, S., Nov, C. V, and Hinton, G. E. (2017). Dynamic routing between capsules. Computer vision and pattern recognition, (Nips)
Boland MV, Markey MK, Murphy RF (1998) Automated recognition of patterns characteristic of subcellular structures in fluorescence microscopy images. Cytometry 33(3):366–375
Murphy RF, Velliste M, Porreca G (2003) Robust numerical features for description and classification of subcellular location patterns in fluorescence microscope images. J VLSI Sig Proc Syst 35(3):311–321
Mellman I (1996) Endocytosis and molecular sorting. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 12:575–625. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.12.1.575
Pavelk M, Mironov AA (2008) The Golgi apparatus: state of the art 110 years after Camillo Golgi’s discovery. Springer, Berlin, p 580 ISBN978-3-211-76310-0
Settembre C, Fraldi A, Medina DL, Ballabio A (2013) Signals from the lysosome: a control centre for cellular clearance and energy metabolism. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14(5):283–296. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3565 PMC 4387238
"Archived copy".Archivedfrom the original on 2014-02-06. Retrieved2014-02-24
Vale RD (2003) The molecular motor toolbox for intracellular transport. Cell 112(4):467–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00111-9.PMID12600311
Campbell NA, Williamson B, Heyden RJ (2006) Biology: exploring life. Pearson prentice Hall, Boston, Massachusetts ISBN978-0-13-250882-7
McBride HM, Neuspiel M, Wasiak S (July 2006) Mitochondria: more than just a powerhouse. Curr Biol 16(14):R551–R560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2006.06.054.PMID16860735
Valero T (2014) Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches. Curr Pharm Des 20(35):5507–5509. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161282035140911142118
Sanchis-Gomar F, García-Giménez JL, Gómez-Cabrera MC, Pallardó FV (2014) Mitochondrial biogenesis in health and disease. Molecular and therapeutic approaches. Curr Pharm Des 20(35):5619–5633. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612820666140306095106
O’Sullivan JM, Pai DA, Cridge AG, Engelke DR, Ganley AR (2013) The nucleolus: a raft adrift in the nuclear sea or the keystone in nuclear structure? Biomol Concepts 4(3):277–286. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmc-2012-0043.PMC5100006.PMID25436580
Olson MO, Dundr M (2015) Nucleolus: structure and function. Encyclopedia Life Sci (eLS). https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470015902.a0005975.pub3.ISBN978-0-470-01617-6
Li, C., and Huang, J. (2013). A novel method for cell phenotype image classification. 3rd international conference on electric and electronics (EEIC 2013), (Eeic), 105–107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhao, SG. Fluorescence microscopy image classification of 2D HeLa cells based on the CapsNet neural network. Med Biol Eng Comput 57, 1187–1198 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-01946-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-01946-z