Abstract
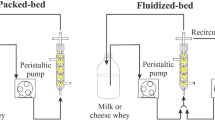
The high prevalence of lactose intolerance was observed in Asian population. Lactose-free milk is a beneficial product to ameliorate this disorder. A lactase immobilized catalytic system for lactose-free milk preparation was established in the present study. The results show that lactase was covalently immobilized on the glass microspheres exhibited a highly efficient catalytic manner (the immobilization yield is about 83.2%) over other three solid carriers (PAN beads, cellulose beads, and nylon pellets). Optimal conditions were determined to be at room temperature and pH 6.0 using O-nitrophenyl-D-galactopyranoside as an indicator. Scanning electron microscopy and electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis provided direct evidence that lactase was successfully immobilized on the glass microspheres. Operational reusability was confirmed for more than 10 batch reactions and the stability was capable of sustaining catalytic activity for 62 days (the relative activity is still around 60%). Flow rate of 60 mL/h in the packed lactase immobilized on glass microspheres reactor is the optimal condition for lactose-free milk preparation. Lactose within milk can be completely hydrolyzed in 33.3 min. These results provided a good indication for the procedure for lactose-free milk preparation in dairy industry.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.W. Horner, M.L. Dunn, D.L. Eggett, L.V. Ogden, J. Dairy Sci. 94(7), 3242–3249 (2011)
J. Li, W. Zhang, C. Wang, Q. Yu, R. Dai, X. Pei, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 96(6), 1499–1506 (2012)
L. Jin, Y. Li, X.H. Ren, J.H. Lee, J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 25(8), 1291–1298 (2015)
C.C. Almeida, S.L. Lorena, C.R. Pavan, H.M. Akasaka, M.A. Mesquita, Nutr Clin Pract. 27(2), 247–251 (2012)
FDA, http://www.fda.gov/forconsumers/consumerupdates/ucm094550.htm. Accessed July 04, 2016 (2009)
M. Hartmann, X. Kostrov, Chem. Soc. Rev. 42(15), 6277–6289 (2013)
A. Illanes, L. Wilson, G. Tomasello, Enzym. Microb. Technol. 27(3-5), 270–278 (2000)
K.I. Chen, Y.C. Lo, N.W. Su, C.C. Chou, K.C. Cheng, J. Agric. Food Chem. 60(51), 12540–12546 (2012)
N. Diano, T. Grimaldi, M. Bianco, S. Rossi, K. Gabrovska, G. Yordanova, T. Godjevargova, V. Grano, C. Nicolucci, L. Mita, U. Bencivenga, P. Canciglia, D.G. Mita, J. Agric. Food Chem. 56(23), 11471–11477 (2008)
K.I. Chen, Y.C. Lo, C.W. Liu, R.C. Yu, C.C. Chou, K.C. Cheng, Food Chem. 139(1-4), 79–85 (2013)
W. Zhao, R.J. Yang, T.T. Qian, X. Hua, W.B. Zhang, W. Katiyo, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14(6), 12073–12089 (2013)
Y. Fan, J. Yi, X. Hua, Y. Zhang, R. Yang, Carbohyr Polym 162, 10–15 (2017)
C.L. Pan, B. Hu, W. Li, Y. Sun, H. Ye, X.X. Zeng, J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 61(3-4), 208–215 (2009)
L.F. Chen, G.T. Tsao, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 19(10), 1463–1473 (1977)
J.E. Hoff, S.S. Nielsen, I.C. Peng, J.V. Chambers, J. Dairy Sci. 70(9), 1785–1796 (1987)
W.H. Wu, W.C. Hung, K.Y. Lo, Y.H. Chen, H.P. Wan, K.C. Cheng, Bioresour. Technol. 201, 27–32 (2016)
S. Chiba, M. Yamada, K. Isobe, J. Biosci. Bioeng. 120(3), 263–267 (2015)
C. Hermida, G. Corrales, F.J. Cañada, J.J. Aragón, A. Fernández-Mayoralas, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 15(14), 4836–4840 (2007)
H. Skovbjerg, H. Sjöström, O. Norén, Eur. J. Biochem. 114(3), 653–661 (1981)
A.A. Mendes, P.C. Oliveira, A.M. Vélez, R.C. Giordano, L. Rde Giordano, H.F. de Castro, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 50(3), 503–511 (2012)
I. Bhushan, R. Parshad, G.N. Qazi, V.K. Gupta, J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 23(6), 552–562 (2008)
S.A. Regenhardt, E.J. Mammarella, A.C. Rubiolo, Chem Process Eng 34, 375–385 (2013)
Z. Zhang, R. Zhang, L. Chen, D.J. McClements, Food Chem. 200, 69–75 (2016)
L.S. Wong, F. Khan, J. Micklefield, Chem. Rev. 109(9), 4025–4053 (2009)
N.J. Ronkainen, H.B. Halsall, W.R. Heineman, Chem. Soc. Rev. 39(5), 1747–1763 (2010)
C. Mateo, R. Monti, B.C. Pessela, M. Fuentes, R. Torres, J.M. Guisán, R. Fernández-Lafuente, Biotechnol. Prog. 20(4), 1259–1262 (2004)
S.A. Ansari, Q. Husain, Food Bioprod Process. 90(2), 351–359 (2012)
W. Li, X. Xiang, S. Tang, B. Hu, L. Tian, Y. Sun, H. Ye, X. Zeng, J. Agric. Food Chem. 57(9), 3927–3933 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This study was partly funded by the National Science Council, Taiwan, under contract no. 104-2221-E-002-125-MY3, Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under contract no. 106-2628-E-002-009-MY3, and the Quanzhou Science and Technology Project, China, under contract No. 2017Z016 and No. 2018Z107.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 46 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, CY., Liu, JM., Chen, KI. et al. Lactose-Free Milk Preparation by Immobilized Lactase in Glass Microsphere Bed Reactor. Food Biophysics 13, 353–361 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9541-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-018-9541-8