Abstract
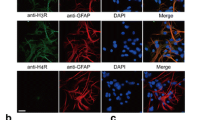
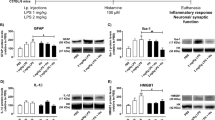
Histamine is a major peripheral inflammatory mediator and a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. We have reported that histamine induces microglia activation and releases proinflammatory factors in primary cultured microglia. Whether histamine has similar effects in vivo is unknown. In the present study, we aimed to investigate the role of histamine and its receptors in the release of inflammatory mediators and activation of microglia in rat brain. We site-directed injected histamine, histamine receptor agonists or histamine receptor antagonists in the rat lateral ventricle using stereotaxic techniques. Flow cytometry was employed to determine histamine receptor expression in rat microglia. Microglia activation was assessed by Iba1 immunohistochemistry. The levels of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) were measured with commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits, TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-10 mRNA expressions were determined with Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR). We found that all four types of histamine receptors were expressed in rat brain microglia. Histamine was able to induce microglia activation and subsequent production of the inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-10, and these effects were partially abolished by H1R and H4R antagonists. However, H2R and H3R antagonists significantly increased production of TNF-α and IL-1β, and decreased IL-10 levels. The H1R or H4R agonists stimulated the production of TNF-α and IL-1β, while the H2R or H3R agonists increased IL-10 release. Our results demonstrate that histamine induces microglia activation and the release of both proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors in rat brain, thus contributing to the development of inflammation in the brain.

Histamine induces microglia activation and the release of both proinflammatory (TNF-α and IL-1β) and anti-inflammatory factors (IL-10) in rat brain, thus contributing to the development of inflammation in the brain.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akundi RS, Candelario-Jalil E, Hess S, Hull M, Lieb K, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Fiebich BL (2005) Signal transduction pathways regulating cyclooxygenase-2 in lipopolysaccharide-activated primary rat microglia. Glia 51(3):199–208
Apolloni S, Fabbrizio P, Amadio S, Napoli G, Verdile V, Morello G, Iemmolo R, Aronica E, Cavallaro S, Volonte C (2017) Histamine regulates the inflammatory profile of SOD1-G93A microglia and the Histaminergic system is dysregulated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Immunol 8:1689
Barata-Antunes S, Cristovao AC, Pires J, Rocha SM, Bernardino L (2017) Dual role of histamine on microglia-induced neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis 1863(3):764–769
Barkauskas DS, Dixon Dorand R, Myers JT, Evans TA, Barkauskas KJ, Askew D, Purgert R, Huang AY (2015) Focal transient CNS vessel leak provides a tissue niche for sequential immune cell accumulation during the asymptomatic phase of EAE induction. Exp Neurol 266:74–85
Biran V, Cochois V, Karroubi A, Arrang JM, Charriaut-Marlangue C, Heron A (2008) Stroke induces histamine accumulation and mast cell degranulation in the neonatal rat brain. Brain Pathol 18(1):1–9
Block ML, Hong JS (2005) Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog Neurobiol 76(2):77–98
Block ML, Zecca L, Hong JS (2007) Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Neurosci 8(1):57–69
Borriello F, Iannone R, Marone G (2017) Histamine release from mast cells and basophils. Handb Exp Pharmacol 241:121–139
Casano AM, Peri F (2015) Microglia: multitasking specialists of the brain. Dev Cell 32(4):469–477
Chikahisa S, Kodama T, Soya A, Sagawa Y, Ishimaru Y, Sei H, Nishino S (2013) Histamine from brain resident MAST cells promotes wakefulness and modulates behavioral states. PLoS One 8(10):e78434
Chiu IM, Morimoto ET, Goodarzi H, Liao JT, O'Keeffe S, Phatnani HP, Muratet M, Carroll MC, Levy S, Tavazoie S, Myers RM, Maniatis T (2013) A neurodegeneration-specific gene-expression signature of acutely isolated microglia from an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mouse model. Cell Rep 4(2):385–401
Ciallella JR, Saporito M, Lund S, Leist M, Hasseldam H, McGann N, Smith CS, Bozyczko-Coyne D, Flood DG (2005) CEP-11004, an inhibitor of the SAPK/JNK pathway, reduces TNF-alpha release from lipopolysaccharide-treated cells and mice. Eur J Pharmacol 515(1–3):179–187
Cianciulli A, Dragone T, Calvello R, Porro C, Trotta T, Lofrumento DD, Panaro MA (2015) IL-10 plays a pivotal role in anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol in activated microglia cells. Int Immunopharmacol 24(2):369–376
Dong H, Zhang W, Zeng X, Hu G, Zhang H, He S, Zhang S (2014) Histamine induces upregulated expression of histamine receptors and increases release of inflammatory mediators from microglia. Mol Neurobiol 49(3):1487–1500
Dong H, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhou X, Qian Y, Zhang S (2017) Suppression of brain mast cells degranulation inhibits microglial activation and central nervous system inflammation. Mol Neurobiol 54(2):997–1007
Dong H, Wang Y, Zhang X, Zhang X, Qian Y, Ding H, Zhang S (2019) Stabilization of brain mast cells alleviates LPS-induced neuroinflammation by inhibiting microglia activation. Front Cell Neurosci 13:191
Elieh-Ali-Komi D, Cao Y (2017) Role of mast cells in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 52(3):436–445
Ferreira R, Santos T, Goncalves J, Baltazar G, Ferreira L, Agasse F, Bernardino L (2012) Histamine modulates microglia function. J Neuroinflammation 9:90
Frick L, Rapanelli M, Abbasi E, Ohtsu H, Pittenger C (2016) Histamine regulation of microglia: gene-environment interaction in the regulation of central nervous system inflammation. Brain Behav Immun 57:326–337
Gao HM, Liu B, Zhang W, Hong JS (2003) Novel anti-inflammatory therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24(8):395–401
Girard S, Tremblay L, Lepage M, Sebire G (2010) IL-1 receptor antagonist protects against placental and neurodevelopmental defects induced by maternal inflammation. J Immunol 184(7):3997–4005
Graeber MB, Streit WJ (2010) Microglia: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 119(1):89–105
Griffin WS, Liu L, Li Y, Mrak RE, Barger SW (2006) Interleukin-1 mediates Alzheimer and Lewy body pathologies. J Neuroinflammation 3:5
Haas HL, Panula P (2016) Histamine receptors. Neuropharmacology 106:1–2
Han Q, Lin Q, Huang P, Chen M, Hu X, Fu H, He S, Shen F, Zeng H, Deng Y (2017) Microglia-derived IL-1beta contributes to axon development disorders and synaptic deficit through p38-MAPK signal pathway in septic neonatal rats. J Neuroinflammation 14(1):52
Hu W, Chen Z (2017) The roles of histamine and its receptor ligands in central nervous system disorders: an update. Pharmacol Ther 175:116–132
Hu X, Leak RK, Shi Y, Suenaga J, Gao Y, Zheng P, Chen J (2015) Microglial and macrophage polarization-new prospects for brain repair. Nat Rev Neurol 11(1):56–64
Iori V, Frigerio F, Vezzani A (2016) Modulation of neuronal excitability by immune mediators in epilepsy. Curr Opin Pharmacol 26:118–123
Jin Y, Silverman AJ, Vannucci SJ (2009) Mast cells are early responders after hypoxia-ischemia in immature rat brain. Stroke 40(9):3107–3112
Joers V, Tansey MG, Mulas G, Carta AR (2017) Microglial phenotypes in Parkinson’s disease and animal models of the disease. Prog Neurobiol 155:57–75
Katoh Y, Niimi M, Yamamoto Y, Kawamura T, Morimoto-Ishizuka T, Sawada M, Takemori H, Yamatodani A (2001) Histamine production by cultured microglial cells of the mouse. Neurosci Lett 305(3):181–184
Kierdorf K, Prinz M (2017) Microglia in steady state. J Clin Invest 127(9):3201–3209
Krakowiak P, Goines PE, Tancredi DJ, Ashwood P, Hansen RL, Hertz-Picciotto I, Van de Water J (2017) Neonatal cytokine profiles associated with autism spectrum disorder. Biol Psychiatry 81(5):442–451
Lannes N, Eppler E, Etemad S, Yotovski P, Filgueira L (2017) Microglia at center stage: a comprehensive review about the versatile and unique residential macrophages of the central nervous system. Oncotarget 8(69):114393–114413
Lenz KM, Nelson LH (2018) Microglia and beyond: innate immune cells as regulators of brain development and behavioral function. Front Immunol 9:698
Lin CC, Edelson BT (2017) New insights into the role of IL-1beta in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 198(12):4553–4560
Lund S, Porzgen P, Mortensen AL, Hasseldam H, Bozyczko-Coyne D, Morath S, Hartung T, Bianchi M, Ghezzi P, Bsibsi M, Dijkstra S, Leist M (2005) Inhibition of microglial inflammation by the MLK inhibitor CEP-1347. J Neurochem 92(6):1439–1451
Ma Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Yang GY (2017) The biphasic function of microglia in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 157:247–272
Medina MA, Quesada AR, Nunez de Castro I, Sanchez-Jimenez F (1999) Histamine, polyamines, and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 57(12):1341–1344
Minghetti L (2005) Role of inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurol 18(3):315–321
Mishra A, Kim HJ, Shin AH, Thayer SA (2012) Synapse loss induced by interleukin-1beta requires pre- and post-synaptic mechanisms. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 7(3):571–578
Morganti JM, Riparip LK, Rosi S (2016) Call off the dog(ma): M1/M2 polarization is concurrent following traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 11(1):e0148001
Mrdjen D, Pavlovic A, Hartmann FJ, Schreiner B, Utz SG, Leung BP, Lelios I, Heppner FL, Kipnis J, Merkler D, Greter M, Becher B (2018) High-dimensional single-cell mapping of central nervous system immune cells reveals distinct myeloid subsets in health, aging, and disease. Immunity 48(2):380–395
Murray KN, Parry-Jones AR, Allan SM (2015) Interleukin-1 and acute brain injury. Front Cell Neurosci 9:18
O’Garra A, Vieira P (2007) T(H)1 cells control themselves by producing interleukin-10. Nat Rev Immunol 7(6):425–428
Orihuela R, McPherson CA, Harry GJ (2016) Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br J Pharmacol 173(4):649–665
Panula P, Nuutinen S (2013) The histaminergic network in the brain: basic organization and role in disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 14(7):472–487
Parsons ME, Ganellin CR (2006) Histamine and its receptors. Br J Pharmacol 147(Suppl 1):S127–S135
Pozzi D, Menna E, Canzi A, Desiato G, Mantovani C, Matteoli M (2018) The communication between the immune and nervous systems: the role of IL-1beta in synaptopathies. Front Mol Neurosci 11:111
Provensi G, Coccurello R, Umehara H, Munari L, Giacovazzo G, Galeotti N, Nosi D, Gaetani S, Romano A, Moles A, Blandina P, Passani MB (2014) Satiety factor oleoylethanolamide recruits the brain histaminergic system to inhibit food intake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(31):11527–11532
Rocha SM, Pires J, Esteves M, Graca B, Bernardino L (2014) Histamine: a new immunomodulatory player in the neuron-glia crosstalk. Front Cell Neurosci 8:120
Rocha SM, Saraiva T, Cristovao AC, Ferreira R, Santos T, Esteves M, Saraiva C, Je G, Cortes L, Valero J, Alves G, Klibanov A, Kim YS, Bernardino L (2016) Histamine induces microglia activation and dopaminergic neuronal toxicity via H1 receptor activation. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):137
Saligrama N, Noubade R, Case LK, del Rio R, Teuscher C (2012) Combinatorial roles for histamine H1-H2 and H3-H4 receptors in autoimmune inflammatory disease of the central nervous system. Eur J Immunol 42(6):1536–1546
Shan L, Bossers K, Luchetti S, Balesar R, Lethbridge N, Chazot PL, Bao AM, Swaab DF (2012a) Alterations in the histaminergic system in the substantia nigra and striatum of Parkinson’s patients: a postmortem study. Neurobiol Aging 33(7):1488.e1–1488.e13
Shan L, Bossers K, Unmehopa U, Bao AM, Swaab DF (2012b) Alterations in the histaminergic system in Alzheimer’s disease: a postmortem study. Neurobiol Aging 33(11):2585–2598
Shan L, Liu CQ, Balesar R, Hofman MA, Bao AM, Swaab DF (2012c) Neuronal histamine production remains unaltered in Parkinson’s disease despite the accumulation of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in the tuberomamillary nucleus. Neurobiol Aging 33(7):1343–1344
Shan L, Swaab DF, Bao AM (2013) Neuronal histaminergic system in aging and age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Exp Gerontol 48(7):603–607
Shan L, Bao AM, Swaab DF (2015) The human histaminergic system in neuropsychiatric disorders. Trends Neurosci 38(3):167–177
Shan Y, Gao Y, Zhang L, Ma L, Shi Y, Liu X (2019) H4 receptor inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB activation by interacting with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6. Neuroscience 398:113–125
Shechter R, Miller O, Yovel G, Rosenzweig N, London A, Ruckh J, Kim KW, Klein E, Kalchenko V, Bendel P, Lira SA, Jung S, Schwartz M (2013) Recruitment of beneficial M2 macrophages to injured spinal cord is orchestrated by remote brain choroid plexus. Immunity 38(3):555–569
Theoharides TC, Stewart JM, Hatziagelaki E, Kolaitis G (2015) Brain “fog,” inflammation and obesity: key aspects of neuropsychiatric disorders improved by luteolin. Front Neurosci 9:225
Tweedie D, Sambamurti K, Greig NH (2007) TNF-alpha inhibition as a treatment strategy for neurodegenerative disorders: new drug candidates and targets. Curr Alzheimer Res 4(4):378–385
Vizuete ML, Merino M, Venero JL, Santiago M, Cano J, Machado A (2000) Histamine infusion induces a selective dopaminergic neuronal death along with an inflammatory reaction in rat substantia nigra. J Neurochem 75(2):540–552
Waetzig V, Czeloth K, Hidding U, Mielke K, Kanzow M, Brecht S, Goetz M, Lucius R, Herdegen T, Hanisch UK (2005) c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) mediate pro-inflammatory actions of microglia. Glia 50(3):235–246
Yang HM, Yang S, Huang SS, Tang BS, Guo JF (2017) Microglial activation in the pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 9:193
Yin JJ, Hu XQ, Mao ZF, Bao J, Qiu W, Lu ZQ, Wu HT, Zhong XN (2017) Neutralization of Interleukin-9 decreasing mast cells infiltration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Chin Med J 130(8):964–971
Zhang X, Wang Y, Dong H, Xu Y, Zhang S (2016) Induction of microglial activation by mediators released from mast cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 38(4):1520–1531
Zhou P, Homberg JR, Fang Q, Wang J, Li W, Meng X, Shen J, Luan Y, Liao P, Swaab DF, Shan L, Liu C (2019) Histamine-4 receptor antagonist JNJ7777120 inhibits pro-inflammatory microglia and prevents the progression of Parkinson-like pathology and behaviour in a rat model. Brain Behav Immun 76:61–73
Zrzavy T, Hametner S, Wimmer I, Butovsky O, Weiner HL, Lassmann H (2017) Loss of ‘homeostatic’ microglia and patterns of their activation in active multiple sclerosis. Brain 140(7):1900–1913
Acknowledgements
This project was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81102422, 81373398, 81570522 and 81501202), Hubei natural science foundation (2018CFB301), but they had no role in the design of the study collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data; or writing of the manuscript. We would like to thank the Core Facility of Jiangsu Provincial People’s Hospital for its help in the detection of experimental samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosure Statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Statement on the Welfare of Animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
All experiments were carried out according to the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (publication no. 85–23, revised 1985) and the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Animals in Neuroscience Research by the Society for Neuroscience and approved by IACUC (Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Nanjing Medical University, NO: 14030126).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y. et al. Histamine Induces Microglia Activation and the Release of Proinflammatory Mediators in Rat Brain Via H1R or H4R. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 15, 280–291 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-019-09887-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-019-09887-6