Abstract
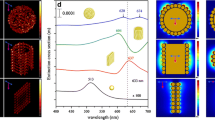
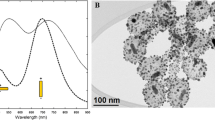
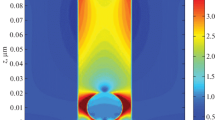
Tunable local surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) enhancement properties of cavity-nanoparticle scaffold-based clusters were investigated via finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulations. Hollow Au-cylinder-based and hollow Au-sphere-based nanocomposites models were presented with calculated optical spectra, near-field distribution, and average enhancement. Focusing on surface curvature, concave and convex Au-surface/Au-nanoparticles were built for further understanding on the local shape dependency in complicate scaffold-based clusters. Tunable near-field enhancement contributions and scaffold-dependency were discussed for potential in plasmonic applications such as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), LSPR sensor, and nanoantenna.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Liu BW, Chen S, Zhang JC, Yao X, Zhong JH, Lin HX, Huang TX, Yang ZL, Zhu JF, Liu S, Lienau C, Wang L, Ren B (2018) A Plasmonic Sensor Array with Ultrahigh Figures of Merit and Resonance Linewidths Down to 3 Nm. Adv Mater 30(12)
Stewart ME, Anderton CR, Thompson LB, Maria J, Gray SK, Rogers JA, Nuzzo RG (2008) Nanostructured plasmonic sensors. Chem Rev 108(2):494–521
Zayats AV, Smolyaninov II, Maradudin AA (2005) Nano-optics of surface plasmon polaritons, physics reports-review Section of. Phys Lett 408(3–4):131–314
Brolo AG (2012) Plasmonics for future biosensors. Nat Photonics 6(11):709–713
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li XN, Rotello VM (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev 112(5):2739–2779
Kim MW, Ku PC (2011) Semiconductor Nanoring Lasers. Appl Phys Lett 98(20)
Wu HY, Liu LJ, Lu M, Cunningham BT (2016) Lasing emission from plasmonic nanodome arrays. Advanced Optical Materials 4(5):708–714
Min CJ, Shen Z, Shen JF, Zhang YQ, Fang H, Yuan GH, Du LP, Zhu SW, Lei T, Yuan XC (2013) Focused Plasmonic Trapping of Metallic Particles. Nat Commun 4
Li JF, Huang YF, Ding Y, Yang ZL, Li SB, Zhou XS, Fan FR, Zhang W, Zhou ZY, Wu DY, Ren B, Wang ZL, Tian ZQ (2010) Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 464(7287):392–395
Kelly KL, Coronado E, Zhao LL, Schatz GC (2003) The Optical Properties of Metal Nanoparticles: The Influence of Size Shape, and Dielectric Environment. J Phys Chem B 107(3):668–677
Knight MW, Wu YP, Lassiter JB, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2009) Substrates matter: influence of an adjacent dielectric on an individual plasmonic nanoparticle. Nano Lett 9(5):2188–2192
Mahmoud MA, O’Neil D, El-Sayed MA (2014) Hollow and solid metallic nanoparticles in sensing and in nanocatalysis. Chem Mater 26(1):44–58
Ni HB, Zhou Y, Liu X, Ali H, Ge L, Pan C, Chang JH, Wang TT, Liu QQ, Wang M (2018) Surface plasmons excited from close-packed nanoring tube arrays produced by nanosphere lithography. Opt Mater Express 8(12):3676–3687
Kasani S, Zheng P, Wu NQ (2018) Tailoring optical properties of a large-area plasmonic gold nanoring array pattern. J Phys Chem C 122(25):13443–13449
Hu Y, Chou TM, Wang HJ, Du H (2014) Monodisperse colloidal gold nanorings: synthesis and utility for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Phys Chem C 118(29):16011–16018
Sun Y, Xia Y (2002) Shape-controlled synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. Science 298(5601):2176–2179
Zhou X, Li HJ, Fu SL, Xie SX, Xu HQ, Wu JJ (2011) Optical properties and plasmon resonance of coupled gold nanoshell arrays. Mod Phys Lett B 25(2):109–118
Prodan E, Radloff C, Halas NJ, Nordlander P (2003) A hybridization model for the plasmon response of complex nanostructures. Science 302(5644):419–422
Larsson EM, Hao F, Eurenius L, Olsson E, Nordlander P, Sutherland DS (2008) Plasmon hybridization in stacked double gold nanorings with reduced symmetry. Small 4(10):1630–1634
Mahmoud MA, Snyder B, El-Sayed MA (2010) Surface Plasmon Fields and Coupling in the Hollow Gold Nanoparticles and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Theory and Experiment. J Phys Chem C 114(16):7436–7443
Halas NJ, Lal S, Chang WS, Link S, Nordlander P (2011) Plasmons in strongly coupled metallic nanostructures. Chem Rev 111(6):3913–3961
Shao L, Fang C, Chen H, Man YC, Wang J, Lin HQ (2012) Distinct plasmonic manifestation on gold nanorods induced by the spatial perturbation of small gold nanospheres. Nano Lett 12(3):1424–1430
Fan JA, Wu C, Bao K, Bao J, Bardhan R, Halas NJ, Manoharan VN, Nordlander P, Shvets G, Capasso F (2010) Self-assembled plasmonic nanoparticle clusters. Science 328(5982):1135–1138
Nordlander P, Oubre C, Prodan E, Li K, Stockman MI (2004) Plasmon hybridization in nanoparticle dimers. Nano Lett 4(5):899–903
Xu H, Bjerneld EJ, Käll M, Börjesson L (1999) Spectroscopy of single hemoglobin molecules by surface enhanced Raman scattering. Phys Rev Lett 83(21):4357–4360
Xu H, Aizpurua J, Käll M, Apell P (2000) Electromagnetic contributions to single-molecule sensitivity in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys Rev E 62(3):4318–4324
You TT, Yin PG, Yang SH (2017) Scaffold-based multi-nanoparticle clusters as tunable Lspr substrates for Sers applications. Plasmonics 12(1):9–17
Chen L-Y, Yu J-S, Fujita T, Chen M-W (2009) Nanoporous copper with tunable nanoporosity for Sers applications. Adv Func Mater 19(8):1221–1226
Chen XW, Sandoghdar V, Agio M (2009) Highly efficient interfacing of guided plasmons and photons in nanowires. Nano Lett 9(11):3756–3761
Ming T, Zhao L, Yang Z, Chen H, Sun L, Wang J, Yan C (2009) Strong polarization dependence of plasmon-enhanced fluorescence on single gold nanorods. Nano Lett 9(11):3896–3903
Yang ZL, Li Y, Li ZP, Wu DY, Kang JY, Xu HX, Sun MT (2009) Surface enhanced Raman scattering of pyridine adsorbed on Au@Pd core/shell nanoparticles. J Chem Phys 130(23):234705
Lombardi JR, Birke RL (2008) A unified approach to surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C 112(14):5605–5617
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22005013, 51872011, and 51902011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, T., Gao, Y., Chen, H. et al. Curvature-Dependent Cavity-Nanoparticle Scaffold-Based Clusters with LSPR Enhancement as SERS Substrates. Plasmonics 16, 1231–1239 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01396-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-021-01396-8