Abstract
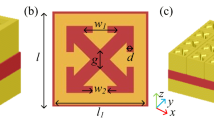
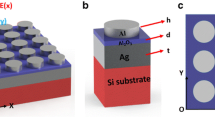
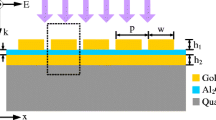
In this study, we present a high-performance tunable plasmonic absorber based on metal-insulator-metal nanostructures. High absorption is supported over a wide range of wavelengths, which is retained well at a very wide range of incident angles too. The coupling process occurs with high absorption efficiency of ∼ 99% by tuning the thickness of the dielectric layer. In addition, a complex trapezoidal nanostructure based on simple metal-insulator-metal structures by stacking different widths of Cu strip-nanostructures in the vertical direction has been put forward to enhance light absorption based on selective absorption. A trapezoidal sample has been designed with a solar absorption as high as 95% at wavelengths ranging from 300 nm to 2000 nm for different operating temperatures. Furthermore, the optical absorber has a very simple geometric structure and is easy to integrate into complex photonic devices. Perfect absorption and easy fabrication of the metal-insulator-metal structure make it an attractive device in numerous photonic applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen M, He Y (2018) Quantifying and comparing the near-field enhancement , photothermal conversion , and local heating performance of plasmonic SiO2@au core-shell nanoparticles. Plasmonics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0889-x
Wang R, Tombelli S, Minunni M et al (2004) Immobilisation of DNA probes for the development of SPR-based sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 20:967–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2004.06.013
West JL, Halas NJ (2003) Engineered nanomaterials for biophotonics applications: improving sensing, imaging, and therapeutics. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 5:285–292. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bioeng.5.011303.120723
Chen M, He Y, Huang J, Zhu J (2017) Investigation into Au nanofluids for solar photothermal conversion. Int J Heat Mass Transf 108:1894–1900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.01.005
Chen M, He Y, Zhu J, Kim DR (2016) Enhancement of photo-thermal conversion using gold nanofluids with different particle sizes. Energy Convers Manag 112:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.01.009
Wang X, He Y, Liu X et al (2017) Investigation of photothermal heating enabled by plasmonic nanofluids for direct solar steam generation. Sol Energy 157:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.08.015
Li H, He Y, Liu Z et al (2017) Synchronous steam generation and heat collection in a broadband ag@TiO2 core–shell nanoparticle-based receiver. Appl Therm Eng 121:617–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.04.102
Chen M, He Y, Wang X, Hu Y (2018) Numerically investigating the optical properties of plasmonic metallic nanoparticles for effective solar absorption and heating. Sol Energy 161:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.12.032
Chen M, He Y, Wang X, Hu Y (2018) Complementary enhanced solar thermal conversion performance of core-shell nanoparticles. Appl Energy 211:735–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.11.087
Shi L, He Y, Wang X, Hu Y (2018) Recyclable photo-thermal conversion and purification systems via Fe3O4@TiO2 nanoparticles. Energy Convers Manag 171:272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.05.106
Huang J, He Y, Chen M et al (2017) Solar evaporation enhancement by a compound film based on au@TiO2core–shell nanoparticles. Sol Energy 155:1225–1232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2017.07.070
Hao J, Wang J, Liu X, Padilla WJ, Zhou L, Qiu M (2010) High performance optical absorber based on a plasmonic metamaterial. Appl Phys Lett 96:3–5. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3442904
Chen M, He Y, Zhu J et al (2015) An experimental investigation on sunlight absorption characteristics of silver nanofluids. Sol Energy 115:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2015.01.031
Baffou G, Quidant R, García De Abajo FJ (2010) Nanoscale control of optical heating in complex plasmonic systems. ACS Nano 4:709–716. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn901144d
Hao J, Zhou L, Qiu M (2011) Nearly total absorption of light and heat generation by plasmonic metamaterials. Phys Rev B Condens Matter 83:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.83.165107
Chen M, He Y, Huang J, Zhu J (2016) Synthesis and solar photo-thermal conversion of au, ag, and au-ag blended plasmonic nanoparticles. Energy Convers Manag 127:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.09.015
Liang Y, Peng W (2013) Theoretical study of transmission characteristics of sub-wavelength nano-structured metallic grating. Appl Spectrosc 67:49–53. https://doi.org/10.1366/12-06718
Chen M, He Y (2018) Plasmonic nanostructures for broadband solar absorption based on the intrinsic absorption of metals. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 188:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2018.09.003
Wang LP, Zhang ZM (2012) Wavelength-selective and diffuse emitter enhanced by magnetic polaritons for thermophotovoltaics. Appl Phys Lett 100:063902. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3684874
Khodasevych IE, Wang L, Mitchell A, Rosengarten G (2015) Micro- and nanostructured surfaces for selective solar absorption. Adv Opt Mater 3:852–881. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201500063
Wang H, Wang L (2015) Tailoring thermal radiative properties with film-coupled concave grating metamaterials. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 158:127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2014.11.015
Wang W, Qu Y, Du K et al (2017) Broadband optical absorption based on single-sized metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic nanostructures with high-ε metals. Appl Phys Lett 110:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4977860
Hao J, Wang J, Liu X, Padilla WJ, Zhou L, Qiu M (2010) High performance optical absorber based on a plasmonic metamaterial. Appl Phys Lett 96:10–13. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3442904
Lei J, Ji B, Lin J (2017) High-performance tunable plasmonic absorber based on the metal-insulator-metal grating nanostructure. Plasmonics 12:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0242-1
Puscasu I, Schaich WL (2008) Narrow-band, tunable infrared emission from arrays of microstrip patches. Appl Phys Lett 92:233102. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2938716
Zhu P, Jay Guo L (2012) High performance broadband absorber in the visible band by engineered dispersion and geometry of a metal-dielectric-metal stack. Appl Phys Lett 101:241116. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4771994
Wang H, Prasad Sivan V, Mitchell A et al (2015) Highly efficient selective metamaterial absorber for high-temperature solar thermal energy harvesting. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 137:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2015.02.019
Chen YB, Zhang ZM (2007) Design of tungsten complex gratings for thermophotovoltaic radiators. Opt Commun 269:411–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2006.08.040
Cui Y, Xu J, Hung Fung K et al (2011) A thin film broadband absorber based on multi-sized nanoantennas. Appl Phys Lett 99:253101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3672002
Wang H, Wang L (2013) Perfect selective metamaterial solar absorbers. Opt Express 21:A1078. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.21.0A1078
Zhao J, Pinchuk AO, Mcmahon JM et al (2008) Methods for describing the electromagnetic properties of silver and gold nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 41:1710–1720
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.6.4370
Querry MR (1968) Direct solution of the generalized Fresnel reflectance equations. Josa 59:876
Sakurai A, Kawamata T (2016) Electromagnetic resonances of solar-selective absorbers with nanoparticle arrays embedded in a dielectric layer. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 184:353–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2016.08.005
Wu D, Liu Y, Xu Z et al (2017) Numerical study of the wide-angle polarization-independent ultra-broadband efficient selective solar absorber in the entire solar spectrum. Sol RRL 1:1700049. https://doi.org/10.1002/solr.201700049
Li P, Liu B, Ni Y et al (2015) Large-scale nanophotonic solar selective absorbers for high-efficiency solar thermal energy conversion. Adv Mater 27:4585–4591. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501686
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51676060), the Natural Science Funds of Heilongjiang Province for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. JC2016009), and the Science Creative Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars in Harbin (Grant No. 2014RFYXJ004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2458 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., He, Y., Ye, Q. et al. Tuning Plasmonic Near-Perfect Absorber for Selective Absorption Applications. Plasmonics 14, 1357–1364 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-00925-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-019-00925-w