Abstract
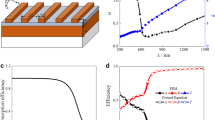
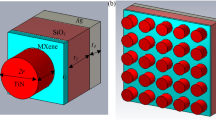
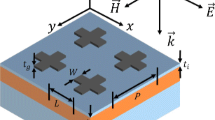
In this paper, a tunable plasmonic absorber based on TiN-nanosphere/liquid crystal (LC) nanocomposite in visible and near-infrared regions is proposed. TiN-nanosphere/LC nanocomposite is a combination of titanium nitride (TiN) nanospheres dispersed in a host of LC and plays the main role in post fabrication tunability. The proposed absorber has three more than 90% absorption peaks and the absorption tunability of about 76 nm. It is shown that TiN-nanospheres are able to support localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR). The Maxwell-Garnett theory is utilized to approximate the permittivity of the composite structure. Also, the effect of geometric parameters on the absorption is studied. Moreover, a single sheet of graphene is utilized to compensate the decrement of the absorption caused by the geometric parameters.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meshram M, Agrawal NK, Sinha B, Misra P (2004) Characterization of M-type barium hexagonal ferrite-based wide band microwave absorber. J Magn Magn Mater 271(2-3):207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2003.09.045
Landy NI, Sajuyigbe S, Mock J, Smith D, Padilla W (2008) Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys Rev Lett 100(20):207402. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.207402
Hao J, Wang J, Liu X, Padilla WJ, Zhou L, Qiu M (2010) High performance optical absorber based on a plasmonic metamaterial. Appl Phys Lett 96(25):251104. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3442904
Wang Y (1995) Voltage induced color selective absorption with surface plasmons. Appl Phys Lett 67(19):2759–2761. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.114584
Liu N, Mesch M, Weiss T, Hentschel M, Giessen H (2010) Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett 10(7):2342–2348. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl9041033
Tittl A, Mai P, Taubert R, Dregely D, Liu N, Giessen H (2011) Palladium-based plasmonic perfect absorber in the visible wavelength range and its application to hydrogen sensing. Nano Lett 11(10):4366–4369. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl202489g
Aydin K, Ferry VE, Briggs RM, Atwater HA (2011) Broadband polarization-independent resonant light absorption using ultrathin plasmonic super absorbers. Nat Commun 2:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1528
Cai Y, Zhu J, Liu QH, Lin T, Zhou J, Ye L, Cai Z (2015) Enhanced spatial near-infrared modulation of graphene-loaded perfect absorbers using plasmonic nanoslits. Opt Express 23(25):32318–32328. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.23.032318
Kang Z, Guo X, Jia Z, Xu Y, Liu L, Zhao D, Qin G, Qin W (2013) Gold nanorods as saturable absorbers for all-fiber passively Q-switched erbium-doped fiber laser. Opt Mater Express 3(11):1986–1991. https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.3.001986
Si G, Zhao Y, Leong ESP, Liu YJ (2014) Liquid-crystal-enabled active plasmonics: a review. Materials 7(2):1296–1317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7021296
Taylor T, Arora S, Fergason J (1970) Temperature-dependent tilt angle in the smectic C phase of a liquid crystal. Phys Rev Lett 25(11):722–726. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.25.722
Isić G, Vasić B, Zografopoulos DC, Beccherelli R, Gajić R (2015) Electrically tunable critically coupled terahertz metamaterial absorber based on nematic liquid crystals. Phys Rev Appl 3(6):064007. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevApplied.3.064007
Su Z, Yin J, Zhao X (2015) Soft and broadband infrared metamaterial absorber based on gold nanorod/liquid crystal hybrid with tunable total absorption. Sci Rep 5(1):16698. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16698
Spector M, Heiney P, Naciri J, Weslowski B, Holt D, Shashidhar R (2000) Electroclinic liquid crystals with large induced tilt angle and small layer contraction. Phys Rev E 61(2):1579–1584. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.61.1579
Zhao Y, Hao Q, Ma Y, Lu M, Zhang B, Lapsley M, Khoo IC, Jun Huang T (2012) Light-driven tunable dual-band plasmonic absorber using liquid-crystal-coated asymmetric nanodisk array. Appl Phys Lett 100(5):053119. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3681808
Fusco V, Cahill R, Hu W, Simms S (2008) Ultra-thin tunable microwave absorber using liquid crystals. Electron Lett 44(1):37–38. https://doi.org/10.1049/el:20082191
Shrekenhamer D, Chen W-C, Padilla WJ (2013) Liquid crystal tunable metamaterial absorber. Phys Rev Lett 110(17):177403. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.177403
Sihvola AH, Kong JA (1988) Effective permittivity of dielectric mixtures. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote 26:420–429. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.3045
Garnett JM (1906) Colours in metal glasses, in metallic films, and in metallic solutions. II. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 76(387-401):370–373. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.1906.0007
Garcıa M, Llopis J, Paje S (1999) A simple model for evaluating the optical absorption spectrum from small Au-colloids in sol–gel films. Chem Phys Lett 315(5-6):313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(99)01206-3
Granqvist C, Hunderi O (1978) Conductivity of inhomogeneous materials: effective-medium theory with dipole-dipole interaction. Phys Rev B 18(4):1554–1561. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.18.1554
Gao D, Gao L (2010) Goos–Hänchen shift of the reflection from nonlinear nanocomposites with electric field tunability. Appl Phys Lett 97(4):041903. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3470000
Yang Y, Wang W, Boulesbaa A, Kravchenko II, Briggs DP, Puretzky A, Geohegan D, Valentine J (2015) Nonlinear fano-resonant dielectric metasurfaces. Nano Lett 15(11):7388–7393. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02802
Gao D, Gao H, Qiu CW (2011) Birefringence-induced polarization-independent and nearly all-angle transparency through a metallic film. EPL-Europhys Lett 95:34004. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/95/34004
Geim AK, Novoselov KS (2007) The rise of graphene. Nat Mater 6(3):183–191. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1849
Nair RR, Blake P, Grigorenko AN, Novoselov KS, Booth TJ, Stauber T, Peres NMR, Geim AK (2008) Fine structure constant defines visual transparency of graphene. Science 320(5881):1308–1308. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1156965
Alaee R, Farhat M, Rockstuhl C, Lederer F (2012) A perfect absorber made of a graphene micro-ribbon metamaterial. Opt Express 20(27):28017–28024. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.20.028017
Thongrattanasiri S, Koppens FH, De Abajo FJG (2012) Complete optical absorption in periodically patterned graphene. Phys Rrev Lett 108(4):047401. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.047401
Yao G, Ling F, Yue J, Luo C, Ji J, Yao J (2016) Dual-band tunable perfect metamaterial absorber in the THz range. Opt Express 24(2):1518–1527. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.24.001518
Zhao B, Zhao J, Zhang Z (2014) Enhancement of near-infrared absorption in graphene with metal gratings. Appl Phys Lett 105(3):031905. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4890624
Lu H, Cumming BP, Gu M (2015) Highly efficient plasmonic enhancement of graphene absorption at telecommunication wavelengths. Opt Lett 40(15):3647–3650. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.40.003647.
Zare MS, Nozhat N, Rashiditabar R (2016) Improving the absorption of a plasmonic absorber using a single layer of graphene at telecommunication wavelengths. Appl Opt 55(34):9764–9768. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.55.009764
Zare MS, Nozhat N, Rashiditabar R (2017) Tunable graphene based plasmonic absorber with grooved metal film in near infrared region. Opt Commun 398:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2017.04.025.
Naik GV, Schroeder JL, Ni X, Kildishev AV, Sands TD, Boltasseva A (2012) Titanium nitride as a plasmonic material for visible and near-infrared wavelengths. Opt Mater Express 2(4):478–489. https://doi.org/10.1364/OME.2.000478
Li J, Wu S-T, Brugioni S, Meucci R, Faetti S (2005) Infrared refractive indices of liquid crystals. J Appl Phys 97(7):073501. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1877815
Khoo I, Werner D, Liang X, Diaz A, Weiner B (2006) Nanosphere dispersed liquid crystals for tunable negative-zero-positive index of refraction in the optical and terahertz regimes. Opt Lett 31(17):2592–2594. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.31.002592
Asadi R, Malek-Mohammad M, Khorasani S (2011) All optical switch based on Fano resonance in metal nanocomposite photonic crystals. Opt Commun 284(8):2230–2235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2010.12.085
Reinholdt A, Pecenka R, Pinchuk A, Runte S, Stepanov A, Weirich TE, Kreibig U (2004) Structural, compositional, optical and colorimetric characterization of TiN-nanoparticles. Eur Phys J D-At Mol Opt Plasma Phys 31(1):69–76. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2004-00129-8
Johnson PB, Christy R-W (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6(12):4370–4379. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.6.4370
Pflüger J, Fink J, Weber W, Bohnen K, Crecelius G (1984) Dielectric properties of TiC x, TiN x, VC x, and VN x from 1.5 to 40 eV determined by electron-energy-loss spectroscopy. Phys Rev B 30(3):1155–1163. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.30.1155
Gao L, Lemarchand F, Lequime M (2012) Exploitation of multiple incidences spectrometric measurements for thin film reverse engineering. Opt Express 20(14):15734–15751. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.20.015734
Hibbins AP, Sambles JR, Lawrence CR (1998) Surface plasmon-polariton study of the optical dielectric function of titanium nitride. J Mod Opt 45(10):2051–2062. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500349808231742
Patsalas P, Logothetidis S (2001) Optical, electronic, and transport properties of nanocrystalline titanium nitride thin films. J Appl Phys 90(9):4725–4734. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1403677
Hanson GW (2008a) Dyadic Green’s functions and guided surface waves for a surface conductivity model of graphene. J Appl Phys 103(6):064302. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2891452
Hanson GW (2008b) Dyadic Green’s functions for an anisotropic, non-local model of biased graphene. IEEE T Antenn Propag 56(3):747–757. https://doi.org/10.1109/TAP.2008.917005
Yang D-K (2014) Fundamentals of liquid crystal devices. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118751992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashiditabar, R., Nozhat, N. & Zare, M.S. Tunable Plasmonic Absorber Based on TiN-Nanosphere Liquid Crystal Hybrid in Visible and Near-Infrared Regions. Plasmonics 13, 1853–1859 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0699-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-018-0699-1