Abstract
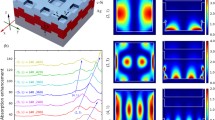
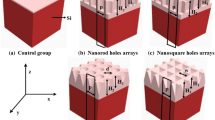
In this work, the effect of circular nanocavity on light trapping in a c-Si solar cell was studied by finite difference time domain (FDTD) simulation. The structure of the solar cell was considered to be Si3N4/c-Si/Ag, where the Ag layer was pattered and conformal growth of Si and Si3N4 was considered. The absorption spectra in the thin Si layer were determined and found 40 times higher at the infrared region (beyond 800 nm). For qualitative analysis, the short-circuit current of the solar cell was determined computationally by AM 1.5G solar illumination and found to be 2.1 times higher in the case of nanocavity as that compared to un-patterned solar cell. The enhancement in absorption in the solar cell is attributed to the different plasmonic modes coupled in the thin c-Si layer. The incident angle-dependent study was performed to observe the effect on enhancement in wide-angle incidence. The thickness-dependent study confirms 2.1 to 1.75 times enhancement in short-circuit current in 100- to 250-nm-thick c-Si layer. Therefore, this observation suggests that this structure has good prospect in achieving high conversion efficiency while reducing the device cost.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 November 2017
The original version of this article unfortunately contained a mistake. Author name Roy Sandipta should read Sandipta Roy.
References
Wang W, Zhang J, Che X, Qin G (2016) Large absorption enhancement in ultrathin solar cells patterned by metallic nanocavity arrays. Sci Rep 6:34219. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34219
Arvind S, Torres P, Tscharner R et al (1999) Photovoltaic technology: the case for thin-film solar. Cells 5428:692–699. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.285.5428.692
Wang KX, Yu Z, Liu V et al (2012) Absorption enhancement in ultrathin crystalline silicon solar cells with antireflection and light-trapping nanocone gratings. Nano Lett 12:1616–1619. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl204550q
Zhang Y, Stokes N, Jia B et al (2014) Towards ultra-thin plasmonic silicon wafer solar cells with minimized efficiency loss. Sci Rep 4:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04939
Bozzola A, Liscidini M, Andreani LC (2012) Light trapping in thin film solar cells with sub-wavelength photonic crystal patterns: In Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), 2012 14th International Conference. IEEE pp. 1-4. 2012.https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTON.2012.6254404
Islam K, Imtiaz F, Kemal A, Nayfeh A (2015) Comparative study of thin film n-i-p a-Si: H solar cells to investigate the effect of absorber layer thickness on the plasmonic enhancement using gold nanoparticles. Sol Energy 120:257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2015.07.018
Mandal P, Sharma S (2016) Progress in plasmonic solar cell efficiency improvement: a status review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 65:537–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.07.031
Zhang Y, Stokes N, Jia B, et al (2014) Towards ultra-thin plasmonic silicon wafer solar cells with minimized efficiency loss. Scientific reports. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep04939
Baryshnikova KV, Petrov MI, Babicheva VE, Belov PA (2016) Plasmonic and silicon spherical nanoparticle antireflective coatings. Sci Rep 6:22136. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22136
Tanabe K (2016) A simple optical model well explains plasmonic-nanoparticle-enhanced spectral photocurrent in optically thin solar cells. Nanoscale Res Lett 11:236. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1449-y
Pfeiffer TV, Ortiz-Gonzalez J, Santbergen R et al (2014) Plasmonic nanoparticle films for solar cell applications fabricated by size-selective aerosol deposition. Energy Procedia 60:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.12.335
Reineck P, Lee GP, Brick D et al (2012) A solid-state plasmonic solar cell via metal nanoparticle self-assembly. Adv Mater 24:4750–4755. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201200994
Wei CY, Lin CH, Hsiao HT et al (2013) Efficiency improvement of HIT solar cells on p-Type si wafers. Materials (Basel) 6:5440–5446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6115440
Adachi D, Hernandez JL, Yamamoto K (2015) Impact of carrier recombination on fill factor for large area heterojunction crystalline silicon solar cell with 25.1% efficiency. Appl Phys Lett 107:105–108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4937224
Atwater HA, Polman A (2010) Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat Mater 9:205–213. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2629
Ferry VE, Polman A, Atwater HA (2011) Modeling light trapping in nanostructured solar cells. ACS Nano 5:10055–10064. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn203906t
Aydin K, Ferry VE, Briggs RM, Atwater HA (2011) Broadband polarization-independent resonant light absorption using ultrathin plasmonic super absorbers. Nat Commun 2:517. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1528
Ferry VE, Verschuuren MA, Li HBT et al (2010) Light trapping in ultrathin plasmonic solar cells. Opt Express 18:A237. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.18.00A237
Ferry VE, Munday JN, Atwater HA (2010) Design considerations for plasmonic photovoltaics. Adv Mater 22:4794–4808. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201000488
Saeta PN, Ferry VE, Pacifici D et al (2009) How much can guided modes enhance absorption in thin solar cells? Opt Express 17:20975–20990. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.17.020975
Catchpole KR, Polman A (2008) Plasmonic solar cells. Opt Express 16:21793. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.16.021793
Detert D (2009) Plasmonic nanostructuredesign for efficient light coupling into solar cells. Nano Lett. 12:4391–4397. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl8022548
Stuart HR, Hall DG (1996) Absorption enhancement in silicon-on-insulator waveguides using metal island films. Appl Phys Lett 69:2327–2329. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.117513
Derkacs D, Lim SH, Matheu P et al (2006) Improved performance of amorphous silicon solar cells via scattering from surface plasmon polaritons in nearby metallic nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 89:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2336629
Yao Y, Yao J, Narasimhan VK et al (2012) Broadband light management using low-Q whispering gallery modes in spherical nanoshells. Nat Commun 3:664. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1664
Han SE, Chen G (2010) Optical absorption enhancement in silicon nanohole arrays for solar photovoltaics. Nano Lett 10:1012–1015. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl904187m
Zhu J, Hsu CM, Yu Z et al (2010) Nanodome solar cells with efficient light management and self-cleaning. Nano Lett 10:1979–1984. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl9034237
Garnett E, Yang P (2010) Light trapping in silicon nanowire solar cells. Nano Lett 10:1082–1087. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl100161z
Yu Z, Raman A, Fan S (2010) Limit of nanophotonic light-trapping in solar cells. Conf Rec IEEE Photovolt Spec Conf 18:76–78. https://doi.org/10.1109/PVSC.2010.5614248
Lin C, Povinelli ML (2009) Optical absorption enhancement in silicon nanowire arrays with a large lattice constant for photovoltaic applications. Opt Express 17:19371. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.17.019371
Zhu J, Yu Z, Burkhard GF et al (2009) Optical absorption enhancement in amorphous silicon nanowire and nanocone arrays. Nano Lett 9:279–282. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl802886y
Hu L, Chen G (2007) Analysis of optical absorption in silicon nanowire arrays for photovoltaic applications. Nano Lett 7:3249–3252. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl071018b
Palik ED (1991) Handbook of optical constants of solids II. Academic, Orlando, FL
Mo L, Yang L, Lee EH, He S (2015) High-efficiency plasmonic metamaterial selective emitter based on an optimized spherical core-shell nanostructure for planar solar thermophotovoltaics. Plasmonics 10:529–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9837-6
Prabhathan P, Murukeshan VM (2016) Surface plasmon polariton-coupled waveguide back reflector in thin-film silicon solar cell. Plasmonics 11:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0045-9
Li X, Zhang X, Yu Y et al (2016) Influences of nanostructure arrays on light absorption in amorphous silicon thin-film solar cells. Plasmonics 11:1073–1079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0144-7
Nesterenko D V., Hayashi S, Aazou S, et al (2017) Absorption enhancement in thin-film solar cells with perforated holes. Plasmonics pp. 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/t-ed.1982.20700 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0591-4
Yablonovitch E (1982) Statistical ray optics. J Opt Soc Am 72:899. https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSA.72.000899
Green MA (2002) Lambertian light trapping in textured solar cells and light-emitting diodes: analytical solutions. Prog Photovolt Res Appl 10:235–241. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.404
Yablonovitch E, Cody GD (1982) Intensity enhancement in textured optical sheets for solar-cells. IEEE Trans Electron Devices 29:300–305. https://doi.org/10.1109/t-ed.1982.20700
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Prof. S. P. Dttagupta and Prof. S. Ganguly, Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Bombay, for accessing the CST microwave studio and Lumerical. The author is also thankful to Arnab Pattanayak, CRNTS, IIT Bombay, for the fruitful discussion in the result and analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The original article has been corrected. Author name Roy Sandipta should read Sandipta Roy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, S. Circular Nanocavity in Ultrathin c-Si Solar Cell for Efficient Light Absorption. Plasmonics 13, 1499–1504 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0656-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0656-4