Abstract
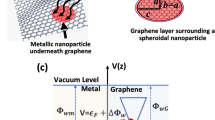
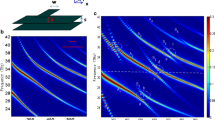
Interest in graphene has been widely increasing since its discovery in 2004. Research on graphene for plasmonic applications has also boomed due to the high potential of these systems. In this article, we discuss the possible interaction between metallic NPs and graphene monolayer. We show how the contact between metallic NPs and graphene results in graphene doping. More importantly, we experimentally put into evidence the possible modulation of the plasmonic resonance of NPs by graphene doping. Understanding and evidencing this interaction is highly important both from a fundamental point of view and for specific applications such as active plasmonic devices.

ᅟ





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geim AK, Novoselov KS (2007) The rise of graphene. Nat Mater 6:183–191
Rao CNR, Sood AK, Subrahmanyam KS, Govindaraj A (2009) Graphene: the new two-dimensional nanomaterial. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:7752–7777
Castro Neto AH, Guinea F, Peres NMR, Novoselov KS, Geim AK (2009) The electronic properties of graphene. Rev Mod Phys 81:109–162
Heersche HB, Jarillo-Herrero P, Oostinga JB, Vandersypen LMK, Morpurgo AF (2007) Bipolar supercurrent in graphene. Nature 446:56–59
Novoselov KS et al (2005) Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 438:197–200
Atwater HA (2007) The promise of plasmonics. Sci Am 296:56–63
Principles of nano-optics. Cambridge University Press Available at: http://www.cambridge.org/us/academic/subjects/physics/optics-optoelectronics-and-photonics/principles-nano-optics-2nd-edition. Accessed 8 Mar 2016
Schuller JA et al (2010) Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation. Nat Mater 9:193–204
Anker JN et al (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7:442–453
Plasmonics, photonics, and materials for sensors and imaging | Institute Of Materials Science & Engineering. Available at: https://imse.wustl.edu/research-plasmonics. Accessed: 22Apr 2016
Liang Z, Sun J, Jiang Y, Jiang L, Chen X (2014) Plasmonic enhanced optoelectronic devices. Plasmonics 9:859–866
Lee K-S, El-Sayed MA (2006) Gold and silver nanoparticles in sensing and imaging: sensitivity of plasmon response to size, shape, and metal composition. J Phys Chem B 110:19220–19225
Guilengui VN, Cerutti L, Rodriguez J-B, Tournié E, Taliercio T (2012) Localized surface plasmon resonances in highly doped semiconductors nanostructures. Appl Phys Lett 101:161113
Nikitin AY, Guinea F, García-Vidal FJ, Martín-Moreno L (2011) Edge and waveguide terahertz surface plasmon modes in graphene microribbons. Phys Rev B 84:161407
Salihoglu O, Balci S, Kocabas C (2012) Plasmon-polaritons on graphene-metal surface and their use in biosensors. Appl Phys Lett 100:213110
Reed JC, Zhu H, Zhu AY, Li C, Cubukcu E (2012) Graphene-enabled silver nanoantenna sensors. Nano Lett 12:4090–4094
Xu G et al (2012) Plasmonic graphene transparent conductors. Adv Mater 24:OP71–OP76
Grigorenko AN, Polini M, Novoselov KS (2012) Graphene plasmonics. Nat Photonics 6:749–758
Szunerits S, Maalouli N, Wijaya E, Vilcot J-P, Boukherroub R (2013) Recent advances in the development of graphene-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) interfaces. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:1435–1443
Choi SH, Kim YL, Byun KM (2011) Graphene-on-silver substrates for sensitive surface plasmon resonance imaging biosensors. Opt Express 19:458–466
Wu L, Chu HS, Koh WS, Li EP (2010) Highly sensitive graphene biosensors based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt Express 18:14395–14400
Giovannetti G et al (2008) Doping graphene with metal contacts. Phys Rev Lett 101:026803
Fang Z et al (2012) Plasmon-induced doping of graphene. ACS Nano 6:10222–10228
Gilbertson AM et al (2015) Plasmon-induced optical anisotropy in hybrid graphene–metal nanoparticle systems. Nano Lett 15:3458–3464
Kim J et al (2012) Electrical control of optical plasmon resonance with graphene. Nano Lett 12:5598–5602
Osváth Z et al (2015) The structure and properties of graphene on gold nanoparticles. Nano 7:5503–5509
Lee J-K, Sung H, Jang MS, Yoon H, Choi M (2015) Reliable doping and carrier concentration control in graphene by aerosol-derived metal nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C 3:8294–8299
Das A et al (2008) Monitoring dopants by Raman scattering in an electrochemically top-gated graphene transistor. Nat Nanotechnol 3:210–215
Lee J, Novoselov KS, Shin HS (2011) Interaction between metal and graphene: dependence on the layer number of graphene. ACS Nano 5:608–612
Maiti R, Haldar S, Majumdar D, Singha A, Ray SK (2017) Hybrid opto-chemical doping in Ag nanoparticle-decorated monolayer graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition probed by Raman spectroscopy. Nanotechnology 28:075707
Paulus M, Gay-Balmaz P, Martin OJF (2000) Accurate and efficient computation of the Green’s tensor for stratified media. Phys Rev E 62:5797–5807
Chaumet PC, Rahmani A, Bryant GW (2003) Generalization of the coupled dipole method to periodic structures. Phys Rev B 67:165404
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Bruna M, Borini S (2009) Optical constants of graphene layers in the visible range. Appl Phys Lett 94:031901
Dawlaty JM et al (2008) Measurement of the optical absorption spectra of epitaxial graphene from terahertz to visible. Appl Phys Lett 93:131905
Gusynin VP, Sharapov SG, Carbotte JP (2007) Sum rules for the optical and hall conductivity in graphene. Phys Rev B 75:165407
Acknowledgment
Financial support of NanoMat (www.nanomat.eu) by the “Ministère de l’enseignement supérieur et de la recherche,” the “Conseil régional Champagne-Ardenne,” the “Fonds Européen de Développement Régional (FEDER) fund,” and the “Conseil général de l’Aube” is acknowledged. T. M thanks the DRRT (Délégation Régionale à la Recherche et à la Technologie) of Champagne-Ardenne, the Labex ACTION project (contract ANR-11-LABX-01-01) and the CNRS via the chaire « optical nanosensors » for the financial support. This work was performed in the context of the COST Action MP1302 Nanospectroscopy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. RN performed the experimental work and the analysis of the results; GL performed the simulations and the analysis of the results. PMA, GL, and TM supervised this work and the analysis of the results.
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicolas, R., Lévêque, G., Adam, PM. et al. Graphene Doping Induced Tunability of Nanoparticles Plasmonic Resonances. Plasmonics 13, 1219–1225 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0623-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0623-0