Abstract
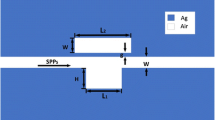
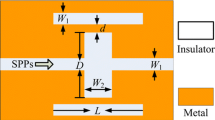
This paper proposes a compact plasmonic structure that is composed of a metal-insulator-metal (MIM) waveguide coupled with a groove and stub resonators, and then investigates it by utilizing the finite element method (FEM). Simulation results show that the interaction between the local discrete state caused by the stub resonator and the continuous spectrum caused by the groove resonator gives rise to one of the two Fano resonances, while the generation of the other resonance relies only on the groove. Meanwhile, the asymmetrical linear shape and the resonant wavelength can be easily tuned by changing the parameters of the structure. By adding stubs on the groove, we excited multiple Fano resonances. The proposed structure can serve as an excellent plasmonic sensor with a sensitivity of 2000 nm/RIU and a figure of merit of about 3.04 × 103, which can find extensive applications for nanosensors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950):824–830
Xu T, Wu YK, Luo X, Guo LJ (2010) Plasmonic nanoresonators for high-resolution colour filtering and spectral imaging. Nature Commun 1(5):59
Chen Z, Chen J, Yu L, Xiao J (2014) Sharp trapped resonances by exciting the anti-symmetric waveguide mode in a metal-insulator-metal resonator. Plasmonics 10(1):131–137
Chen J, Li Z, Lei M, Fu X, Xiao J, Gong Q (2012) Plasmonic Y-splitters of high wavelength resolution based on strongly coupledresonator effects. Plasmonics 7(3):441–445
Chen J, Wang C, Zhang R, Xiao J (2012) Multiple plasmon-induced transparencies in coupled-resonator systems. Opt Lett 37(24):5133–5135
Veronis G, Fan SH (2005) Bends and splitters in metal-dielectricmetal subwavelength plasmonic waveguides. Appl Phys Lett 87(13):131102
Economou EN (1969) Surface plasmons in thin films. Phys Rev 182(2):539–554
Lin XS, Huang XG (2008) Tooth-shaped plasmonic waveguide filters with nanometeric sizes. Opt Lett 33(23):2874–2876
Zhang Q, Huang XG, Lin XS, Tao J, Jin XP (2009) A subwavelength coupler-type MIM optical filter. Opt Exp 17(9):7549–7554
Tao J, Huang XG, Lin XS, Zhang Q, Jin XP (2009) A narrow-band subwavelength plasmonic waveguide filter with asymmetrical multiple teeth-shaped structure. Opt Exp 17(16):13 989–13 994
Chen Z, Yu L (2014) Multiple fano resonances based on different waveguide modes in a symmetry breaking plasmonic system. IEEE Photon J 6(6). doi:10.1109/JPHOT.2014.2368779
Chen Z, Cao XY, Song XK, Wang LL, Yu L (2015) Side-coupled cavity-induced Fano resonance and its application in nanosensor. Plasmonics 11(16):307–313
Rahimzadegan A et al (2014) Improved plasmonic filter, ultra-compact demultiplexer, and splitter. J Opt Soc Korea 18(3):261–273
Wang GX, Lu H, Liu XM, Mao D, Duan LN (2011) Tunable multi-channel wavelength demultiplexer based on MIM plasmonic nanodisk resonators at telecommunication regime. Opt Exp 19(4):3513–3518
Noual A, Akjouj A, Pennec Y, Gillet J, Djafari-Rouhani B (2009) Modeling of two-dimensional nanoscale Y-bent plasmonic waveguides with cavities for demultiplexing of the telecommunication wavelengths. New J Phys 11(10):19
Fano U (1961) Effects of configuration interaction on intensities and phase shifts. Phys Rev 124(16):1866–1878
Miroshnichenko AE, Flach S, Kivshar YS (2009) Fano resonances in nanoscale structures. Rev Mod Phys 82(3):2257–2298
Luk’yanchuk B et al (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9:707–715
Chen JJ, Li Z, Zhang X, Xiao JH, Gong QH (2013) Submicron bidirectional all-optical plasmonic switches. Sci Rep 3(3):1451
Heuck M, Kristensen PT, Elesin Y, Mork J (2013) Improved switching using Fano resonances in photonic crystal structures. Opt Lett 38(14):2466–2468
Yun BF, Zhang RH, Hu GH, Cui YP (2016) Ultra sharp fano resonances induced by coupling between plasmonic stub and circular cavity resonators. Plasmonics 11(4):1157–1162
Chen Z, Wang WH, Cui NL, Yu L, Duan GY, Zhao FY, Xiao JH (2015) Spectral splitting based on electromagnetically induced transparency in plasmonic waveguide resonator system. Plasmonics 10(3):721–727
Chen Z, Yu L, Wang LL, Duan GY, Zhao FY, Xiao JH (2015) A refractive index nanosensor based on Fano resonance in the plasmonic waveguide system. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 27(16):1695–1698
Chen Z, Cui LN, Song XK, Yu L, Xiao JH (2015) High sensitivity plasmonic sensing based on Fano interference in a rectangular ring waveguide. Opt Commun 340(340):1–4
Lu H, Liu XM, Mao D, Wang GX (2012) Plasmonic nanosensor based on Fano resonance in waveguide-coupled resonators. Opt Lett 37(18):3780–3782
Qi JW, Chen ZQ, Chen J, Li YD, Qiang W, Xu JJ, Sun Q (2014) Independently tunabledouble Fano resonances in asymmetric MIM waveguide structure. Opt Express 22(12):14688–14695
Zhou Z, Hu F, Yi H (2011) Wavelength demultiplexing structure based on arrayed plasmonic slot cavities. Opt Lett 36(8):1500–1502
Liu N, Mesch M, Weiss T, Hentschel M, Giessen H (2010) Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett 10(7):2342–2348
Becker J, Trügler A, Jakab A, Hohenester U, Sönnichsen C (2010) The optimal aspect ratio of gold nanorods for plasmonic bio-sensing. Plasmonics 5(2):161–167
Chen Z, Yu L, Wang LL, Duan GY, Zhao YF, Xiao JH (2015) Sharp asymmetric line shapes in a plasmonic waveguide system and its application in nanosensor. J Lighwave Tec 33(15):3250–3253
Ameling R, Langguth L, Hentschel M, Mesch M (2010) Cavity-enhanced localized plasmon resonance sensing. Appl Phys Lett 97(25):253116
Zhang YY, Li SL, Chen Z, Jing P, Jiao RZ, Zhang Y, Wang LL, Yu L (2016) Ultra-high Sensitivity Plasmonic Nanosensor Based on Multiple Fano Resonance in the MDM Side-Coupled Cavities. Plasmonics (4):1–7. doi:10.1007/s11468-016-0363-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, T., Yu, S. Ultra-High Sensitivity Nanosensor Based on Multiple Fano Resonance in the MIM Coupled Plasmonic Resonator. Plasmonics 13, 1115–1120 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0610-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-017-0610-5