Abstract
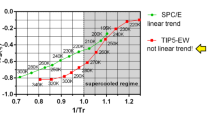
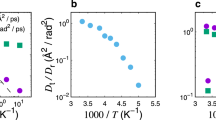
The aim of this paper is to discuss the relationship between the dynamics and thermodynamics of water in the supercooled region. Reviewed case studies comprehend bulk water simulated with the SPC/E, TIP4P and TIP4P/2005 potentials, water at protein interfaces, and water in solution with electrolytes. Upon supercooling, the fragile to strong crossover in the α-relaxation of water is found to occur when the Widom line emanating from the liquid-liquid critical point is crossed. This appears to be a general characteristic of supercooled water, not depending on the applied interaction potential and/or different local environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Gallo, K. Amann-Winkel, C. A. Angell, M. A. Anisimov, F. Caupin, C. Chakravarty, E. Lascaris, T. Loerting, A. Z. Panagiotopoulos, J. Russo, J. A. Sellberg, H. E. Stanley, H. Tanaka, C. Vega, L. Xu, and G. M. P. Lars, Water: A tale of two liquids, Chem. Rev. 116(13), 7463 (2016)
P. Ball, Water -An enduring mystery, Nature 452(7185), 291 (2008)
P. G. Debenedetti, Supercooled and glassy water, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 15(45), R1669 (2003)
C. A. Angell, R. D. Bressel, M. Hemmati, E. J. Sare, and J. C. Tucker, Water and its anomalies in perspective: Tetrahedral liquids with and without liquid-liquid phase transitions, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2(8), 1559 (2000)
P. G. Debenedetti, Metastable Liquids: Concepts and Principles, Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1996
A. Sakai, T. Matsumoto, D. Hirai, and T. Niino, Newly developed encapsulation-dehydration protocol for plantcryopreservation, Cryo Lett. 21(1), 53 (1999)
W. Kauzmann, Some factors in the interpretation of protein denaturation, Adv. Protein Chem. 14, 1 (1959)
F. Franks, Water: A Matrix of Life, RSC Paperbacks, 2nd edition, Cambridge, UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2000
P. G. Debenedetti and H. E. Stanley, Supercooled and glassy water, Phys. Today 56(6), 40 (2003)
C. A. Angell, J. Shuppert, and J. C. Tucker, Anomalous properties of supercooled water. Heat capacity, expansivity, and proton magnetic resonance chemical shift from 0 to -38%, J. Phys. Chem. 77(26), 3092 (1973)
R. J. Speedy and C. A. Angell, Isothermal compressibility of supercooled water and evidence for a thermodynamic singularity at -45 °C, J. Chem. Phys. 65(3), 851 (1976)
O. Mishima and H. E. Stanley, The relationship between liquid, supercooled and glassy water, Nature 396(6709), 329 (1998)
P. H. Poole, F. Sciortino, U. Essmann, and H. E. Stanley, Phase behaviour of metastable water, Nature 360(6402), 324 (1992)
K. Winkel, M. S. Elsaesser, E. Mayer, and T. Loerting, Water polyamorphism: Reversibility and (dis) continuity, J. Chem. Phys. 128(4), 044510 (2008)
O. Mishima and H. E. Stanley, Decompression-induced melting of ice IV and the liquid-liquid transition in water, Nature 392(6672), 164 (1998)
O. Mishima, L. D. Calvert, and E. Whalley, An apparently first-order transition between two amorphous phases of ice induced by pressure, Nature 314(6006), 76 (1985)
K. Winkel, E. Mayer, and T. Loerting, Equilibrated high-density amorphous ice and its first-order transition to the low-density form, J. Phys. Chem. B 115(48), 14141 (2011)
C. U. Kim, B. Barstow, M. V. Tate, and S. M. Gruner, Evidence for liquid water during the high-density to lowdensity amorphous ice transition, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106(12), 4596 (2009)
G. Franzese and H. E. Stanley, The widom line of supercooled water, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 19(20), 205126 (2007)
L. Xu, P. Kumar, S. V. Buldyrev, S. H. Chen, P. H. Poole, F. Sciortino, and H. E. Stanley, Relation between the Widom line and the dynamic crossover in systems with a liquid-liquid phase transition, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102(46), 16558 (2005)
D. Corradini, M. Rovere, and P. Gallo, A route to explain water anomalies from results on an aqueous solution of salt, J. Chem. Phys. 132(13), 134508 (2010)
J. L. F. Abascal and C. Vega, Widom line and the liquidliquid critical point for the TIP4P/2005 water model, J. Chem. Phys. 133(23), 234502 (2010)
P. Gallo, F. Sciortino, P. Tartaglia, and S. H. Chen, Slow dynamics of water molecules in supercooled states, Phys. Rev. Lett. 76(15), 2730 (1996)
F. Sciortino, P. Gallo, P. Tartaglia, and S. H. Chen, Supercooled water and the kinetic glass transition, Phys. Rev. E 54(6), 6331 (1996)
W. Gotze and L. Sjogren, Relaxation processes in supercooled liquids, Rep. Prog. Phys. 55(3), 241 (1992)
W. Götze, Complex Dynamics of Glass-Forming Liquids: A Mode-Coupling Theory, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009
P. Gallo and M. Rovere, Mode coupling and fragile to strong transition in supercooled TIP4P water, J. Chem. Phys. 137(16), 164503 (2012)
P. Gallo, D. Corradini, and M. Rovere, Fragile to strong crossover at the Widom line in supercooled aqueous solutions of NaCl, J. Chem. Phys. 139(20), 204503 (2013)
P. Gallo, M. Rovere, and E. Spohr, Supercooled confined water and the mode coupling crossover temperature, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(20), 4317 (2000)
P. Gallo, M. Rovere, and E. Spohr, Glass transition and layering effects in confined water: A computer simulation study, J. Chem. Phys. 113(24), 11324 (2000)
P. Gallo, M. Rovere, and S. H. Chen, Dynamic crossover in supercooled confined water: Understanding bulk properties through confinement, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 1(4), 729 (2010)
P. Gallo, M. Rovere, and S. H. Chen, Water confined in MCM-41: A mode coupling theory analysis, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 24(6), 064109 (2012)
M. De Marzio, G. Camisasca, M. Rovere, and P. Gallo, Mode coupling theory and fragile to strong transition in supercooled TIP4P/2005 water, J. Chem. Phys. 144(7), 074503 (2016)
A. Dehaoui, B. Issenmann, and F. Caupin, Viscosity of deeply supercooled water and its coupling to molecular diffusion, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112(39), 12020 (2015)
R. Torre, P. Bartolini, and R. Righini, Structural relaxation in supercooled water by time-resolved spectroscopy, Nature 428(6980), 296 (2004)
F. W. Starr, F. Sciortino, and H. E. Stanley, Dynamics of simulated water under pressure, Phys. Rev. E 60(6), 6757 (1999)
A. Faraone, L. Liu, C. Y. Mou, C. W. Yen, and S. H. Chen, Fragile-to-strong liquid transition in deeply supercooled confined water, J. Chem. Phys. 121(22), 10843 (2004)
L. Liu, S. H. Chen, A. Faraone, C. W. Yen, and C. Y. Mou, Pressure dependence of fragile-to-strong transition and a possible second critical point in supercooled confined water, Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(11), 117802 (2005)
F. Mallamace, M. Broccio, C. Corsaro, A. Faraone, U. Wanderlingh, L. Liu, C. Y. Mou, and S. H. Chen, The fragile-to-strong dynamic crossover transition in confined water: nuclear magnetic resonance results, J. Chem. Phys. 124(16), 161102 (2006)
Y. Zhang, M. Lagi, E. Fratini, P. Baglioni, E. Mamontov, and S. H. Chen, Dynamic susceptibility of supercooled water and its relation to the dynamic crossover phenomenon, Phys. Rev. E 79(4), 040201 (2009)
L. Liu, S. H. Chen, A. Faraone, C.W. Yen, C. Y. Mou, A. I. Kolesnikov, E. Mamontov, and J. Leao, Quasielastic and inelastic neutron scattering investigation of fragile-to-strong crossover in deeply supercooled water confined in nanoporous silica matrices, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 18(36), S2261 (2006)
Z. Wang, P. Le, K. Ito, J. B. Leão, M. Tyagi, and S. H. Chen, Dynamic crossover in deeply cooled water confined in mcm-41 at 4 kbar and its relation to the liquidliquid transition hypothesis, J. Chem. Phys. 143(11), 114508 (2015)
Y. Xu, N. G. Petrik, R. S. Smith, B. D. Kay, and G. A. Kimmel, Growth rate of crystalline ice and the diffusivity of supercooled water from 126 to 262 K, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113(52), 14921 (2016)
J. M. Zanotti, M. C. Bellissent-Funel, and S. H. Chen, Relaxational dynamics of supercooled water in porous glass, Phys. Rev. E 59(3), 3084 (1999)
P. Gallo, M. Rovere, and S. H. Chen, Anomalous dynamics of water confined in MCM-41 at different hydrations, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 22(28), 284102 (2010)
W. L. Jorgensen, J. Chandrasekhar, J. D. Madura, R. W. Impey, and M. L. Klein, Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water, J. Chem. Phys. 79(2), 926 (1983)
J. L. F. Abascal and C. Vega, A general purpose model for the condensed phases of water: TIP4P/2005, J. Chem. Phys. 123(23), 234505 (2005)
G. Camisasca, M. De Marzio, D. Corradini, and P. Gallo, Two structural relaxations in protein hydration water and their dynamic crossovers, J. Chem. Phys. 145(4), 044503 (2016)
J. C. Herman, Berendsen, J. R. Grigera, and T. P. Straatsma. The missing term in effective pair potentials, J. Phys. Chem. 91(24), 6269 (1987)
A. D. MacKerell, D. Bashford, M. Bellott, R. L. Dunbrack, J. D. Evanseck, M. J. Field, S. Fischer, J. Gao, H. Guo, S. Ha, D. Joseph-McCarthy, L. Kuchnir, K. Kuczera, F. T. Lau, C. Mattos, S. Michnick, T. Ngo, D. T. Nguyen, B. Prodhom, W. E. Reiher, B. Roux, M. Schlenkrich, J. C. Smith, R. Stote, J. Straub, M. Watanabe, J. Wiórkiewicz-Kuczera, D. Yin, and M. Karplus, All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins, J. Phys. Chem. B 102(18), 3586 (1998)
A. D. MacKerell, M. Feig, and C. L. Brooks, Extending the treatment of backbone energetics in protein force fields: limitations of gas-phase quantum mechanics in reproducing protein conformational distributions in molecular dynamics simulations, J. Comput. Chem. 25(11), 1400 (2004)
A. Scala, F. W. Starr, E. La Nave, H. E. Stanley, and F. Sciortino, Free energy surface of supercooled water, Phys. Rev. E 62(6), 8016 (2000)
D. Corradini and P. Gallo, Liquid-liquid coexistence in nacl aqueous solutions: a simulation study of concentration effects, J. Phys. Chem. B 115, 1461 (2011)
D. Corradini, M. Rovere, and P. Gallo, Structural properties of high and low density water in a supercooled aqueous solution of salt, J. Phys. Chem. B 115(6), 1461 (2011)
C. Vega, J. L. F. Abascal, M. M. Conde, and J. L. Aragones, What ice can teach us about water interactions: A critical comparison of the performance of different water models, Faraday Discuss. 141, 251 (2009)
K. P. Jensen and W. L. Jorgensen, Halide, ammonium, and alkali metal ion parameters for modeling aqueous solutions, J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2(6), 1499 (2006)
A. Magno and P. Gallo, Understanding the Mechanisms of Bioprotection: A Comparative Study of Aqueous Solutions of Trehalose and Maltose upon Supercooling, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2(9), 977 (2011)
D. Corradini, E. G. Strekalova, H. E. Stanley, and P. Gallo, Microscopic mechanism of protein cryopreservation in an aqueous solution with trehalose, Sci. Rep. 3(1), 1218 (2013)
P. Kumar, Z. Yan, Limei Xu, M. G. Mazza, S. V. Buldyrev, S. H. Chen, S. Sastry, and H. E. Stanley, Glass transition in biomolecules and the liquid-liquid critical point of water, Phys. Rev. Lett. 97(17), 177802 (2006)
S. H. Chen, L. Liu, E. Fratini, P. Baglioni, A. Faraone, E. Mamontov, and M. Fomina, Observation of fragileto-strong dynamic crossover in protein hydration water, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103(24), 9012 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Marzio, M., Camisasca, G., Rovere, M. et al. Fragile to strong crossover and Widom line in supercooled water: A comparative study. Front. Phys. 13, 136103 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-017-0714-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-017-0714-6