Abstract
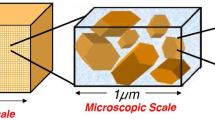
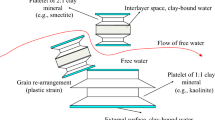
Unsaturated clay is a heterogeneous porous medium consisting of three phases, namely solid soil skeleton, pore water, and pore air. It has been well recognized that the variation of the chemical property of pore fluid in clay can affect the hydromechanical behavior of this material remarkably. In this study, we formulate a non-local chemo-hydromechanical model for unsaturated clay via the constitutive correspondence principle in the state-based peridynamics—a reformulation of classical continuum mechanics using integral equations instead of partial differential equations. We numerically implement this non-local constitutive model through the implicit return mapping algorithm at the material particle level and then integrate the material subroutine into a computational peridynamics code. We conduct a series of numerical simulations of unsaturated clay samples under different chemical loading rates. The numerical results demonstrate that the proposed non-local model can capture the dramatic impact of organic chemicals on the mechanical behavior of unsaturated clay. The numerical results also show that the proposed non-local numerical model can simulate localized deformation in chemically active unsaturated clay because of the intrinsic length scale embedded in the integral equations.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso EE, Gens A, Josa A (1990) A constitutive model for partially saturated soils. Géotechnique 40(3):405–430
Barbour SL, Fredlund DG (1989) Mechanisms of osmotic flow and volume change in clay soils. Can Geotech J 26(4):551–562
Belytschko T, Lu YY, Gu L (1994) Element-free galerkin methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37(2):229–256
Bolt GH (1956) Physico-chemical analysis of the compressibility of pure clays. Géotechnique 6(2):86–93
Bolt G, Miller R (1955) Compression studies of illite suspensions 1. Soil Sci Soc Am J 19(3):285–288
Bolzon G, Schrefler B, Zienkiewicz O (1996) Elastoplastic soil constitutive laws generalized to partially saturated states. Géotechnique 46(2):279–289
Borja RI (2004) Cam-clay plasticity. Part V: a mathematical framework for three-phase deformation and strain localization analyses of partially saturated porous media. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(48–51):5301–5338
Borja RI (2006) On the mechanical energy and effective stress in saturated and unsaturated porous continua. Int J Solids Struct 43(6):1764–1786
Borja RI (2013) Plasticity: modeling & computation. Springer Science & Business Media, New York
Borja RI, Koliji A (2009) On the effective stress in unsaturated porous continua with double porosity. J Mech Phys Solids 57(8):1182–1193
Borja RI, Song X, Rechenmacher AL, Abedi S, Wu W (2013) Shear band in sand with spatially varying density. J Mech Phys Solids 61(1):219–234
Borja RI, Song X, Wu W (2013) Critical state plasticity. part vii: triggering a shear band in variably saturated porous media. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 261:66–82
Boukpeti N, Charlier R, Hueckel T (2004) Modelling contamination of clays. Elsevier Geo Eng Book Ser 2:523–528
Bunger AP (2010) The mandelcryer effect in chemoporoelasticity. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 34(14):1479–1511
Cao J, Jung J, Song X, Bate B (2018) On the soil water characteristic curves of poorly graded granular materials in aqueous polymer solutions. Acta Geotech 13(1):103–116
Castellanos E, Villar M, Romero E, Lloret A, Gens A (2008) Chemical impact on the hydro-mechanical behaviour of high-density febex bentonite. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C 33:S516–S526 Clays in Natural & Engineered Barriers for Radioactive Waste Confinement
Chen G, Gallipoli D, Ledesma A (2007) Chemo-hydro-mechanical coupled consolidation for a poroelastic clay buffer in a radioactive waste repository. Transp Porous Media 69:189–213
Cleall P (1998) An investigation of the thermo/hydraulic/mechanical behaviour of unsaturated soils, including expansive soils. Ph.D. thesis, University of Wales Cardiff, UK
DeJong J, Soga K, Kavazanjian E, Burns S, Van Paassen L, Al Qabany A, Aydilek A, Bang S, Burbank M, Caslake LF et al (2013) Biogeochemical processes and geotechnical applications: progress, opportunities and challenges. Geotechnique 63(4):287
Detournay E, Sarout J, Tan C, Caurel J (2005) Chemoporoelastic parameter identification of a reactive shale, vol. 125 of Solid Mechanics and its Applications, pp 125–132
D’Onza F, Gallipoli D, Wheeler S, Casini F, Vaunat J, Khalili N, Laloui L, Mancuso C, Mašín D, Nuth M et al (2011) Benchmark of constitutive models for unsaturated soils. Géotechnique 61(4):283–302
Du Q, Gunzburger M, Lehoucq RB, Zhou K (2013) A nonlocal vector calculus, nonlocal volume-constrained problems, and nonlocal balance laws. Math Models Methods Appl Sci 23(03):493–540
Fernandez F, Quigley RM (1985) Hydraulic conductivity of natural clays permeated with simple liquid hydrocarbons. Can Geotech J 22(2):205–214
Fernandez F, Quigley RM (1988) Viscosity and dielectric constant controls on the hydraulic conductivity of clayey soils permeated with water-soluble organics. Can Geotech J 25(3):582–589
Fernandez F, Quigley RM (1991) Controlling the destructive effects of clay-organic liquid interactions, by application of effective stresses. Can Geotech J 28(3):388–398
Fisher R (1926) On the capillary forces in an ideal soil; correction of formulae given by wb haines. J Agric Sci 16(3):492–505
Flanagan D, Taylor L (1987) An accurate numerical algorithm for stress integration with finite rotations. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 62(3):305–320
Foster JT, Silling SA, Chen WW (2010) Viscoplasticity using peridynamics. Int J Numer Methods Eng 81(10):1242–1258
Gajo A, Loret B (2003) Finite element simulations of chemo-mechanical coupling in elasticplastic homoionic expansive clays. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192(31):3489–3530
Gajo A, Loret B, Hueckel T (2002) Electro-chemo-mechanical couplings in saturated porous media: elastic–plastic behaviour of heteroionic expansive clays. Int J Solids Struct 39(16):4327–4362
Gallipoli D, Gens A, Sharma R, Vaunat J (2003) An elasto-plastic model for unsaturated soil incorporating the effects of suction and degree of saturation on mechanical behaviour. Géotechnique 53(1):123–136
Ganzenmller G, Hiermaier S, May M (2015) On the similarity of meshless discretizations of peridynamics and smooth-particle hydrodynamics. Comput Struct 150:71–78
Gens A (2010) Soil-environment interactions in geotechnical engineering. Géotechnique 60(1):3–74
Guimarães LdN, Gens A, Olivella S (2007) Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical and chemical analysis of expansive clay subjected to heating and hydration. Transp Porous Media 66(3):341–372
Hueckel T (1997) Chemo-plasticity of clays subjected to stress and flow of a single contaminant. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 21(1):43–72
Hueckel T (2002) Reactive plasticity for clays during dehydration and rehydration. Part 1: concepts and options. Int J Plast 18(3):281–312
Kaczmarek M (2001) Chemically induced deformation of a porous layer coupled with advectivedispersive transport. Analytical solutions. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 25(8):757–770
Kaczmarek M, Hueckel T (1998) Chemo-mechanical consolidation of clays: analytical solutions for a linearized one-dimensional problem. Transp Porous Media 32:49–74
Kenney T (1967) The influence of mineral composition on the residual strength of natural soils. In: Proceedings of the geotechnical conference on shear strength properties of natural soils and rocks, Oslo, Norway, vol 1, pp 123–129
Khalili N, Zargarbashi S (2010) Influence of hydraulic hysteresis on effective stress in unsaturated soils. Geotechnique 60(9):729–734
Khalili N, Geiser F, Blight G (2004) Effective stress in unsaturated soils: review with new evidence. Int J Geomech 4(2):115–126
Lehoucq RB, Silling SA (2008) Force flux and the peridynamic stress tensor. J Mech Phys Solids 56(4):1566–1577
Lei X, Wong H, Fabbri A, Limam A, Cheng Y (2014) A thermo-chemo-electro-mechanical framework of unsaturated expansive clays. Comput Geotech 62:175–192
Lei X, Wong H, Fabbri A, Limam A, Cheng Y (2016) A chemo-elasticplastic model for unsaturated expansive clays. Int J Solids Struct 88–89:354–378
Li Y-C, Cleall PJ, Thomas H (2011) Multi-dimensional chemo-osmotic consolidation of clays. Comput Geotech 38(4):423–429
Liu Z, Boukpeti N, Li X, Collin F, Radu J-P, Hueckel T, Charlier R (2005) Modelling chemo-hydro-mechanical behaviour of unsaturated clays: a feasibility study. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 29(9):919–940
Loret B, Khalili N (2002) An effective stress elastic–plastic model for unsaturated porous media. Mech Mater 34(2):97–116
Loret B, Hueckel T, Gajo A (2002) Chemo-mechanical coupling in saturated porous media: elasticplastic behaviour of homoionic expansive clays. Int J Solids Struct 39(10):2773–2806
Lu N, Godt JW, Wu DT (2010) A closed-form equation for effective stress in unsaturated soil. Water Resour Res 46(5):1–14
Lu N, Khalili N, Nikooee E, Hassanizadeh SM (2014) Principle of effective stress in variably saturated porous media. Vadose Zone J 13(5):1–4
Macek RW, Silling SA (2007) Peridynamics via finite element analysis. Finite Elem Anal Des 43(15):1169–1178
Madsen FT, Mitchell JK (1989) Chemical effects on clay farbric and hydraulic conductivity. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 201–251
Maio CD (1996) Exposure of bentonite to salt solution: osmotic and mechanical effects. Géotechnique 46(4):695–707
Mesri G, Olson R (1971) Mechanisms controlling the permeability of clays. Clays Clay Miner 19:151–158
Michaels AS, Lin C (1954) Permeability of kaolinite. Ind Eng Chem 46(6):1239–1246
Mitchell JK, Witherspoon PA, Greenberg JA. Chemico-osmotic effects in fine-grained soils. J Soil Mech Found Div Am Soc Civ Eng (United States) 99:SM4, 04 1973
Mitchell J K, Soga K et al (2005) Fundamentals of soil behavior, vol 3. Wiley, New York
Monaghan JJ (1992) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Ann Rev Astron Astrophys 30(1):543–574
Moyne C, Murad MA (2002) Electro-chemo-mechanical couplings in swelling clays derived from a micro/macro-homogenization procedure. Int J Solids Struct 39(25):6159–6190
Nalbantoglu Z, Tuncer ER (2001) Compressibility and hydraulic conductivity of a chemically treated expansive clay. Can Geotech J 38(1):154–160
Nova R, Castellanza R, Tamagnini C (2003) A constitutive model for bonded geomaterials subject to mechanical and/or chemical degradation. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 27(9):705–732
Nuth M, Laloui L (2008) Effective stress concept in unsaturated soils: clarification and validation of a unified framework. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 32(7):771–801
O’ Donnell S T, Rittmann B E, Kavazanjian E Jr (2017) Midp: Liquefaction mitigation via microbial denitrification as a two-stage process. I: Desaturation. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 143(12):04017094
O’ Donnell S T, Kavazanjian E Jr, Rittmann B E (2017) Midp: Liquefaction mitigation via microbial denitrification as a two-stage process. II: Micp. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 143(12):04017095
Ouchi H, Katiyar A, York J, Foster JT, Sharma MM (2015) A fully coupled porous flow and geomechanics model for fluid driven cracks: a peridynamics approach. Comput Mech 55(3):561–576
Peters GP, Smith DW (2004) The influence of advective transport on coupled chemical and mechanical consolidation of clays. Mech Mater 36(5):467–486 Coupled Chemo-Mechanical Phenomena
Quigley RM, Fernandez F, Yanful E, Helgason T, Margaritis A, Whitby J (1987) Hydraulic conductivity of contaminated natural clay directly below a domestic landfill. Can Geotech J 24(3):377–383
Sarout J, Detournay E (2011) Chemoporoelastic analysis and experimental validation of the pore pressure transmission test for reactive shales. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 48(5):759–772
Seetharam S, Thomas H, Cleall PJ (2007) Coupled thermo/hydro/chemical/mechanical model for unsaturated soilsnumerical algorithm. Int J Numer Methods Eng 70(12):1480–1511
Sherwood J (1993) Biot poroelasticity of a chemically active shale. Proc R Soc Lond A Math Phys Eng Sci 440(1909):365–377
Silling SA (2000) Reformulation of elasticity theory for discontinuities and long-range forces. J Mech Phys Solids 48(1):175–209
Silling SA, Askari E (2005) A meshfree method based on the peridynamic model of solid mechanics. Comput Struct 83(17–18):1526–1535
Silling SA, Lehoucq R (2010) Peridynamic theory of solid mechanics. Adv Appl Mech 44:73–168
Silling SA, Epton M, Weckner O, Xu J, Askari E (2007) Peridynamic states and constitutive modeling. J Elast 88(2):151–184
Simo J, Hughes T (1998) Computational inelasticity. Springer, New York
Song X (2014) Strain localization in unsaturated porous media. Ph.D. thesis. Stanford University
Song X (2017) Transient bifurcation condition of partially saturated porous media at finite strain. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 41(1):135–156
Song X, Borja RI (2014) Finite deformation and fluid flow in unsaturated soils with random heterogeneity. Vadose Zone J 13(5):1–11
Song X, Borja RI (2014) Mathematical framework for unsaturated flow in the finite deformation range. Int J Numer Methods Eng 97(9):658–682
Song X, Wang K, Ye M (2018) Localized failure in unsaturated soils under non-isothermal conditions. Acta Geotech 13(1):73–85
Song X, Idinger G, Borja RI, Wu W (2012) Finite element simulation of strain localization in unsaturated soils. In: Unsaturated soils: research and applications. Springer, pp 189–195
Song X, Ye M, Wang K. Strain localization in a solid-water-air system with random heterogeneity via stabilized mixed finite elements. Int J Numer Methods Eng. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.5590
Sridharan A (1991) Engineering behaviour of fine grained soils: a fundamental approach. Indian Geotehn J
Sridharan A, Rao GV (1973) Mechanisms controlling volume change of saturated clays and the role of the effective stress concept. Géotechnique 23(3):359–382
Taron J, Elsworth D (2009) Thermal-hydrologic-mechanical-chemical processes in the evolution of engineered geothermal reservoirs. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(5):855–864
Taron J, Elsworth D, Min K-B (2009) Numerical simulation of thermal-hydrologic-mechanical-chemical processes in deformable, fractured porous media. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(5):842–854
Thomas H, Cleall P (1999) Inclusion of expansive clay behaviour in coupled thermo hydraulic mechanical models. Eng Geol 54(1):93–108
Thomas H, Cleall P (1997) Chemico-osmotic effects on the behaviour of unsaturated expansive clays. In: Geoenvironmental Engineering: Contaminated Ground
Thomas H, Cleall P, Seetharam S (2002) Numerical modelling of the thermal-hydraulic-chemical-mechanical behaviour of unsaturated clay. Environ Geomech Monte Verità, pp 125–136
Ulm F-J, Coussy O (1995) Modeling of thermochemomechanical couplings of concrete at early ages. J Eng Mech 121(7):785–794
Van Genuchten MT (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44(5):892–898
Wheeler S, Sivakumar V (1995) An elasto-plastic critical state framework for unsaturated soil. Géotechnique 45(1):35–53
Witteveen P, Ferrari A, Laloui L (2013) An experimental and constitutive investigation on the chemo-mechanical behaviour of a clay. Geotechnique 63(3):244
Zhang H, Zhou L (2008) Implicit integration of a chemo-plastic constitutive model for partially saturated soils. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 32(14):1715–1735
Acknowledgements
Support for this work was provided by the Geotechnical Engineering and Materials Program of the US National Science Foundation (NSF) under contract number CMMI-1659932 to the University of Florida. The support is gratefully acknowledged. Any opinions or positions expressed in this article are those of the authors only and do not reflect any opinions or positions of the NSF. We also thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive reviews.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Menon, S. Modeling of chemo-hydromechanical behavior of unsaturated porous media: a nonlocal approach based on integral equations. Acta Geotech. 14, 727–747 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-018-0679-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-018-0679-9