Abstract
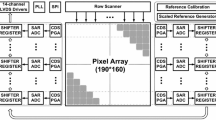
A low power 8T global shutter pixel with extended FD voltage swing range is proposed for large format high speed CMOS image sensor. The pixel has a negative threshold reset transistor, two in-pixel source followers, and a sample-and-hold circuit. The in-pixel first source follower is employed for reducing the pixel average current and maximum transient current. The negative threshold reset transistor is applied to extend the voltage swing of FD. Using pixel level sample-and-hold circuit, the kTC noise on FD node can be effectively nullified by correlated double sampling operation. A high speed 1000 fps 256 × 256 CMOS image sensor is implemented in 0.18 μm CMOS process. Two 10-bit cyclic ADC arrays are integrated in this prototype sensor chip. The active area of the chip is 10 mm × 7 mm with a pixel size of 14 μm × 14 μm. The developed sensor achieves an average current of 23 nA per pixel, a maximum transit current per pixel as low as 1113 nA, and a large FD voltage swing of 1.78 V. The sensor temporal noise level is 103 e- and full well capacity has 27000 e-which results in 48.3 dB signal dynamic range
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Furuta M, Nishikawa Y, Inoue T, et al. A high-speed, high-sensitivity digital CMOS image sensor with a global shutter and 12-bit column-parallel cyclic A/D converters. IEEE J Solid-State Circuit, 2007, 42: 766–774
Krymski A I, Tu N. A 9-V/Lux-s 5000-frames/s 512×512 CMOS sensor. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2003, 50: 136–143
Bock N, Krymski A, Sarwari A, et al. A wide-VGA CMOS image sensor with global shutter and extended dynamic range. In: Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on Charge Coupled Devices and Advanced Image Sensors, Karuizawa, 2005. 222–225
Takayanagi I, Mo Y, Ando H, et al. A 600×600 Pixel, 500 fps CMOS image sensor with a 4.4 μm pinned photodiode 5-transistor global shutter pixel. In: Proceedings of International Image Sensor Workshop, Ogunquit, 2007. 278–290
Zhou Y F, Cao Z X, Qin Q, et al. A high speed 1000 fps CMOS image sensor with low noise global shutter pixels. Sci China Inf Sci, 2014, 57: 042405
Wang X Y, Bogaerts J, Vanhorebeek G, et al. A 2.2 M CMOS image sensor for high speed machine vision application. In: Proceedings of SPIE 6536, Sensors, Cameras, and Systems for Industrial/Scientific Applications XI, San Jose, 2010. 75360M
Yasutomi K, Itoh S, Kawahito S, et al. Two-stage charge transfer pixel using pinned diodes for low-noise global shutter imaging. In: Proceedings of International Image Sensor Workshop, Bergen, 2009. 333–336
Nixon R H, Kemeny S E, Pain B, et al. 256× 256 CMOS active pixel sensor camera-on-a-chip. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1996, 31: 2046–2050
Takahashi H, Noda T, Matsuda T, et al. A 1/2.7-in 2.96 MPixel CMOS image sensor with double CDS architecture for full high-definition camcorders. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42: 2960–2967
Cheon J, Han G. Noise analysis and simulation method for a single-slope ADC with CDS in a CMOS image sensor. IEEE Trans Circuit Syst I-Regul Pap, 2008, 55: 2980–2987
Mutoh H. 3-D optical and electrical simulation for CMOS image sensors. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2003, 50: 19–25
Inoue I, Tanaka N, Yamashita H, et al. Low-leakage-current and low-operating-voltage buried photodiode for a CMOS imager. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2003, 50: 43–47
Cao Z X, Zhou Y F, Li Q L, et al. Design of pixel for high speed CMOS image sensors. In: Proceedings of International Image Sensor Workshop, Snowbird, 2013. 229–232
Zhou Y F, Cao Z X, Li Q L, et al. Design of four-transistor pixel for high speed CMOS image. In: Proceedings of IEEE 9th International Conference on ASIC, Xiamen, 2011. 171–174
Kawai N, Kawahito S. Noise analysis of high-gain, low-noise column readout circuits for CMOS image sensors. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2004, 51: 185–194
Kawai N, Kawahito S. A low-noise signal readout circuit using double-stage noise cancelling architecture for CMOS image sensors. In: Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on Charge Coupled Devices and Advanced Image Sensors, Karuizawa, 2005. 27–30
Kim B C, Jeon J, Shin H, et al. Temporal noise analysis and reduction method in CMOS image sensor readout circuit. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2009, 56: 2489–2495
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Cao, Z., Han, Y. et al. A low power global shutter pixel with extended FD voltage swing range for large format high speed CMOS image sensor. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 58, 1–10 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-014-5272-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-014-5272-8