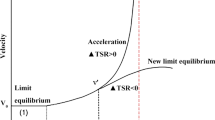
Abstract
Predicting the failure time of unstable slopes is one of the most pivotal issues. In this paper, the inverse square root acceleration (INSRA) method was proposed to estimate the time-of-failure (TOF) of landslides. Four collapsed slopes were presented in the three open-pit mines, two of them were probed by ground-based radar, and two of them were obtained from previous scientific papers. The inverse velocity (INV) method and INSRA method were adopted to analyze these four landslides and one slope which had great deformation but did not reach failure. Compared with the traditional INV method, the INSRA method can promote the forecasting effectiveness and has the advantage of higher accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thiebes B, Bell R, Glade T, et al. Integration of a limit-equilibrium model into a landslide early warning system. Landslides, 2014, 11: 859–875
Intrieri E, Gigli G, Mugnai F, et al. Design and implementation of a landslide early warning system. Eng Geol, 2012, 147–148: 124–136
Greco R, Giorgio M, Capparelli G, et al. Early warning of rainfall-induced landslides based on empirical mobility function predictor. Eng Geol, 2013, 153: 68–79
Intrieri E, Carlà T, Gigli G. Forecasting the time of failure of landslides at slope-scale: A literature review. Earth-Sci Rev, 2019, 193: 333–349
Newcomen W, Dick G. An update to the strain-based approach to pit wall failure prediction, and a justification for slope monitoring. J S Afr Inst Min Metall, 2016, 116: 5
Deng J. Grey Forecasting and Decision Making. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 1988. 86–128
Yang S. Engineering Application of Time Series Analysis. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology Press, 1992
Ding J X, Yang Z F, Shang Y J, et al. A new method for spatiotemporal prediction of rainfall-induced landslide. Sci China Ser DEarth Sci, 2006, 49: 421–430
Liu Z, Shao J, Xu W, et al. Comparison on landslide nonlinear displacement analysis and prediction with computational intelligence approaches. Landslides, 2014, 11: 889–896
Yao W, Zeng Z, Lian C, et al. Training enhanced reservoir computing predictor for landslide displacement. Eng Geol, 2015, 188: 101–109
Du J, Yin K, Lacasse S. Displacement prediction in colluvial landslides, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides, 2013, 10: 203–218
Lian C, Zeng Z, Yao W, et al. Multiple neural networks switched prediction for landslide displacement. Eng Geol, 2015, 186: 91–99
Chousianitis K, Del Gaudio V, Kalogeras I, et al. Predictive model of Arias intensity and Newmark displacement for regional scale evaluation of earthquake-induced landslide hazard in Greece. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng, 2014, 65: 11–29
Du W, Wang G. A one-step Newmark displacement model for probabilistic seismic slope displacement hazard analysis. Eng Geol, 2016, 205: 12–23
Hwang G S, Chen C H. A study of the Newmark sliding block displacement functions. Bull Earthq Eng, 2013, 11: 481–502
Zhao Z, Zhou X P, Qian Q H. Fracture characterization and perme-ability prediction by pore scale variables extracted from X-ray CT images of porous geomaterials. Sci China Tech Sci, 2020, 63: 755–767
Yiğit A. Prediction of amount of earthquake-induced slope displacement by using Newmark method. Eng Geol, 2020, 264: 105385
Fukuzono T. A new method for predicting the failure time of a slope. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference and Field Workshop on Landslides. Tokyo, 1985. 145–150
Voight B. A method for prediction of volcanic eruptions. Nature, 1988, 332: 125–130
Mufundirwa A, Fujii Y, Kodama J. A new practical method for prediction of geomechanical failure-time. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci, 2010, 47: 1079–1090
Crosta G B, Agliardi F. How to obtain alert velocity thresholds for large rockslides. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C, 2002, 27: 1557–1565
Dick G J, Eberhardt E, Cabrejo-Liévano A G, et al. Development of an early-warning time-of-failure analysis methodology for open-pit mine slopes utilizing ground-based slope stability radar monitoring data. Can Geotech J, 2015, 52: 515–529
Rose N D, Hungr O. Forecasting potential rock slope failure in open pit mines using the inverse-velocity method. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci, 2007, 44: 308–320
Carlà T, Farina P, Intrieri E, et al. On the monitoring and early-warning of brittle slope failures in hard rock masses: Examples from an open-pit mine. EngGeol, 2017, 228: 71–81
Saito M. Forecasting time of occurrence of a slope failure. In: Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Oxford, Pergamon, 1965. 537–541
Yoshida T, Yachi M. On the velocity of landslide (in Japanese). In: Proceedings of the 23rd Meeting of Japan Landslide Society, 1984. 136–139
Chen M X, Jiang Q. An early warning system integrating time-of-failure analysis and alert procedure for slope failures. Eng Geol, 2020, 272: 105629
Crosta G B, Agliardi F. Failure forecast for large rock slides by surface displacement measurements. Can Geotech J, 2003, 40: 176–191
Antonello G, Casagli N, Farina P, et al. Ground-based SAR inter-ferometry for monitoring mass movements. Landslides, 2004, 1: 21–28
Li Y S, Jiao Q S, Hu X H, et al. Detecting the slope movement after the 2018 Baige Landslides based on ground-based and space-borne radar observations. Int J Appl Earth Observ Geoinf, 2020, 84: 101949
Zhang Y, Meng X M, Dijkstra T A, et al. Forecasting the magnitude of potential landslides based on InSAR techniques. Remote Sens Environ, 2020, 241: 111738
Zhou X P, Liu L J, Xu C. A modified inverse-velocity method for predicting the failure time of landslides. Eng Geol, 2020, 268: 105521
Xu Q, Yuan Y, Zeng Y P, et al. Some new pre-warning criteria for creep slope failure. Sci China Tech Sci, 2011, 54: 210–220
Han M, Rao Y Z, Chen J L, et al. Landslide warning model of creep ion-adsorption rare earth ore slope based on displacement-time curve. Chin Rare Earths, 2019, 40: 1–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51839009 and 51679017).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Ye, T. Inverse-square-root-acceleration method for predicting the failure time of landslides. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 64, 1127–1136 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-020-1722-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-020-1722-2