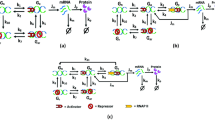
Abstract
A gene is often regulated by a variety of transcription factors, leading to complex promoter structure. However, how this structure affects gene expression remains elusive. Here, this paper studies a stochastic gene model with the promoter containing arbitrarily many active and inactive states. First, the authors use the binomial moment method to derive analytical steady-state distributions of the mRNA and protein numbers. Then, the authors analytically investigate how the promoter structure impacts the mean expression levels and the expression noise. Third, numerical simulation finds interesting phenomena, e.g., the common on-off model overestimates the expression noise in contrast to multiple-state models; the multi-on mechanism can reduce the expression noise more than the multi-off mechanism if the mean expression level is kept the same; and multiple exits of transcription can result in multimodal distributions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanchez A, Garcia H G, Jones D, et al., Effect of promoter architecture on the cell-to-cell variability in gene expression, PLoS Comput. Biol., 2011, 7: e1001100.
Pedraza J M and Paulsson J, Effects of molecular memory and bursting on fluctuations in gene expression, Science, 2008, 319: 339–343.
Boeger H, Griesenbeck J, and Kornberg R D, Nucleosome retention and the stochastic nature of promoter chromatin remodeling for transcription, Cell, 2008, 133: 716–726.
Larson D R, What do expression dynamics tell us about the mechanism of transcription? Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 2011, 21: 591–599.
Blake W J, Kærn M, Cantor C R, et al., Noise in eukaryotic gene expression, Nature, 2003, 422: 633–637.
Raser J and O’Shea E, Control of stochasticity in eukaryotic gene expression, Science, 2003, 304: 1811–1814.
Chubb J R, Trcek T, Shenoy S M, et al., Transcriptional pulsing of a developmental gene, Curr. Biol., 2006, 16: 1018–1025.
Sanchez A and Kondev J, Transcriptional control of noise in gene expression, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2008, 105: 5081–5086.
Mariani L, Schulz E G, Lexberg M H, et al., Short-term memory in gene induction reveals the regulatory principle behind stochastic IL-4 expression, Mol. Syst. Biol., 2010, 6: 359–372.
Qiu H H and Zhou T S, Exact distributions in the full models of gene expression, Sci. Sin. Math., 2017, 47: 1863–1878 (in Chinese).
Eldar A and Elowitz M B, Functional roles for noise in genetic circuits, Nature, 2010, 467: 167–173.
Yu J, Xiao J, Ren X J, et al., Probing gene expression in live cells, one protein molecule at a time, Science, 2006, 311: 1600–1603.
Cai L, Friedman N, and Xie X S, Stochastic protein expression in individual cells at the single molecule level, Nature, 2006, 440: 358–362.
Golding I, Paulsson J, Zawilski S M, et al., Real-time kinetics of gene activity in individual bacteria, Cell, 2005, 123: 1025–1036.
Raj A, Peskin C S, Tranchina D, et al., Stochastic mRNA synthesis in mammalian cells, PLoS Biol., 2006, 4: e309.
Chubb J R and Liverpool T B, Bursts and pulses: Insights from single cell studies into transcriptional mechanisms, Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 2010, 20: 478–484.
Suter D M, Molina N, Gatfield D, et al., Mammalian genes are transcribed with widely different bursting kinetics, Science, 2011, 332: 472–474.
Harper C V, Finkenstädt B, Woodcock D J, et al., Dynamic analysis of stochastic transcription cycles, PLoS Biol., 2011, 9: e1000607.
Dobrzynski M and Bruggeman F J, Elongation dynamics shape bursty transcription and translation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2009, 106: 2583–2588.
Rinott R, Jaimovich A, and Friedman N, Exploring transcription regulation through cell-to-cell variability, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2011, 108: 6329–6334.
Huh D and Paulsson J, Non-genetic heterogeneity from stochastic partitioning at cell division, Nat. Genet., 2011, 43: 95–100.
Bintu L, Buchler N E, and Garcia H G, Transcriptional regulation by the numbers: Models, Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 2005, 15: 116–124.
Coulon A, Gandrillon O, and Beslon G, On the spontaneous stochastic dynamics of a single gene: Complexity of the molecular interplay at the promoter, BMC Syst. Biol., 2010, 4(1): 2.
Simpson M L, Cox C D, and Sayler G S, Frequency domain chemical Langevin analysis of stochasticity in gene transcriptional regulation, J. Theor. Biol., 2004, 229: 383–394.
Höfer T and Rasch M J, On the kinetic design of transcription, Genome Inform., 2005, 16: 73–82.
Carey L B, van Dijk D, and Sloot P M, Promoter sequence determines the relationship between expression level andnoise, PLoS Biol., 2013, 11: e1001528.
Brown C R, Mao C, and Falkovskaia E, Linking stochastic fluctuations in chromatin structure and gene expression, PLoS Biol., 2013, 11: e1001621.
Zhou T S, Advance research of gene expression systems: Probability distribution, J. Jiangxi Norm. Uni. (Nat. Sci. Edit.), 2012, 36(3): 221–229.
Peccoud J and Ycart B, Markovian modelling of gene product synthesis, Theor. Popul. Biol., 1995, 48: 222–234.
Kepler T B and Elston T C, Stochasticity in transcriptional regulation: Origins, consequences, and mathematical representations, Biophys. J., 2001, 81: 3116–3036.
Paulsson J, Models of stochastic gene expression, Phys. Life Rev., 2005, 2: 157–175.
Shahrezaei V and Swain P S, Analytical distributions for stochastic gene expression, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2008, 105: 17256–17261.
Karmakar R and Bose I, Graded and binary responses in stochastic gene expression, Phys. Biol., 2004, 1: 197–204.
Iyer-Biswas S, Hayot F, and Jayaprakash C, Stochasticity of gene products from transcriptional pulsing, Phys. Rev. E, 2009, 79: 031911.
Mugler A, Walczak A M, and Wiggins C H, Spectral solutions to stochastic models of gene expression with bursts and regulation, Phys. Rev. E, 2009, 80: 041921.
Zhang J J, Chen L N, and Zhou T S, Analytical distribution and tunability of noise in a model of promoter progress, Biophys. J., 2012, 102: 1247–1257.
Zhou T S and Zhang J J, Analytical results for a multistate gene model, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 2012, 72: 789–818.
Sanchez A, Choubey S, and Kondev J, Stochastic models of transcription: From single molecules to single cells, Methods, 2013, 62(1): 13–25.
To T L and Maheshri N, Noise can induce bimodality in positive transcriptional feedback loops without bistability, Science, 2010, 327: 1142–1145.
Blake W J, Balázsi G, and Kohanski M A, Phenotypic consequences of promoter-mediated transcriptional noise, Mol. Cell., 2006, 6: 853–865.
Zhang J J, Nie Q, and Zhou T S, A moment-convergence method for stochastic analysis of biochemical reaction networks, J. Chem. Phys., 2016, 144(19): 018620.
Zhou T S, Binomial moments and attribute factors for biochemical reaction systems, J. Jiangxi Norm. Uni. (Nat. Sci. Edit.), 2016, 40(1): 1–4.
Gillespie D T, Exact stochastic simulation of coupled chemical reactions, J. Phys. Chem., 1977, 81: 2340–2361.
Zhang J J and Zhou T S, Promoter architecture-mediated transcriptional dynamics, Biophys. J., 2014, 106: 479–488.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This research was supported by Science and Technology Department under Grant No. 2014CB964703, the Natural Science Foundation under Grant Nos. 91530320, 11401448, 61573011, the Hubei Province Education Department under Grant No. B2016062, and the Science and Technology Department of Hubei Province under Grant Nos. 2017CFB682 and 2018CFB688.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor SUN Jian.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, H., Zhang, B. & Zhou, T. Influence of Complex Promoter Structure on Gene Expression. J Syst Sci Complex 32, 600–614 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-018-7224-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-018-7224-7