Abstract
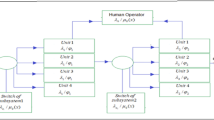
The availability equivalence of different designs for a repairable multi-state series-parallel system (RMSPS) is discussed in this paper. The system components are assumed to be independent, and their failure and repair rates to be constant. The system availability is defined as the ability of the system to satisfy consumer demand. Factor improvement method and standby redundancy method are used to improve the system design. To evaluate availability of the both original and improved systems, a fast technique, based on universal generating function, is adopted. The availability equivalence factor is introduced to compare different system designs. Two types of availability equivalence factors of the system are derived. A numerical example is provided to illustrate how to utilize the obtained results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Råde L, Reliability equivalence: Studies in statistical quality control and reliability, Mathematical Statistics, Chalmers University of Technology, 1989.
Sarhan A M, Reliability equivalence factors of a parallel system, Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2005, 87(3): 405–411.
Mustafa A and El-Faheem A A, Reliability equivalence factors of a general parallel system with mixture of lifetimes, Applied Mathematical Sciences, 2012, 6(76): 3769–3784.
Lewis E E, Introduction to Reliability Engineering, 2nd ed. Wiley, New York, 1996.
Råde L, Performance measures for reliability systems with a cold standby with a random switch, studies in statistical quality control and reliability, mathematical statistics, Chalmers University of Technology, 1991.
Råde L, Reliability equivalence, Microelectronics Reliability, 1993, 33(3): 323–325.
Råde L, Reliability survival equivalence, Microelectronics Reliability, 1993, 33(6): 881–894.
Sarhan A M, Reliability equivalence of independent and non-identical components series systems, Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2000, 67(3): 293–300.
Sarhan A M, Reliability equivalence with a basic series/parallel system, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2002, 132(1): 115–133.
Sarhan A M, Reliability equivalence factors of a bridge network system, International Journal of Reliability and Applications, 2004, 2(1): 81–103.
Sarhan A M, Reliability equivalence factors of a general series-parallel system, Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2009, 94(2): 229–236.
Montaser M and Sarhan A M, Reliability equivalence of a parallel system with non-identical components, International Mathematical Forum, 2008, 3(34): 1693–1712.
Sarhan A M and Mustafa A, Reliability equivalence of a series system consists of n independent and non-identical components, International Journal of Reliability and Applications, 2006, 7(2): 111–125.
Sarhan A M, Al-Ruzaiza A S, Alwasel I A, et al., Reliability equivalence of a series-parallel system, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2004, 154: 257–277.
Xia Y and Zhang G, Reliability equivalence factors in gamma distribution, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2007, 187(2): 567–573.
Mustafa A, Reliability equivalence factor of n-component series system with non-constant failure rates, International Journal of Reliability and Applications, 2009, 10(1): 43–45.
Mustafa A, Reliability equivalence of some systems with mixture Weibull failure rates, African Journal of Mathematics and Computer Science Research, 2009, 2(1): 6–13.
Pogány T K, Tomas V, and Tudor M, Hot duplication versus survivor equivalence in Gamma-Weibull distribution, Journal of Statistics Applications and Probability, 2013, 2(1): 1–10.
Mustafa A and El-Faheem A A, Reliability equivalence factors of a system with 2 non-identical mixed lifetimes and delayed time, Journal of Mathematics and Statistics, 2011, 7(3): 169–176.
Shawky A I, Abdelkader Y H, and Al-Ohally M I, Reliability equivalence factors in exponentiated exponential distribution, WULFENIA Journal, 2013, 20(3): 75–85.
Hu L M, Yue D Q, and Zhao D M, Availability equivalence analysis of a repairable series-parallel system, Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2012, Article ID 957537: 1–15, doi: 10.1155.
Sarhan A M and Mustafa A, Availability equivalence factors of a general repairable series-parallel system, International Journal of Reliability and Applications, 2013, 14(1): 11–26.
Mustafa A and Sarhan A M, Availability equivalence factors of a general repairable parallel-series system, Applied Mathematics, 2014, 5: 1713–1723.
Murchland J, Fundamental concepts and relations for reliability analysis of multi-state systems, reliability and fault tree analysis, Theoretical and Applied Aspects of System Reliability, 1975, 581–618.
Lisnianski A and Levitin G, Multi-State System Reliability Assessment, Optimization, Applications, World Scientific, Singapore, 2003.
Ushakov I, Universal generating function, Soviet Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 1986, 24(5): 118–129.
Levitin G, Universal Generating Function and Its Application, Springer, Berlin, 2005.
Castro H and Cavalca K L, Maintenance resources optimization applied to a manufacturing system, Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2006, 91(4): 413–420.
Tian Z, Levitin G, and Zuo M J, A joint reliability-redundancy optimization approach for multistate series-parallel systems, Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2009, 94(10): 1568–1576.
Nourefath M and Ait-Kadi D, Optimization of series-parallel multi-state systems under maintenance policies, Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2007, 92(12): 1620–1626.
Liu Y and Zheng H, Study on reliability of warm standby’s repairable system with n identity units and k repair facilities, Journal of Wenzhou University, 2010, 31(3): 24–29 (in Chinese).
Gu J and Wei Y, Reliability quantities of an n-unit cold standby repairable system with two repair facility, Journal of Gansu Lianhe University, 2006, 20(2): 17–20 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research work was supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province under Grant Nos. A2014203096 and G2012203136, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 11201408, and the Science Research Project of Yanshan University under Grant No. 13LGA017.
This paper was recommended for publication by Editor WANG Shouyang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, L., Yue, D. & Tian, R. Availability equivalence analysis of a repairable multi-state series-parallel system. J Syst Sci Complex 29, 1596–1616 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-016-4300-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-016-4300-8