Abstract
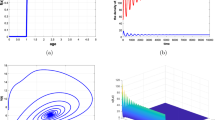
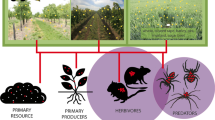
This paper studies a three tier ecological food chain model consisting of nutrient, autotroph, and herbivore populations. Regeneration of nutrient from dead autotroph and herbivore biomass by decomposers present in the soil is included. The time required for maturation of the herbivore population is incorporated as a distributed time delay. Next, the authors introduce the time lag required for regeneration of nutrient from the dead herbivore as a discrete time delay. Stability and bifurcation behavior of the one- and two-delay models are carried out and a comparative study of the significance of these delays in controlling the system dynamics is performed. Numerical simulations are done to justify analytical results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. L. Smith, Food Webs, Chapman and Hall, London, UK, 1982.
A. K. Sarkar, D. Mitra, and A. B. Roy, Permanence and oscilatory co-existence of a detritus-based prey predator model, Ecol. Model., 1991, 53: 147–156.
A. K. Sarkar and A. B. Roy, Oscilatory behavior in a resource-based plant-herbivore model with random herbivor attack, Ecol. Model., 1993, 68: 213–226.
D. Ghosh and A. K. Sarkar, Oscillatory behaviour of an autotroph herbivore system with a type-III uptake function, Int. J. Syst. Sci., 1997, 28(3): 259–264.
D. Ghosh and A. K. Sarkar, Qualitative analysis of autotroph herbivore system with nutrient diffusion, Korean J. Comput. Appl. Math., 1999, 6: 589–599.
D. Mukherjee, S. Ray, and D. K. Sinha, Bifurcation analysis of a detritus-based ecosystem with time delay, J. Biol. Syst., 2000, 8(3): 255–261.
D. Ludwig, D. D. Jones, and C. S. Holling, Qualitayive anlysis of insect outbreak systems: The spruce budworm and forest, J Anim. Eco., 1978, 47: 315–332.
M. J. Crawley, Herbivory: The Dynamics of Animal Plant Interaction, Studies in Ecology, University of Califonia Press, Berkley, CA, 1983, 10.
M. Farkas and H. I. Freedman, The stable coexistence of competeting species on a renewable resource, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 1989, 138, 461–472.
A. Sikder and A. B. Roy, Limit cycles in prey predator systems, Appl. Math. Lett., 1993, 6(3): 91–95.
S. Muratori and S. Rinaldi, Low and high-frequency oscilations in three dimensional food chain system, SIAM J. Appl. Math., 1992, 52(52): 1688–1706.
R. Bhattacharyya and B. Mukhopadhyay, Oscillation and persistence in a mangrove ecosystem in presence of delays, J. Biol. Syst., 2003, 11(4): 351–364.
M. Bandyopadhyay, R. Bhattacharyya, and B. Mukhopadhyay, Dynamics of an autotroph-herbivore ecosystem with nutrient recycling, Ecol. Model., 2004, 176: 201–209.
G. Hallam, Structural sensitivity of grazing formulation in nutrient controlled plankton models, J. Math. Biol., 1978, 5: 261–280.
T. Powell and P. J. Richardson, Temporal variation, spatial heterogeneity and competition for resources in plankton systems: Theoretical models, Am. Nat., 1985, 125: 431–463.
E. Beltrami and T. O. Carroll, Modelling the role of viral diseases in recurrent phytoplankton blooms, J. Math. Biol., 1994, 32: 857–863.
S. Ruan, Persistence and co-existence in zooplankton phytoplankton nutrient models with instantaneous nutrient recycling, J. Math. Biol., 1993, 31: 633–654.
S. Ruan, The effect of delays on stability and persistence in plankton models, Nonlinear Anal., 1995, 24: 575–585.
S. Ruan, Oscilations in plankton models with nutrient recycling, J. Theor. Biol., 2001, 208: 15–26.
S. Ruan and G. Wolkowicz, Uniform persistence in plankton models with delayed nutrient recycling, Canad. Appl. Math. Quart., 1995, 3: 219–235.
S. R. J. Jang, Dynamics of variable-yield nutrient phytoplankton zooplankton models with nutrient recycling and self-shedding, J. Math. Biol., 2000, 40: 229–250.
O. Pardo, Global stability for a phytoplankton nutrient system, J. Biol. Syst., 2000, 8(2): 195–209.
B. Mukhopadhyay and R. Bhattacharyya, A delay-diffution model of marine plankton ecosystem exhibiting cyclic nature of blooms, J. Biol. Phy., 2005, 31(1): 3–22.
B. Mukhopadhyay and R. Bhattacharyya, Modelling phytoplankton allelopathy in a nutrientplankton model with spatial heterogeneity, Ecol. Model., 2006, 198(1–2): 163–173.
B. Mukhopadhyay and R. Bhattacharyya, Modelling the role of diffusion coefficients on Turing instability in a reaction-diffusion prey-predator system, Bull. Math. Biol., 2006, 68: 293–313.
P. Colinvaux, Ecology-I, Wiley, USA, 1993.
R. M. Nisbet, J. Mckinstry, and W. S. C. Gurney, A strategic model of material cycling in a close ecosystem, Math. Biosci., 1983, 64: 99–113.
Y. M. Svirezhev and D. O. Logofet, Stability of Biological Communities, Mir, Moscow, 1983.
D. L. De Angelis, Dynamics of Nutrient Recycling and Food Webs, Chapman and Hall, London, 1992.
D. Ghosh and A. K. Sarkar, Stability and osilations in a resource-based model of two interacting species with nutrient cycling, Ecol. Model., 1998, 107: 25–33.
E. Beretta, G. I. Bischi, and F. Solimano, Stability in chemostat equations with delayed nutrient recycling, J. Math. Biol., 1990, 28: 99–111.
G. I. Bischi, Effects of time lag on transient characteristics of a nutrient recycling model, Math. BioSci., 1992, 109: 151–175.
D. L. De Angelis, S. M. Bartell, and A. L. Brenkert, Effect of nutrient recycling and food chain lenght on the resilience, Am. Nat., 1989, 134: 778–805.
N. MacDonald, Biological Delay Systems: Linear Stability Theory, Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is supported by the Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Human Resource Development, Govt. of India under Grant No. SR/S4/MS:296/05.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharyya, R., Bera, A. & Mukhopadhyay, B. Role of different system delays on ecological food chain dynamics: Mathematical modelling and analysis. J Syst Sci Complex 23, 727–737 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-010-8190-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11424-010-8190-x