Abstract
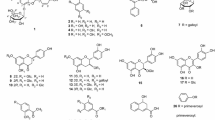
A methanol extract of mace, the aril of Myristica fragrans (Myristicaceae), was found to inhibit the release of β-hexosaminidase, a marker of antigen-IgE-stimulated degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia cells (RBL-2H3, IC50 = 45.7 μg/ml). From the extract, three new 8-O-4′ type neolignans, maceneolignans I–K (1–3), were isolated, and the stereostructures of 1–3 were elucidated based on spectroscopic and chemical evidence. Among the isolates, maceneolignans A (5), D (6), and H (8), (−)-(8R)-∆8′-4-hydroxy-3,3′,5′-trimethoxy-8-O-4′-neolignan (13), (−)-(8R)-∆8′-3,4,5,3′,5′-pentamethoxy-8-O-4′-neolignan (14), (−)-erythro-(7R,8S)-∆8′-7-acetoxy-3,4-methylenedioxy-3′,5′-dimethoxy-8-O-4′-neolignan (17), (+)-licarin A (20), nectandrin B (24), verrucosin (25), and malabaricone C (29) were investigated as possible degranulation inhibitors (IC50 = 20.7–63.7 μM). These inhibitory activities were more potent than those of the antiallergic agents tranilast (282 μM) and ketotifen fumalate (158 μM). Compounds 5, 25, and 29 also inhibited antigen-stimulated tumor necrosis factor-α production (IC50 = 39.5–51.2 μM), an important process in the late phase of type I allergic reactions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paul S, Hwang JK, Kim HY, Jeon WK, Chung C, Han J-S (2013) Multiple biological properties of macelignan and its pharmacological implications. Arch Pharm Res 36:264–272
Nagja T, Vimal K, Sanjeev A (2016) Myristica fragrans: a comprehensive review. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 8:27–30
Acuña UM, Carcache PJB, Matthew S, de Blanco EJC (2016) New acyclic bis phenylpropanoid and neolignans, from Myristica fragrans Houtt., exhibiting PARP-1 and NF-κB inhibitory effects. Food Chem 202:269–275
Cao G-Y, Xu W, Yang X-W, Gonzalez FJ, Li F (2015) New neolignans from the seeds of Myristica fragrans that inhibit nitric oxide production. Food Chem 173:231–237
Morikawa T, Hachiman I, Matsuo K, Nishida E, Ninomiya K, Hayakawa T, Yoshie O, Muraoka O, Nakayama T (2016) Neolignans from the arils of Myristica fragrans as potent antagonists of CC chemokine receptor 3. J Nat Prod 79:2005–2013
Platts-Mills TAE (2001) The role of immunoglobulin E in allergy and asthma. Am J Respir Criti Care Med 164:S1–S5
Matsubara M, Masaki S, Ohmori K, Karasawa A, Hasegawa K (2004) Differential regulation of IL-4 expression and degranulation by anti-allergic olopatadine in rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-2H3) cells. Biochem Pharmacol 67:1315–1326
Matsuda H, Nakamura S, Yoshikawa M (2016) Degranulation inhibitors from medicinal plants in antigen-stimulated rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-2H3) cells. Chem Pharm Bull 64:96–103
Tanaka Y, Takagaki Y, Nishimune T (1991) Effects of metal elements on β-hexosaminidase release from rat basophilic leukemia cells (RBL-2H3). Chem Pharm Bull 39:2072–2076
Matsuda H, Morikawa T, Managi H, Yoshikawa M (2003) Antiallergic principles from Alpinia galanga: structural requirements of phenylpropanoids for inhibition of degranulation and release of TNF-α and IL-4 in RBL-2H3 cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:3197–3202
Matsuda H, Morikawa T, Ueda K, Managi H, Yoshikawa M (2002) Structural requirements of flavonoids for inhibition of antigen-induced degranulation, TNF-α and IL-4 production from RBL-2H3 cells. Bioog Med Chem 10:3123–3128
Matsuda H, Tewtrakul S, Morikawa T, Yoshikawa M (2004) Anti-allergic activity of stilbenes from Korean rhubarb (Rheum undulatum L.): structure requirements for inhibition of antigen-induced degranulation and their effects on the release of TNF-α and IL-4 in RBL-2H3 cells. Bioorg Med Chem 12:4871–4876
Morikawa T, Xu F, Matsuda H, Yoshikawa M (2010) Structures of novel norstilbene dimer, longusone A, and three new stiblene dimers, longusols A, B, and C, with antiallergic and redical scavenging activities from Egyptian natural medicine Cyperus longus. Chem Pharm Bull 58:1379–1385
Matsuda H, Morikawa T, Tao J, Ueda K, Yoshikawa M (2002) Bioactive constituents of Chinese natural medicines. VII. inhibitors of degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells and absolute stereostructures of three new diarylphetanoid glycosides from the bark of Myrica rubra. Chem Pharm Bull 50:208–215
Morikawa T, Tao J, Ueda K, Matsuda H, Yoshikawa M (2003) Medicinal foodstuffs. XXXI. structures of new aromatic constituents and inhibitors of degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells from a Japanese folk medicine, the stem bark of Acer nikoense. Chem Pharm Bull 51:62–67
Matsuda H, Tewtrakul S, Morikawa T, Nakamura A, Yoshikawa M (2004) Anti-allergic principles from Thai zedoary: structural requiremtns of curcuminoids for inhibition of degranulation and effect on the release of TNF-α and IL-4 in RBL-2H3 cells. Bioorg Med Chem 12:5891–5898
Morikawa T, Matsuda H, Sakamoto Y, Ueda K, Yoshikawa M (2002) New farnesane-type sesquiterpenes, hedychiols A and B 8,9-diacetate, and inhibitors of degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells from the rhizome of Hedychium coronarium. Chem Pharm Bull 50:1045–1049
Morikawa T, Matsuda H, Toguchida I, Ueda K, Yoshikawa M (2002) Absolute stereostructures of three new sesquiterpenes from the fruit of Alpinia oxyphylla with inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production and degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells. J Nat Prod 65:1468–1474
Tao J, Morikawa T, Ando S, Matsuda H, Yoshikawa M (2003) Bioactive constituents from Chinese natural medicines. XI. Inhibitors on NO production and degranulation in RBL-2H3 from Rubia yunnanensis: structures of rubianosides II, III, and IV, rubianol-g, and rubianthraquinone. Chem Pharm Bull 51:654–662
Morikawa T, Nakamura S, Kato Y, Muraoka O, Matsuda H, Yoshikawa M (2007) Bioactive saponins and glycosides. XXVIII. new triterpene saponins, foliatheasaponins I, II, III, IV, and V, from tencha (the leaves of Camellia sinensis). Chem Pharm Bull 55:293–298
Matsuda H, Sugimoto S, Morikawa T, Matsuhira K, Mizuguchi E, Nakamura S, Yoshikawa M (2007) Bioactive constituents from Chinese natural medicines. XX. Inhibitors of antigen-induced degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells from the seeds of Psoralea corylifolia. Chem Pharm Bull 55:106–110
Sun B, Morikawa T, Matsuda H, Tewtrakul S, Wu LJ, Harima S, Yoshikawa M (2004) Structures of new β-carboline-type alkaloids with antiallegic effects from Stellaria dichotoma. J Nat Prod 67:1464–1469
Morikawa T, Sun B, Matsuda H, Wu LJ, Harima S, Yoshikawa M (2004) Bioactive constituents from Chinese natural medicines. XIV. New glycosides of β-carboline-type alkaloid, neolignan, and phenylpropanoid from Stellaria dichotoma L. var. lanceolata and their antiallergic activities. Chem Pharm Bull 52:1194–1199
Sawasdee K, Chaowasku T, Lipipun V, Dufat T-H, Michel S, Likhitwitayawuid K (2013) New neolignans and a lignan from Miliusa fragrans, and their anti-herpetic and cytotoxic activities. Tetrahedron Lett 54:4259–4263
Kasahara H, Miyazawa M, Kameoka H (1995) Absolute configuration of 8-O-4′-neolignans from Myristica fragrans. Phytochemistry 40:1515–1517
Besombes S, Robert D, Utille J-P, Taravel FR, Mazeau K (2003) Molecular modeling of syringyl and p-hydroxyphenyl β-O-4 dimers, comparative study of the compound and experimental conformational properties of lignan β-O-4 model compounds. J Agric Food Chem 51:34–42
Zacchino SA, Badano H (1991) Enantioselective synthesis and absolute configuration assignment of erythro-(3,4-methylenedioxy-7-hydroxy-1′-allyl-3′,5′-dimethoxy)-8.0.4′-neolignan and its acetate, isolated from nutmeg (Myristica fragrans). J Nat Prod 54:155–160
Greca MD, Molinaro A, Monaco P, Previtera L (1994) Neolignans from Arum italicum. Phytochemistry 35:777–779
Giang PM, Son PT, Matsunami K, Otsuka H (2006) New neolignans and lignans from Vietnamese medicinal plant Machilus odoratissima Nees. Chem Pharm Bull 54:380–383
Hattori M, Yang X-W, Shu Y-Z, Kakiuchi N, Tezuka Y, Kikuchi T, Namba T (1988) New constituents of the aril of Myristica fragrans. Chem Pharm Bull 36:648–653
Hattori M, Yang X-W, Miyashiro H, Namba T (1993) Inhibitory effects of monomeric and dimeric phenylpropanoids from mace on lipid peroxidation in vivo and in vitro. Phytother Res 7:395–401
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the MEXT-Supported Program for the Strategic Research Foundation at Private Universities, 2014–2018, Japan (S1411037, T. M.), as well as the JSPS KAKENHI, Japan, grant nos. 15K08008 (T. M.), 15K08009 (K. N.), and 16K08313 (O. M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morikawa, T., Hachiman, I., Ninomiya, K. et al. Degranulation inhibitors from the arils of Myristica fragrans in antigen-stimulated rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Nat Med 72, 464–473 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1170-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1170-x