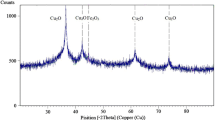
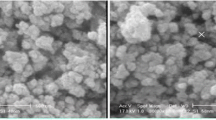
Abstract
Purpose
The present study investigates the possible use and effectiveness of starch-stabilized Fe/Cu nanoparticles for in situ immobilization of arsenic in contaminated soils.
Materials and methods
For this purpose, 0.04 wt.% starch-stabilized Fe/Cu nanoparticles were synthesized and tested through batch and column tests for the immobilization of arsenic in a loamy soil contaminated by chromated copper arsenate (CCA).
Results and discussion
When the CCA-contaminated loamy soil was treated with 0.4 g/L of starch-stabilized Fe/Cu nanoparticles (0.04 wt.%) at a soil-to-liquid ratio of 0.1, water-leachable arsenic was reduced by 92% and the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP) leachability was reduced by 98%. Column elution experiments showed that through application of starch-stabilized Fe/Cu nanoparticles to CCA-contaminated soil, nearly all water-soluble arsenic was transferred to the nanoparticle phase. The TCLP leachability of arsenic remaining in the soil column was reduced by 70% due to the immobilization of arsenic by nanoparticles.
Conclusions
In addition to an extremely high arsenic sorption capacity, starch-stabilized Fe/Cu nanoparticles exhibited excellent mobility in the soil environment. Both the high sorption capacity and the excellent mobility in the soil environment suggest potential for application of these nanoparticles to the contaminated soil for potential in situ arsenic immobilization.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altavilla C, Ciliberto E (2011) Inorganic nanoparticles. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida
An B, Steinwinder TR, Zhao DY (2005) Selective removal of arsenate from drinking water using a polymeric ligand exchanger. Water Res 39(20):4993–5004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.10.014
An B, Zhao D (2012) Immobilization of As(III) in soil and groundwater using a new class of polysaccharide stabilized Fe–Mn oxide nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 212:332–341 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.062
ASTM (2013) D4972-13: standard test method for pH of soils. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA www.astm.org
ASTM (2014) D2974-14: standard test methods for moisture, ash, and organic matter of peat and other organic soils. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA www.astm.org
ASTM (2006) D7100-06: standard test method for hydraulic conductivity compatibility testing of soils with aqueous solutions. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA www.astm.org
Azcue JM, Nriagu JO (1994) Arsenic: historical perspectives. In: Nriagu JO (ed) Arsenic in the environment, part I: cycling and characterization. John Wiley and Sons, Inc, New York, NY, pp 1–16
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (1999) Canadian soil quality guidelines for the protection of environmental and human health: chromium (total 1997) (VI 1999). In: Canadian environmental quality guidelines, 1999, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg
Ding M, Jong BHWS, Roosendaal SJ, Vredenberg A (2000) XPS studies on the electronic structure of bonding between solid and solutes: adsorption of arsenate, chromate, phosphate, Pb21, and Zn21 ions on amorphous black ferric oxyhydroxide. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64(7):1209–1219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00386-5
El-Temsah YS, Joner EJ (2013) Effects of nano-sized zero-valent iron (nZVI) on DDT degradation in soil and its toxicity to collembola and ostracods. Chemosphere 92(1):131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.039
EPA (1994) EPA-902-B-94-001: technical assistance document for complying with the TC rule and implementing the toxicity characteristic leaching procedure (TCLP). United States Environmental Protection Agency, Region 2, RCRA Outreach Program, http://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/P1007NTD.PDF?Dockey=P1007NTD.PDF
Hartley W, Edwards R, Lepp NW (2004) Arsenic and heavy metal mobility in iron oxide-amended contaminated soils as evaluated by short- and long-term leaching test. Environ Pollut 131(3):495–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.02.017
Health Canada (2014) Guidelines for Canadian drinking water quality—summary table. Water and Air Quality Bureau, Healthy Environments and Consumer Safety Branch, Health Canada, Ottawa, Ontario
He F, Zhang M, Qian TW, Zhao DY (2009) Transport of carboxymethyl cellulose stabilized iron nanoparticles in porous media: column experiments and modeling. J Colloid Interf Sci 334(1):96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.02.058
IPCS (2001) Arsenic and arsenic compounds, 2nd ed. Geneva, World Health Organization, International Program on Chemical Safety (Environmental Health Criteria 224; http://whqlibdoc.who.int/ehc/WHO_EHC_224.pdf
Khin MM, Sreekumaran Nair A, Jagadeesh Babu V, Murugan R, Ramakrishna S (2012) A review on nanomaterials for environmental remediation. Energy Environ Sci 5(8):8075–8109. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ee21818f
Klaine SJ, Alvarez PJJ, Batley GE, Fernandes TF, Handy RD, Lyon DY, Mahendra S, McLaughlin MJ, Lead JR (2008) Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 27(9):1825–1851. https://doi.org/10.1897/08-090.1
Kretzschmar R, Borkovec M, Grolimund D, Elimelech M (1999) Mobile subsurface colloids and their role in contaminant transport. Adv Agron 66:121–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2113(08)60427-7
Liang QQ, Zhao DY, Qian TW, Freeland K, Feng YC (2012) Effects of stabilizers and water chemistry on arsenate sorption by polysaccharide-stabilized magnetite nanoparticles. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(5):2407–2418. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie201801d
Liang W, Dai C, Zhou X, Zhang Y (2014) Application of zero-valent iron nanoparticles for the removal of aqueous zinc ions under various experimental conditions. PLoS One 9(1):e85686. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085686
Liang Q, Zhao D (2014) Immobilization of arsenate in a sandy loam soil using starch-stabilized magnetite nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 271:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.055
Liu CH, Chuang YH, Chen TY, Tian Y, Li H, Wang MK, Zhang W (2015) Mechanism of arsenic adsorption on magnetite nanoparticles from water: thermodynamic and spectroscopic studies. Environ Sci Technol 49(13):7726–7734. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00381
Maharjan M, Watanabe C, Aktar Ahmad SK, Ohtsuka R (2005) Short report: arsenic contamination in drinking water and skin manifestations in lowland Nepal: the first community-based survey. American Journal of Tropical Medicine Hygiene 73(2):477–479
Morales-Luckie RA, Sanchez-Mendieta V, Arenas-Alatorre JA, López-Castañares R, Perez-Mazariego JL, Marquina-Fabrega V, Wayne Gómez R (2008) One-step aqueous synthesis of stoichiometric Fe–Cu nanoalloy. Material Letters 62(26):4195–4197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2008.06.039
Mulligan CN, Yong RN, Gibbs BF (2001) Remediation technologies for metal contaminated soils and groundwater: an evaluation. Eng Geol 60(1–4):193–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(00)00101-0
O’Carroll D, Sleep B, Krol M, Boparai H, Kocur C (2013) Nanoscale zero valent iron and bimetallic particles for contaminated site remediation. Adv Water Resour 51:104–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2012.02.005
Peters GR, McCurdy RF, Thomas J, Hindmarch JT (1996) Environmental aspects of arsenic toxicity. CRC Cr Rev Cl Lab Sci 33(6):457–493. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408369609080055
Petosa AR, Jaisi DP, Quevedo IR, Elimelech M, Tufenkji N (2010) Aggregation and deposition of engineered nanomaterials in aquatic environments: role of physicochemical interactions. Environ Sci Technol 44(17):6532–6549. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100598h
Phenrat T, Saleh N, Sirk K, Kim HJ, Tilton RD, Lowry GV (2008) Stabilization of aqueous nanoscale zerovalent iron dispersions by anionic polyelectrolytes: adsorbed anionic polyelectrolyte layer properties and their effect on aggregation and sedimentation. J Nanopart Res 10(5):795–814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-007-9315-6
Raj Kanel S, Manning B, Charlet L, Choi H (2005) Removal of arsenic (III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39(5):1291–1298. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048991u
Raveendran P, Fu J, Wallen SL (2003) Complete “green” synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125(46):13940–13941. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja029267j
Sadiq M, Zaidi TH, Mian AA (1983) Environmental behavior of arsenic in soils: theoretical. Water Air Soil Pollut 20(4):369–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208511
Sirk KM, Saleh NB, Phenart T et al (2009) Effect of adsorbed polyelectrolytes on nanoscale zerovalent iron particle attachment to soil surface models. Environ Sci Technol 43(10):3803–3808. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803589t
Wang S, Mulligan CN (2009) Effect of natural organic matter on arsenic mobilization from mine tailings. J Hazard Mater 168(2–3):721–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.02.088
Wang Y, Liu W, Wanga T, Ni J (2015) Arsenate adsorption onto Fe-TNTs prepared by a novel water–ethanol hydrothermal method: mechanism and synergistic effect. J Colloid Interf Sci 440:253–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.10.036
Welch AH, Lico MS, Hughes JL (1988) Arsenic in groundwater of the western United States. Groundwater 26(3):333–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1988.tb00397.x
Wiesner MR, Bottero JY (2007) Environmental nanotechnology. The McGraw-Hill Companies, New York
Wu TH (1976) Soil mechanics. Allyn and Bacon, Boston
Xu Y, Zhao D (2007) Reductive immobilization of chromate in water and soil using stabilized iron nanoparticles. Water Res 41(10):2101–2108. 10.1016/j.watres.2007.02.037
Yong RN, Galvez-Cloutier R, Phadungchewit Y (1993) Selective sequential extraction analysis of heavy-metal retention in soil. Can Geotech J 30(5):834–847. https://doi.org/10.1139/t93-074
Zhang W (2003) Nanoscale iron particles for environmental remediation: an overview. J Nanopart Res 5(3/4):323–332. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025520116015
Zhang Y, Yang M, Dou X-M, He H, Wang D-S (2005) Arsenate adsorption on an Fe-Ce bimetal oxide adsorbent: role of surface properties. Environ Sci Technol 39(18):7246–7253. https://doi.org/10.1021/es050775d
Zhang S, Li X, Chen JP (2010) An XPS study for mechanisms of arsenate adsorption onto a magnetite-doped activated carbon fiber. J Colloid Interf Sci 343(1):232–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2009.11.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Dong-Mei Zhou
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 17 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babaee, Y., Mulligan, C.N. & Rahaman, M.S. Arsenic immobilization in soil using starch-stabilized Fe/Cu nanoparticles: a case study in treatment of a chromated copper arsenate (CCA)-contaminated soil at lab scale. J Soils Sediments 18, 1610–1619 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1882-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1882-2