Abstract
Purpose
Over-fertilization has caused low nitrogen (N) use efficiency and N pollution in China. A better understanding of the fate of fertilizer N is critical for improved appropriate N management practices.
Materials and methods
We examined the fate of urea-N applied to a typical black soil-maize system and the response to straw incorporation in Northeast China using the field 15N labeling technique. Large plots (25 m2) were used to reduce artificial disturbance and facilitate multiple samplings in one growing season.
Results and discussion
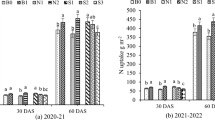
We found that of the applied N (200 kg N ha−1), 52% was taken up by crops at harvest and 24% was retained in the soil (0–40 cm). The unrecovered 23% was likely lost via gases emission or leaching, which mainly occurred in the early days of maize cultivation. Fertilizer N contributions to the crop N uptake were 42% during vegetative growth and 30% during reproductive growth, which indirectly indicates that native soil N was the dominant N source for maize growth. However, high N uptake by maize resulted in low replenishment of fertilizer N to soil N. As a potential nutrient management approach, straw incorporation (2.4 t ha−1) stimulated N retention and reduced N loss, with 14% unrecovered fertilizer N.
Conclusions
To maintain long-term soil N supplies, straw incorporation could be a valid agronomic practice to prevent the degradation of black soil because of long-term N depletion during maize cultivation in Northeast China.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkanani T, MacKenzie AF (1996) Banding urea and lignosulfonate in corn (Zea mays L.) production and 15N recovery. Can J Soil Sci 76:365–371
Blesh J, Drinkwater LE (2014) Retention of 15N-labeled fertilizer in an Illinois prairie soil with winter rye. Soil Sci Soc Am J 78:496–508
Bundy LG, Andraski TW (2005) Recovery of fertilizer nitrogen in crop residues and cover crops on an irrigated sandy soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:640–648
Chen Y, Wu CY, Tang X, Yang SM, Wang JY (2010) Fate of nitrogen from organic and inorganic sources in rice-wheat rotation cropping system. Agri Sci China 9:1017–1025
Chen ZM, Wang HY, Liu XW, Lu DJ, Zhou JM (2016) The fates of 15N-labeled fertilizer in a wheat-soil system as influenced by fertilization practice in a loamy soil. Sci Rep 6:34754
Cui ZL, Chen XP, Zhang FS (2010) Current nitrogen management status and measures to improve the intensive wheat-maize system in China. Ambio 39:376–384
Galloway JN, Townsend AR, Erisman JW, Bekunda M, Cai ZC, Freney JR, Martinelli LA, Seitzinger SP, Sutton MA (2008) Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 320:889–892
Gao LW, Ma L, Zhang WF, Wang FH, Ma WQ, Zhang FS (2009) Estimation of nutrient resource quantity of crop straw and its utilization situation in China. Trans CSAE 25:173–179 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gardner JB, Drinkwater LE (2009) The fate of nitrogen in grain cropping systems: a meta-analysis of 15N field experiments. Ecol Appl 19:2167–2184
Heffer P, Prud’homme M (2015) Fertilizer outlook. International Fertilizer Association (IFA), Paris, pp 2016–2020
Hong JL, Ren LJ, Hong JM, Xu CQ (2016) Environmental impact assessment of corn straw utilization in China. J Clean Prod 112:1700–1708
Ju XT (2014) The concept and meaning of nitrogen fertilizer availability ratio—discussing misunderstanding of traditional nitrogen use efficiency. Acta Pedo Sin 51:921–933 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ju XT, Xing GX, Chen XP, Zhang SL, Zhang LJ, Liu XJ, Cui ZL, Yin B, Christie P, Zhu ZL, Zhang FS (2009) Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc Nat Acad Sci 106:3041–3046
Kettering J, Ruidisch M, Gaviria C, Ok YS, Kuzyakov Y (2013) Fate of fertilizer 15N in intensive ridge cultivation with plastic mulching under a monsoon climate. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 95:57–72
Kramer AW, Doane TA, Horwath WR, van Kessel C (2002) Combining fertilizer and organic inputs to synchronize N supply in alternative cropping systems in California. Agric Ecosyst Environ 91:233–243
Ku H (1966) Notes on the use of propagation of error formulas. J Res Natl Bur Stand 70:263–273
Kumar K, Goh KM (2002) Recovery of 15N-labelled fertilizer applied to winter wheat and perennial ryegrass crops and residual N-15 recovery by succeeding wheat crops under different crop residue management practices. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 62:123–130
Kuzyakov Y, Xu XL (2013) Competition between roots and microorganisms for nitrogen: mechanisms and ecological relevance. New Phytol 198:656–669
Li XH, Nishio T, Uemiya Y, Inubushi K (2002) Gaseous losses of applied nitrogen from a corn field determined by 15N abundance of N2 and N2O. Commu Soil Sci Plan 33:2715–2727
Li XH, Wang SX, Duan L, Hao JM, Li C, Chen YS, Yang L (2007) Particulate and trace gas emissions from open burning of wheat straw and corn stover in China. Environ Sci Technol 41:6052–6058
Liang B, Yang XY, Murphy DV, He XH, Zhou JB (2013a) Fate of 15N-labeled fertilizer in soils under dryland agriculture after 19 years of different fertilizations. Biol Fert Soils 49:977–986
Liang B, Zhao W, Yang XY, Zhou JB (2013b) Fate of nitrogen-15 as influenced by soil and nutrient management history in a 19-year wheat-maize experiment. Field Crop Res 144:126–134
Liu SL, Huang DY, Chen AL, Wei WX, Brookes PC, Li Y, Wu JS (2014) Differential responses of crop yields and soil organic carbon stock to fertilization and rice straw incorporation in three cropping systems in the subtropics. Agric Ecosyst Environ 184:51–58
Liu X, Hu GQ, He HB, Liang C, Zhang W, Bai Z, Wu YY, Lin GF, Zhang XD (2016) Linking microbial immobilization of fertilizer nitrogen to in situ turnover of soil microbial residues in an agro-ecosystem. Agric Ecosyst Environ 229:40–47
Liu XE, Li XG, Guo RY, Kuzyakov Y, Li FM (2015) The effect of plastic mulch on the fate of urea-N in rain-fed maize production in a semiarid environment as assessed by 15N-labeling. Eur J Agron 70:71–77
Ma L (2008) Mechanism and regulatory strategies of nitrogen flow in food chain of China. Agricultural University of Hebei, Ph.D. thesis
Malhi SS, Nyborg M, Solberg ED (1989) Recovery of 15N-labelled urea as influenced by straw addition and method of placement. Can J Soil Sci 69:543–550
Pan JR, Ju XT, Liu XJ, Chen XP, Zhang FS, Mao DR (2009a) Fate of fertilizer nitrogen for winter wheat/summer maize rotation in North China Plian under optimization of irrigation and fetilization. J Nucl Agr Sci 23:334–340 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Pan KW, ZH X, Blumfield TJ, Tutua S, Lu MX (2009b) Application of (15NH4)2SO4 to study N dynamics in hoop pine plantation and adjacent native forest of subtropical Australia: the effects of injection depth and litter addition. J Soils Sediments 9:515–525
Powlson DS, Jenkinson DS, Pruden G, Johnston AE (1985) The effect of straw incorporation on the uptake of nitrogen by winter-wheat. J Sci Food Agr 36:26–30
Powlson DS, Pruden G, Johnston AE, Jenkinson DS (1986) The nitrogen-cycle in the broadbalk wheat experiment—recovery and losses of 15N-labeled fertilizer applied in spring and inputs of nitrogen from the atmosphere. J Agr Sci 107:591–609
Reddy GB, Reddy KR (1993) Fate of nitrogen-15 enriched ammonium nitrate applied to corn. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:111–115
Rees RM, Roelcke M, Li SX, Wang XQ, Li SQ, Stockdale EA, McTaggart IP, Smith KA, Richter J (1997) The effect of fertilizer placement on nitrogen uptake and yield of wheat and maize in Chinese loess soils. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 47:81–91
Rimski-Korsakov H, Rubio G, Lavado RS (2012) Fate of the nitrogen from fertilizers in field-grown maize. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 93:253–263
Schindler FV, Knighton RE (1999) Fate of fertilizer nitrogen applied to corn as estimated by the isotopic and difference methods. Soil Sci Soc Am J 63:1734–1740
Sebilo M, Mayer B, Nicolardot B, Pinay G, Mariotti A (2013) Long-term fate of nitrate fertilizer in agricultural soils. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 110:18185–18189
Shcherbak I, Millar N, Robertson GP (2014) Global metaanalysis of the nonlinear response of soil nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions to fertilizer nitrogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:9199–9204
Stevens WB, Hoeft RG, Mulvaney RL (2005) Fate of nitirogen-15 in a long-term nitrogen rate study: II. Nitrogen uptake efficiency. Agron J 97:1046–1053
Torbert HA, Mulvaney RL, Vandenheuvel RM, Hoeft RG (1992) Soil type and moisture regime effects on fertilizer efficiency calculation methods in a N-15 tracer study. Agron J 84:66–70
Tran TS, Giroux M (1998) Fate of 15N-labelled fertilizer applied to corn grown on different soil types. Can J Soil Sci 78:597–605
Varvel GE, Peterson TA (1990) Nitrogen-fertilizer recovery by corn in monoculture and rotation systems. Agron J 82:935–938
Walters DT, Malzer GL (1990) Nitrogen management and nitrification inhibitor effects on N-15 urea. I. Yield and fertilizer use efficiency. Soil Sci Soc Am J 54:115–122
Wang SJ, Luo SS, Yue SC, Shen YF, Li SQ (2016) Fate of 15N fertilizer under different nitrogen split applications to plastic mulched maize in semiarid farmland. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 105:129–140
Wang XY, Peng YJ, Wang W, Liu XY, Ju XT, Zhang LJ (2014) Exploration of N fertilizer fate and quantitative soil nitrogen pool budget in growing season of summer maize in North China plain. Ecol Environ Sci 23:1610–1615 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu MJ, Zhang L, Wang XY, Peng YJ, Zhang LJ, Ju XT (2015) Effects of different management patterns on uptake, distribution and fate of nitrogen in summer maize. J Plant Nutr Fert 21:36–45 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yan XY, Ti CP, Vitousek P, Chen DL, Leip A, Cai ZC, Zhu ZL (2014) Fertilizer nitrogen recovery efficiencies in crop production systems of China with and without consideration of the residual effect of nitrogen. Environ Res Lett 9:138–142
Yang L, Guo S, Chen QW, Chen FJ, Yuan LX, Mi GH (2016) Use of the stable nitrogen isotope to reveal the source-sink regulation of nitrogen uptake and remobilization during grain filling phase in maize. PLoS One 11:e0162201
Yu W, Zhou H, Ma Q, Shen S (2010) Effect of N fertilizer on uptake of soil N by crops with special discussion on fertilizer nitrogen recovery rate. Acta Pedologica Sinica 47:90–96 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang FS, Wang JQ, Zhang WF, Cui ZL, Ma WQ, Chen XP, Jiang RF (2008) Nutrient use eficiencies of major cereal crops in China andd measures for improvement. Acta Pedo Sin 45:915–924 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang L, Wu Z, Jiang Y, Chen L, Song Y, Wang L, Xie J, Ma X (2010) Fate of applied urea 15N in a soil-maize system as affected by urease inhibitor and nitrification inhibitor. Plant Soil Environ 56:8–15
Zhang P, Wei T, Jia ZK, Han QF, Ren XL (2014) Soil aggregate and crop yield changes with different rates of straw incorporation in semiarid areas of northwest China. Geoderma 230-231:41–49
Zhang WF, Cao GX, Li XL, Zhang HY, Wang C, Liu QQ, Chen XP, Cui ZL, Shen JB, Jiang RF, Mi GH, Miao YX, Zhang FS, Dou ZX (2016) Closing yield gaps in China by empowering smallholder farmers. Nature 537:671–674
Zhao H, Sun BF, Lu F, Zhang G, Wang XK, Ouyang ZY (2015b) Straw incorporation strategy on cereal crop yield in china. Crop Sci 55:1773–1781
Zhao W, Liang B, Yang XY, Zhou JB (2015a) Fate of residual 15N-labeled fertilizer in dryland farming systems on soils of contrasting fertility. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 61:846–855
Zhong Q (2004) Studies of nitrogen environmental endurance of winter wheat/summer maize rotation system in North China Plain. In: Master thesis. China Agricultural University
Zhou P, Sheng H, Li Y, Tong CL, Ge TD, Wu JS (2016) Lower C sequestration and N use efficiency by straw incorporation than manure amendment on paddy soils. Agric Ecosyst Environ 219:93–100
Zhu ZL (2008) Research on soil nitrogen in China. Acta Pedologica Sinica 45:778–783 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Hongguang Cai, Dr. Yang Wang, and Xuegong Yan in Jilin Academy of Agricultural Sciences for their help with field sampling. We also thank Xiaoming Fang, Meixia Gao, Linlin Song, and Ying Tu in Institute of Applied Ecology, CAS for their help with sample processing and laboratory analysis.
Funding
This study was grateful supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant number: XDB15020200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 41701309; 31422009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Weijin Wang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quan, Z., Li, S., Zhu, F. et al. Fates of 15N-labeled fertilizer in a black soil-maize system and the response to straw incorporation in Northeast China. J Soils Sediments 18, 1441–1452 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1857-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-017-1857-3