Abstract
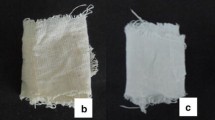
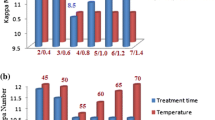
The objective of this research was to find out the potential of bioscouring using xylano-pectinolytic enzymes, for degumming of aloe fibers. Bioscouring was optimized with 1 : 20 fiber to buffer ratio, using 10 IU xylanase and 3.2 IU pectinase in 50 mM buffer (pH 8.5), EDTA (3 mM), and Tween 80 (1%), at 50°C temperature with agitation rate of 50 rpm and treatment period of 60 min. Enzymatic treatment of aloe fibers increased brightness and whiteness by 55.67% and 24.88%, respectively and decreased yellowness by 44.11% as compared to alkaline fiber scouring, thereby replacing chemical scouring completely. Additionally, the pretreatment of aloe fibers with enzymes resulted in a 50% less consumption of bleaching chemicals with similar optical properties as obtained by 100% bleaching. This is the first report showing the eco-friendly bioscouring approach of aloe fibers, using enzymes produced concurrently from a bacterial isolate.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Halim ES, Fahmy HM, Fouda MM (2008) Bioscouring of linen fabric in comparison with conventional chemical treatment. Carbohydr Polym 74:707–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.04.044
Abdulrachman D, Thongkred P, Kocharin K, Nakpathom M, Somboon B, Narumol N, Chantasingh D (2017) Heterologous expression of Aspergillus aculeatus endo-polygalacturonase in Pichia pastoris by high cell density fermentation and its application in textile scouring. BMC Biotechnol 17(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-017-0334-9
Akin DE, Henriksson G, Evans JD, Adamsen APS, Foulk JA, Dodd RB (2004) Progress in enzyme-retting of flax. J Nat Fibers 1:21–47
Aly AS, Moustafa AB, Hebeish A (2004) Bio-technological treatment of cellulosic textiles. J Clean Prod 12:697–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0959-6526(03)00074-X
ASTM-E-313 (1974) Standard test methods for indices of whiteness and yellowness of near white opaque materials. In: Annual Book of ASTM Standard, vol E 12.02. American Society for Testing Materials, Philadelphia, p 225
Chiliveri SR, Linga VR (2014) A novel thermostable, alkaline pectate lyase from Bacillus tequilensis SV11 with potential in textile industry. Carbohydr Polym 111:264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.04.065
Foulk JA, Akin DE, Dodd RB (2008) Influence of pectinolytic enzymes on retting effectiveness and resultant fiber properties. Bioresources 3:155–169
Hunter RS (1975) In: Hunter RS, Harold RW (eds) Measurement of appearance. A wiley: Interscience Publication, Reston Virginia, pp 169–175
ISO 2469 and 2470 (1977) Paper and board: measurement of diffused blue reflectance factor (ISO-brightness), 2nd edn. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, p 1
Kaur A, Mahajan R, Singh A, Garg G, Sharma J (2010) Application of cellulase free xylano-pectinolytic enzymes from the same bacterial isolate in biobleaching of kraft pulp. Bioresour Technol 101:9150–9155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.07.020
Kaur A, Singh A, Patra AK, Mahajan R (2016) Cost-effective scouring of flax fibers using cellulase-free xylano-pectinolytic synergism from a bacterial isolate. J Clean Prod 131:107–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.05.069
Kaur A, Singh A, Dua A, Mahajan R (2017) Cost-effective and concurrent production of industrially valuable xylano-pectinolytic enzymes by a bacterial isolate Bacillus pumilus AJK. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 47(1):8–18
Losonczi A, Csiszar E, Szakacs G, Bezur L (2005) Role of the EDTA chelating agent in bioscouring of cotton. Text Res J 75(5):411–417. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517505053812
Ma W, Shen K, Xiang N, Zhang S (2017) Combinative scouring, bleaching, and cationization pretreatment of greige knitted cotton fabrics for facilely achieving salt-free reactive dyeing. Molecules 22(12):2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22122235
Miller GL (1959) Modified DNS method for reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Mojsov K (2018) Enzymatic scouring and bleaching of cotton terry fabrics–opportunity of the improvement on some physicochemical and mechanical properties of the fabrics. J Nat Fibers 15:740–751. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2017.1361884
Rouette HK, Schwager B (2001) Encyclopedia of textile finishing, vol 23. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–3
Shahid M, Mohammad F, Chen G, Tang RC, Xing T (2016) Enzymatic processing of natural fibres: white biotechnology for sustainable development. Green Chem 18:2256–2281. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6gc00201c
Singh A, Kaur A, Patra AK, Mahajan R (2016) Xylano-pectinolytic synergism from a bacterial isolate for ecofriendly processing of jute fabric. J Clean Prod 124:120–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.063
Singh A, Kaur A, Patra AK, Mahajan R (2018) A sustainable and green process for scouring of cotton fabrics using xylano-pectinolytic synergism: switching from noxious chemicals to eco-friendly catalys. 3 Biotech 8:184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1193-3
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author thankfully acknowledges Chandra Prakash Shah, Director of M/s Chandra Prakash & Company, India, for providing valuable guidance during the course of this study.
Funding
The financial support was provided by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Ministry of Science & Technology, Government of India (Grant Number: BT/PR 20438/BCE/8/1220/2016 for 3 years).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
1. Ritu Mahajan (corresponding author): idea of concept, planning, and designing of various experiments done for this manuscript; experimental work done by the first author for this manuscript under the corresponding author’s supervision
2. Amanjot Kaur (first author): all experimental work mentioned in this manuscript done by her
3. Libin Mathew Varghese: microscopic analysis and manuscript written by him under the supervision of the corresponding author
4. Bindu Battan: spectral analysis was done by her
5. Arun Kumar Patra: optical testing (brightness, whiteness, and yellowness) of various samples was done by him
6. Rishi Pal Madhan: checking of rough draft of the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaur, A., Varghese, L.M., Battan, B. et al. An environmental management technology for the processing of American aloe fibers using xylano-pectinolytic enzymes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 15565–15573 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12915-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12915-9