Abstract
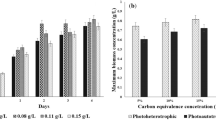
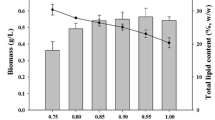
Algae have long been acclaimed as the attractive renewable source for generating third-generation biofuels, particularly biodiesel. Under the present investigation, the trends of production of biomass and lipid during the autotrophic and heterotrophic growth of newly isolated blue-green algae, Leptolyngbya subtilis JUCHE1, were compared and correlated with the variation in C-sources. In the autotrophic and heterotrophic growth studies, CO2 and glycerol were respectively used as the inorganic and organic C-sources maintaining equivalence in the initial amount of carbon. Light was used as the source of energy in both cases. The concentration of CO2 in the feed gas stream was varied from 5 to 20% (% v/v). Equivalent quantity of carbon was supplied through glycerol during heterotrophic growth. Small-scale closed algal bioreactors were used for growing the algae at 37 °C and 2.5 kLux light illumination in batch mode for 0–4 days. Primarily, higher biomass production from glycerol compared with CO2 was observed. In case of photoautotrophic growth, the maximum values of biomass and lipid productivity, obtained at 15% CO2, were 0.1857 g/L/d and of 0.020 g/L/d respectively. The maximum biomass productivity of 0.2733 g/L/d was obtained for photoheterotrophic growth at a glycerol concentration equivalent to 15% CO2 (v/v). Under photoheterotrophic growth of Leptolyngbya subtilis JUCHE1, lipid productivity of 0.0702 g/L/d was obtained at glycerol concentration equivalent to 5% (v/v) CO2, which is 4.66-fold higher than that obtained under corresponding photoautotrophic condition. The “switch-over” from the autotrophy to the photoheterotrophy instigated the oleaginous anabolism and consequent lipid enrichment in L. subtilis JUCHE1, which can be extracted and converted to biodiesel.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abomohra AEF, Eladel H, El-Esawi M, Wang S, Wang Q, He Z, Hanelt D (2018) Effect of lipid-free microalgal biomass and waste glycerol on growth and lipid production of Scenedesmus obliquus: innovative waste recycling for extraordinary lipid production. Bioresour Technol 249:992–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.102
Aubert S, Gout E, Bligny R, Douce R (1994) Multiple effects of glycerol on plant cell metabolism. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance studies. J Biol Chem 269(34):21420–21427 https://www.jbc.org/content/269/34/21420.full.pdf
Badger MR, Price GD, Long BM, Woodger FJ (2006) The environmental plasticity and ecological genomics of the cyanobacterial CO2 concentrating mechanism. J Exp Bot 57(2):249–265. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri286
Bondioli P, Della Bella L (2005) An alternative spectrophotometric method for the determination of free glycerol in biodiesel. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 107(3):153–157. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.200401054
Chen CY, Yeh KL, Aisyah R, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2011) Cultivation, photobioreactor design and harvesting of microalgae for biodiesel production: a critical review. Bioresour Technol 102(1):71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.159
Choi SA, Jung JY, Kim K, Lee JS, Kwon JH, Kim SW, Park JY (2014) Acid-catalyzed hot-water extraction of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)-rich lipids from Aurantiochytrium sp. KRS101 Bioresour Technol 161(469):472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.03.153
Chowdhury R, Das S, Ghosh S (2018) CO2 Capture and utilization (CCU) in coal-fired power plants: prospect of in-situ algal cultivation. In Sustainable energy technology and policies, Springer, Singapore, pp 231-254. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7188-1_10.
Das S, Mahato S, Chowdhury R (2020) Studies on growth kinetics and lipid accumulation of a power plant algae: L. Subtilis JUCHE1 by variation of nitrogen concentrations (NaNO3). 9th ICONSWM-CE2019, 25:20.
Drapcho CM, Nhuan NP, Walker T H (2008) Biofuels engineering process technology. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Duarte JH, de Morais EG, Radmann M, Costa JAV (2017) Biological CO2 mitigation from coal power plant by Chlorella fusca and Spirulina sp. Bioresour Technol 234(472):475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.066
Eloka-Eboka AC, Inambao FL (2017) Effects of CO2 sequestration on lipid and biomass productivity in microalgal biomass production. Appl Energy 195(1100):1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.03.071
Heredia-Arroyo T, Wei W, Ruan R, Hu B (2011) Mixotrophic cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris and its potential application for the oil accumulation from non-sugar materials. Biomass Bioenergy 35(5):2245–2253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.02.036
Ho SH, Chen CY, Chang JS (2012) Effect of light intensity and nitrogen starvation on CO2 fixation and lipid/carbohydrate production of an indigenous microalga Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N. Bioresour Technol 113:244–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.133
Jajesniak P, HEMO A, Wong TS (2014) Carbon dioxide capture and utilization using biological systems: opportunities and challenges. J Bioprocess Biotech 4(155):2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9821.1000155
Jacob-Lopes E, Lacerda LMCF, Franco TT (2008) Biomass production and carbon dioxide fixation by Aphanothece microscopica Nägeli in a bubble column photobioreactor. Biochem Eng J 40(1):27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2007.11.013
Khanra A, Vasistha S, Rai MP (2017) Glycerol on lipid enhancement and fame characterization in algae for raw material of biodiesel. Int J Renew Energy Res 7(4):1970–1978 https://www.ijrer.com/index.php/ijrer/article/view/6367
Kim S, Park JE, Cho YB, Hwang SJ (2013) Growth rate, organic carbon and nutrient removal rates of Chlorella sorokiniana in autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic conditions. Bioresour Technol 144:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.06.068
Li T, Xu J, Wu H, Wang G, Dai S, Fan J, He H, Xiang W (2016) A saponification method for chlorophyll removal from microalgae biomass as oil feedstock. Mar Drugs 14(9):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14090162
Leite GB, Paranjape K, Abdelaziz AE, Hallenbeck PC (2015) Utilization of biodiesel-derived glycerol or xylose for increased growth and lipid production by indigenous microalgae. Bioresour Technol 184:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.117
Li T, Zheng Y, Yu L, Chen S (2014) Mixotrophic cultivation of a Chlorella sorokiniana strain for enhanced biomass and lipid production. Biomass Bioenergy 66:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2014.04.010
Li J, Tang X, Pan K, Zhu B, Li Y, Ma X, Zhao Y (2020) The regulating mechanisms of CO2 fixation and carbon allocations of two Chlorella sp. strains in response to high CO2 levels. Chemosphere 125814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125814
Mandotra SK, Kumar P, Suseela MR, Ramteke PW (2014) Fresh water green microalga Scenedesmus abundans: a potential feedstock for high quality biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 156:42–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.127
Narayan MS, Manoj GP, Vatchravelu K, Bhagyalakshmi N, Mahadevaswamy M (2005) Utilization of glycerol as carbon source on the growth, pigment and lipid production in Spirulina platensis. Int J Food Sci Nutr 56(7):521–528. https://doi.org/10.1080/09637480500410085
Pradhan L, Bhattacharjee V, Mitra R, Bhattacharya I, Chowdhury R (2015) Biosequestration of CO2 using power plant algae (Rhizoclonium hieroglyphicum JUCHE2) in a Flat Plate Photobio-Bubble-Reactor–Experimental and modeling. Chem Eng J 275:381–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.037
Ota M, Kato Y, Watanabe H, Watanabe M, Sato Y, Smith RL Jr, Inomata H (2009) Effect of inorganic carbon on photoautotrophic growth of microalga Chlorococcum littorale. Biotechnol Prog 25(2):492–498. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.123
Sachdeva N, Kumar GD, Gupta RP, Mathur AS, Manikandan B, Basu B, Tuli DK (2016) Kinetic modeling of growth and lipid body induction in Chlorella pyrenoidosa under heterotrophic conditions. Bioresour Technol 218:934–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.063
Sander R (2015) Compilation of Henry’s law constants (version 4.0) for water as solvent. Atmos Chem Phys 15(8). https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/d4fc/8ef222674503cde2058657992646a7809197.pdf
Taher H, Al-Zuhair S, Al-Marzouqi A, Haik Y, Farid M (2014) Growth of microalgae using CO2 enriched air for biodiesel production in supercritical CO2. Renew Energy 82:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2014.08.013
Tan X, Yao L, Gao Q, Wang W, Qi F, Lu X (2011) Photosynthesis driven conversion of carbon dioxide to fatty alcohols and hydrocarbons in cyanobacteria. Metab Eng 13(2):169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2011.01.001
Thimijan RW, Heins RD (1983) Photometric, radiometric, and quantum light units of measure: a review of procedures for interconversion. HortScience 18(6):818–822 https://www.plantgrower.org/uploads/6/5/5/4/65545169/light_conversion_paper_thimijan_1983_ocr.pdf
Wang YZ, Hallenbeck PC, Leite GB, Paranjape K, Huo DQ (2016) Growth and lipid accumulation of indigenous algal strains under photoautotrophic and mixotrophic modes at low temperature. Algal Res 16:195–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2016.03.017
Yang J, Rasa E, Tantayotai P, Scow KM, Yuan H, Hristova KR (2011) Mathematical model of Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341 growth and lipid production under photoheterotrophic fermentation conditions. Bioresour Technol 102(3):3077–3082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.049
Yamane YI, Utsunomiya T, Watanabe M, Sasaki K (2001) Biomass production in mixotrophic culture of Euglena gracilis under acidic condition and its growth energetics. Biotechnol Lett 23(15):1223–1228. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010573218863
Zheng Y, Chi Z, Lucker B, Chen S (2012) Two-stage heterotrophic and phototrophic culture strategy for algal biomass and lipid production. Bioresour Technol 103(1):484–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.122
Zeebe RE, Wolf-Gladrow D (2001). CO2 in seawater: equilibrium, kinetics, isotopes (No. 65). Gulf Professional Publishing. http://geosci.uchicago.edu/~kite/doc/Zeebe_CO2_In_Seawater_Ch_1.pdf
Funding
The authors received financial support from the RUSA 2.0 scheme of Jadavpur University in order to conduct the experimental studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ta Yeong Wu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, S., Nath, K. & Chowdhury, R. Comparative studies on biomass productivity and lipid content of a novel blue-green algae during autotrophic and heterotrophic growth. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 12107–12118 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09577-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09577-4