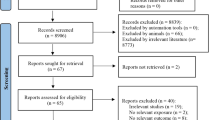
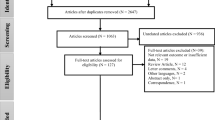
Abstract
Several studies have been published about the potential health effects due to long-term exposure to sulphur dioxide (SO2) and the relative risks (RRs) for different causes of mortality. Broad differences in the RR values are found, however. In this study, we performed an analysis of these studies aiming finding potential explanations for the high variability of the RR reported. The RRs for stratified subgroups were also analysed to identify more susceptible subgroups. A total of 14 studies were identified. Some of them related strong associations between mortality and long-term ambient SO2 exposure, while others found insignificant or no associations to the same mortality indexes. The mean RR values ranged from 0.95 to 1.14 for mortality due to all causes, 0.99 to 3.05 for lung cancer, 0.87 to 1.3 for respiratory diseases, 0.96 to 1.14 cardiovascular diseases and 0.97 to 1.05 for cardiopulmonary diseases mortality. Among the factors that may affect the RR estimations, only the size of studied population and the spatial scales used in exposure assessment showed notable influences. The female population was found to be more susceptible to long-term SO2 exposure. For other stratified subgroups including age, smoking status and income levels, no obvious relationship with RR was observed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbey DE, Mills PK, Petersen FF, Beeson WL (1991) Long-term ambient concentrations of total suspended particulates and oxidants as related to incidence of chronic disease in California Seventh-day Adventists. Environ Health Perspect 94:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.94-1567944
Abbey DE, Nishino N, McDonnell WF, Burchette RJ, Knutsen SF, Beeson WL, Yang JX (1999) Long-term inhalable particles and other air pollutants related to mortality in nonsmokers. Am J Resp Crit Care 159:373–382. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.159.2.9806020
Albuquerque TTA, West J, Andrade MF, Ynoue RY, Andreão WL, Santos FS, Maciel FM, Pedruzzi R, Mateus VO, Martins JA, Martins LD, Nascimento EGS, Moreira DM (2019) Analysis of PM2.5 concentrations under pollutant emission control strategies in the metropolitan area of São Paulo, Brazil. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06447-6
Atkinson RW, Carey IM, Kent AJ, Van Staa TP, Ross Anderson H, Cook DG (2013) Long-term exposure to outdoor air pollution and incidence of cardiovascular diseases. Epidemiology 2013:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0b013e318276ccb8
Becklake MR, Kauffmann F (1999) Gender differences in airway behaviour over the human life span. Thorax 54:1119–1138. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.54.12.1119
Beelen R, Hoek G, van den Brandt PA, Goldbohm RA, Fischer P, Schouten LJ, Jerrett M, Hughes E, Armstrong B, Brunekreefet B (2008) Long-term effects of traffic-related air pollution on mortality in a Dutch cohort (NLCS-AIR Study). Environ Health Perspect 116:196–202. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10767
Beeson WL, Abbey DE, Knutsen SF (1998) Long-term concentrations of ambient air pollutants and incident lung cancer in California adults: results from the AHSMOG study. Environ Health Perspect 106:813–822
Bell ML, Dominici F, Samet JM (2005) A meta-analysis of time-series studies of ozone and mortality with comparison to the national morbidity, mortality, and air pollution study. Epidemiology 16:436–445
Bentayeb M, Wagner V, Stempfelet M, Zins M, Goldberg M, Pascal M, Larrieu S, Beaudeau P, Cassadou S, Eilstein D, Filleul L, Le Tertre A, Medina S, Pascal S, Prouvost H, Quénel P, Zeghnoun A, Lefranc A (2015) Association between long-term exposure to air pollution and mortality in France: a 25-year follow-up study. Environ Int 85:5–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2015.08.006
Cao J, Yang C, Li J, Chen R, Chen B, Gu D, Kan H (2011) Association between long-term exposure to outdoor air pollution and mortality in China: a cohort study. J Hazard Mater 186:1594–1600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.12.036
Carey IM, Atkinson RW, Kent AJ, Van Staa T, Cook DG, Anderson HR (2013) Mortality associations with long-term exposure to outdoor air pollution in a national English cohort. Am J Resp Crit Care 187:1226–1233. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201210-1758OC
Cesaroni G, Badaloni C, Gariazzo C, Stafoggia M, Sozzi R, Davoli M, Forastiere F (2013) Long-term exposure to urban air pollution and mortality in a cohort of more than a million adults in Rome. Environ Health Perspect 121:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1205862
Chen X, Zhang LW, Huang JJ, Song FJ, Zhang LP, Qian ZM, Trevathan E, Mao HJ, Han B, Vaughn M, Chen KX, Liu YM, Chen J, Zhao BX, Jiang GH, Gu Q, Bai ZP, Dong GH, Tang NJ (2016) Long-term exposure to urban air pollution and lung cancer mortality: a 12-year cohort study in northern China. Sci Total Environ 571:855–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.064
Choi KS, Inoue S, Shinozaki R (1997) Air pollution, temperature, and regional differences in lung cancer mortality in Japan. Arch Environ Health 52:160–168. https://doi.org/10.1080/00039899709602881
Crouse DL, Peters PA, Van Donkelaar A, Goldberg MS, Villeneuve PJ, Brion O, Khan S, Atari DO, Jerrett M, Pope CA III, Brauer M, Brook JR, Martin RV, Stieb D, Burnett RT (2012) Risk of nonaccidental and cardiovascular mortality in relation to long-term exposure to low concentrations of fine particulate matter: a Canadian national-level cohort study. Environ Health Perspect 120:708–714. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1104049
Crouse DL, Peters PA, Hystad P, Brook JR, van Donkelaar A, Martin RV, Villeneuve PJ, Jerrett M, Goldberg MS, Pope CA III, Brauer M, Brook RD, Robichaud A, Menard R, Burnett RT (2015) Ambient PM2.5, O3, and NO2 exposures and associations with mortality over 16 years of follow-up in the Canadian Census Health and Environment Cohort (CanCHEC). Environ Health Perspect 123:1180–1186. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1409276
Di Angelantonio E, Bhupathiraju SN, Wormser D, Gao P, Kaptoge S, Gonzales AB, Cairns BJ, Huxley R, Jackson CL, Joshy G, Lewington S, Manson JE, Murphy N, Patel AV, Samet JM, Woodward M, Zheng W, Zhou M, Bansal N, Barricarte A, Carter B, Cerhan JR, Collins R, Smith GD, Fang X, Franco OH, Green J, Halsey J, Hildebrand JS, Jung KL, Korda RJ, McLerran DF, Moore SC, O’Keeffe LM, Paige E, Ramond A, Reeves GK, Rolland B, Sarcedote C, Sattar N, Sofianopoulou E, Stevens J, Thun M, Ueshima H, Yang L, Yun YD, Willeit P, Banks E, Beral V, Chen Z, Gapstur SM, Gunter MJ, Hartge P, Jee SH, Lam T-H, Peto R, Potter JD, Willett WC, Thompson SG, Danesh J, Hu FB (2016) Body-mass index and all-cause mortality: individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents. Lancet 288:776–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30175-1
Dockery DW, Pope CA III, Xu X, Spengler JD, Ware JH, Fay ME, Ferris BG Jr, Speizer FE (1993) An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. New Engl J Med 329:1753–1759. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199312093292401
Dong GH, Zhang P, Sun B, Zhang L, Chen X, Ma N, Yu F, Guo H, Huang H, Lee YL, Tang N, Chen J (2012) Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and respiratory disease mortality in Shenyang, China: a 12-year population-based retrospective cohort study. Respiration 84:360–368. https://doi.org/10.1159/000332930
EEA (2015) Sulphur dioxide (SO2) emissions. European Environment Agency. http://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/indicators/eea-32-sulphur-dioxide-so2-emissions-1/assessment-1. Accessed April 7th, 2018
Elliott P, Shaddick G, Wakefield JC, De Hoogh C, Briggs DJ (2007) Long-term associations of outdoor air pollution with mortality in Great Britain. Thorax 62:1088–1094. https://doi.org/10.1136/thx.2006.076851
Filleul L, Rondeau V, Vandentorren S, Le Moual N, Cantagrel A, Annesi-Maesano I, Charpin D, Declercq C, Neukirch F, Paris C, Vervloet D, Brochard P, Tessier JF, Kauffmann F, Baldi I (2005) Twenty five year mortality and air pollution: results from the French PAARC survey. Occup Environ Med 62:453–460. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.2004.014746
Hansell A, Ghosh RE, Blangiardo M, Perkins C, Vienneau D, Goffe K, Briggs D, Gulliver J (2016) Historic air pollution exposure and long-term mortality risks in England and Wales: prospective longitudinal cohort study. Thorax 71:330–338. https://doi.org/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-207111
Hedley AJ, Wong CM, Thach TQ, Ma S, Lam TH, Anderson HR (2002) Cardiorespiratory and all-cause mortality after restrictions on sulphur content of fuel in Hong Kong: an intervention study. Lancet 360:1646–1652. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11612-6
HEI (2000) Reanalysis of the Harvard Six Cities study and the American Cancer Society study of particulate air pollution and mortality: a special report of the Institute’s particle epidemiology reanalysis project. Health Effects Institute, Cambridge
Hoek G, Krishnan RM, Beelen R, Peters A, Ostro B, Brunekreef B, Kaufman JD (2013) Long-term air pollution exposure and cardio-respiratory mortality: a review environmental health. Environ Health 12:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-069X-12-43
Jerret M, Burnett RT, Pope CA III, Ito K, Thurston G, Krewski D, Shi Y, Calle E, Thun M (2009) Long-term ozone exposure and mortality. New Engl J Med 360:1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0803894
Jerrett M, Burnett RT, Brook J, Kanaroglou P, Giovis C, Finkelstein N, Hutchison B (2004) Do socioeconomic characteristics modify the short term association between air pollution and mortality? Evidence from a zonal time series in Hamilton, Canada. J Epidemiol Community Health 58:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.58.1.31
Katanoda K, Sobue T, Satoh H, Tajima K, Suzuki T, Nakatsuka H, Takezak T, Nakayama T, Nitta H, Tanabe K, Tominaga S (2011) An association between long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and mortality from lung cancer and respiratory diseases in Japan. J Epidemiol 21:132–143. https://doi.org/10.2188/jea.JE20100098
Klimont Z, Smith SJ, Cofala J (2013) The last decade of global anthropogenic sulfur dioxide: 2000-2011 emissions. Environ Res Lett 8. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/8/1/014003
Krewski D, Jerrett M, Burnett RT, Ma R, Hughes E, Shi Y, Turner MC, Pope CA III, Thurston G, Calle EE, Thun MJ, Beckerman B, DeLuca P, Finkelstein N, Ito K, Moore DK, Newbold KB, Ramsay T, Ross Z, Shin H, Tempalski B (2009) Extended follow-up and spatial analysis of the American Cancer Society study linking particulate air pollution and mortality. Res Rep Health Eff Inst 140:5–114
Laden F, Schwartz J, Speizer FE, Dockery DW (2006) Reduction in fine particulate air pollution and mortality: extended follow-up of the Harvard six cities study. Am J Resp Crit Care 173:667–672. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200503-443OC
Lee WJ, Teschke K, Kauppinen T, Andersen A, Jäppinen P, Szadkowska-Stanczyk I, Pearce N, Persson B, Bergeret A, Facchini LA, Kishi R, Kielkowski D, Rix BA, Henneberger P, Sunyer J, Colin D, Kogevinas M, Boffetta P (2002) Mortality from lung cancer in workers exposed to sulfur dioxide in the pulp and paper industry. Environ Health Perspect 110:991–995
Lefler JS, Higbee JD, Burnett RT, Ezzati M, Coleman NC, Mann DD, Marshall JD, Bechle M, Wang Y, Robinson AL, Pope CA III (2019) Air pollution and mortality in a large, representative U.S. cohort: multiple pollutant-analyses, and spatial and temporal decompositions. Environ Health 18:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-019-0544-9
Lepeule J, Laden F, Dockery D, Schwartz J (2012) Chronic exposure to fine particles and mortality: an extended follow-up of the Harvard Six Cities study from 1974 to 2009. Environ Health Perspect 120:965–970. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1104660
Lipfert FW (2017) A critical review of the ESCAPE project for estimating long-term health effects of air pollution. Environ Int 99:87–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.11.028
Lu Z, Streets DG, Zhang Q, Wang S, Carmichael GR, Cheng YF, Wei C, Chin M, Diehl T, Tan Q (2010) Sulfur dioxide emissions in China and sulfur trends in East Asia since 2000. Atmos Chem Phys 10:6311–6331. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-6311-2010
Nafstad P, Håheim LL, Wisløff T, Gram F, Oftedal B, Holme I, Hjermann I, Leren P (2004) Urban air pollution and mortality in a cohort of Norwegian men. Environ Health Perspect 112:610–615. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.6684
PAARC, Groupe coopératif (1982) Pollution atmosphérique et affections respiratoires chroniques ou à répétition. Méthodes et matériel. Bull Europ Physiopath Resp 18:87–99
Pascal M, de Crouy CP, Wagner V, Corso M, Tillier C, Bentayeb M, Blanchard M, Cochet A, Pascal L, Host S, Goria S, Le Tertre A, Chatignoux E, Ung A, Beaudeau P, Medina S (2016) The mortality impacts of fine particles in France. Sci Total Environ 571:416–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.213
Pope CA III, Thun MJ, Namboodiri MM, Dockery DW, Evans JS, Speizer FE, Heath CW Jr (1995) Particulate air pollution as a predictor of mortality in a prospective study of U.S. adults. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:669–674. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/151.3_Pt_1.669
Pope CA III, Burnett RT, Thun MJ, Calle EE, Krewski D, Ito K, Thurston GD (2002) Lung cancer, cardiopulmonary mortality, and long-term exposure to fine particulate air pollution. J Am Med Assoc 287:1132–1141. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.287.9.1132
Pope CA III, Burnett RT, Thurston GD, Thun MJ, Calle EE, Krewski D, Godleski JJ (2004) Cardiovascular mortality and long-term exposure to particulate air pollution: epidemiological evidence of general pathophysiological pathways of disease. Circulation 109:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000108927.80044.7F
Pope CA III, Lefler JS, Ezzati M, Higbee JD, Marshall JD, Kim S-Y, Bechle M, Gilliat KS, Vernon SE, Robinson AL, Burnett RT (2019) Mortality risk and fine particulate air pollution in a large, representative cohort of U.S. adults. Environ Health Perspect 127:077007-1–077007-9. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP4438
Riordan D, Adeeb F (2004) Air quality monitoring for sulphur dioxide in metropolitan Adelaide. Environment Protection Authority South Australia, Adelaide
Thurston GD, Burnett RT, Turner MC, Shi Y, Krewski D, Lall R, Ito K, Jerrett M, Gapstur SM, Diver WR, Pope CA III (2016) Ischemic heart disease mortality and long-term exposure to source-related components of U.S. fine particle air pollution. Environ Health Perspect 124:785–794. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1509777
USEPA, 2016. Sulfur dioxide trends. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/air-trends/sulfur-dioxide-trends. Accessed April 7th, 2018
van den Brandt PA, Goldbohm RA, van‘t Veer P, Volovics A, Hermus RJ, Sturmans F (1990) A large-scale prospective cohort study on diet and cancer in the Netherlands. J Clin Epidemiol 43:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/0895-4356(90)90009-e
Vodonos A, Awad YA, Schwartz J (2018) The concentration-response between long-term PM2.5 exposure and mortality; a meta-regression approach. Environ Res 166:677–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.06.021
Wang L, Zhong B, Vardoulakis S, Zhang F, Pilot E, Li Y, Yang L, Wang W, Krafft T (2016) Air quality strategies on public health and health equity in Europe - a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13121196
WHO (2006) Air quality guidelines: global update 2005. World Health Organization, Copenhagen
Yunginger JW, Reed CE, O'Connell EJ, Melton LJ III, O'Fallon WM, Silverstein MD (1992) A community-based study of the epidemiology of asthma: incidence rates, 1964-1983. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:888–894. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm/146.4.888
Zhang P, Dong G, Sun B, Zhang L, Chen X, Ma N, Yu F, Guo H, Huang H, Lee YL, Tang N, Chen J (2011) Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and mortality due to cardiovascular disease and cerebrovascular disease in Shenyang, China. PLoS One 6. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020827
Funding
This research was partially funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Espírito Santo (FAPES), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, Y., Santos, J.M., Mill, J.G. et al. Mortality risks due to long-term ambient sulphur dioxide exposure: large variability of relative risk in the literature. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 35908–35917 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07867-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07867-5