Abstract
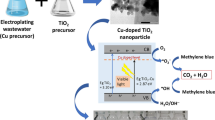
Photocatalysis is one of the most promising advanced oxidation processes due to the capability of solid catalyst to continuously produce oxidant species under light irradiation. The use of conventional UV lamps is high cost intensive, which undermines the possible implementation in developing countries. Visible light active photocatalysts can overcome these challenges and find a market opportunity for competitive technology implementation. This work proposes the synthesis of visible light active catalyst following a facile sol-gel synthesis that introduces CuSO4 as dopant in TiO2. Results present complete abatement of methylene blue in 120 min of treatment under 50 mW cm−2 of blue light (λ = 450 nm), while commercial P25 TiO2 presented null abatement under identical conditions. Synthesis parameters including dopant level and calcination temperature allowed defining optimum synthesis conditions based on material characteristics modification and catalytic activity enhancement. A doping level of 0.21 mol% CuSO4 was identified as optimum condition to enable visible light photocatalysis of doped TiO2 catalysts calcined at 300 °C. Finally, operational parameters were evaluated defining a wide range of pH operation under 3.0 g L−1 of catalyst dose to treat up to 20 g L−1 of highly recalcitrant phenothiazine dye. These optimum conditions allowed complete dye removal under visible light after 120 min of treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
AlSalka Y, Granone LI, Ramadan W et al (2019) Iron-based photocatalytic and photoelectrocatalytic nano-structures: facts, perspectives, and expectations. Appl Catal B Environ 244:1065–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.014
Batista LMB, dos Santos AJ, da Silva DR et al (2017) Solar photocatalytic application of NbO<inf>2</inf>OH as alternative photocatalyst for water treatment. Sci Total Environ:596–597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.019
Bensouici F, Bououdina M, Dakhel AA et al (2017) Optical, structural and photocatalysis properties of Cu-doped TiO2 thin films. Appl Surf Sci 395:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.034
Byrne C, Subramanian G, Pillai SC (2018) Recent advances in photocatalysis for environmental applications. J Environ Chem Eng 6:3531–3555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.080
Byrne C, Moran L, Hermosilla D et al (2019) Effect of Cu doping on the anatase-to-rutile phase transition in TiO2 photocatalysts: theory and experiments. Appl Catal B Environ 246:266–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.01.058
Cerrón-Calle GA, Aranda-Aguirre AJ, Luyo C et al (2019) Photoelectrocatalytic decolorization of azo dyes with nano-composite oxide layers of ZnO nanorods decorated with Ag nanoparticles. Chemosphere 219:296–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.12.003
Chen J, Loeb S, Kim J (2017) LED revolution: fundamentals and prospects for UV disinfection applications. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 3:188–202. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EW00241B
de Luna MDG, Lin JC-T, Gotostos MJN, Lu M (2016) Photocatalytic oxidation of acetaminophen using carbon self-doped titanium dioxide. Sustain Environ Res 26:161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2016.02.001
De Luna MDG, Laciste MT, Tolosa NC, Lu M (2018) Effect of catalyst calcination temperature in the visible light photocatalytic oxidation of gaseous formaldehyde by multi-element doped titanium dioxide. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:15216–15225
Dimapilis EAS, Hsu C, Mendoza RMO, Lu M (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles for water disinfection. Sustain Environ Res 28:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2017.10.001
Dominguez S, Huebra M, Han C et al (2017) Magnetically recoverable TiO 2 -WO 3 photocatalyst to oxidize bisphenol A from model wastewater under simulated solar light. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:12589–12598. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7564-6
Dosta S, Robotti M, Garcia-Segura S et al (2016) Influence of atmospheric plasma spraying on the solar photoelectro-catalytic properties of TiO2 coatings. Appl Catal B Environ 189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.02.048
Fagan R, Mccormack DE, Dionysiou DD, Pillai SC (2016) A review of solar and visible light active TiO2 photocatalysis for treating bacteria , cyanotoxins and contaminants of emerging concern. Mater Sci Semicond Process 42:2–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.07.052
Fujishima A, Zhang X, Tryk DA (2008) TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf Sci Rep 63:515–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfrep.2008.10.001
Gallego-schmid A, Ricardo R, Tarpani Z (2019) Life cycle assessment of wastewater treatment in developing countries: a review. Water Res 153:63–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.01.010
Gómez-Pastora J, Dominguez S, Bringas E et al (2017) Review and perspectives on the use of magnetic nanophotocatalysts (MNPCs) in water treatment. Chem Eng J 310:407–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.140
Heck KN, Garcia-Segura S, Westerhoff P, Wong MS (2019) Catalytic converters for water treatment. Acc Chem Res 52:906–915. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00642
Jiang X, Manawan M, Feng T et al (2018) Anatase and rutile in evonik aeroxide P25: heterojunctioned or individual nanoparticles? Catal Today 300:12–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.06.010
Jianna F, Villaluz A, Daniel M et al (2019) Removal of 4-chlorophenol by visible-light photocatalysis using ammonium iron ( II ) sulfate-doped nano-titania. Process Saf Environ Prot 125:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2019.03.001
Kalikeri S, Kodialbail VS (2018) Solar light-driven photocatalysis using mixed-phase bismuth ferrite water : kinetics and comparison with artificial UV and visible light-mediated photocatalysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13881–13893
Khedr TM, El-sheikh SM, Ismail AA et al (2017) Highly active non-metals doped mixed-phase TiO2 for photocatalytic oxidation of ibuprofen under visible light. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 346:530–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.07.004
Lee C, Javed H, Zhang D et al (2018) Porous electrospun fibers embedding TiO2 for adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of water pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 52:4285–4293. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06508
Likodimos V, Chrysi A, Calamiotou M et al (2016) Microstructure and charge trapping assessment in highly reactive mixed phase TiO2 photocatalysts. Appl Catal B Environ 192:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.03.068
Lin JC, de Luna MDG, Gotostos MJN, Lu M-C (2016) Effects of doping amounts of potassium ferricyanide with titanium dioxide and calcination durations on visible-light degradation of pharmaceuticals. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:22721–22733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7470-y
Lin JC, Sopajaree K, Jitjanesuwan T, Lu M (2018) Application of visible light on copper-doped titanium dioxide catalyzing degradation of chlorophenols. Sep Purif Technol 191:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.09.027
Loeb SK, Alvarez PJJ, Brame JA et al (2019) The technology horizon for photocatalytic water treatment: sunrise or sunset? Environ Sci Technol 53:2937–2947. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b05041
Manenti DR, Soares PA, Silva TFCV et al (2014) Performance evaluation of different solar advanced oxidation processes applied to the treatment of a real textile dyeing wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:833–845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2767-1
Mansouri J, Harrisson S, Chen V (2010) Strategies for controlling biofouling in membrane filtration systems: challenges and opportunities. J Mater Chem 20:4567–4586. https://doi.org/10.1039/b926440j
Marcelino RBP, Amorim CC (2019) Towards visible-light photocatalysis for environmental applications : band-gap engineering versus photons absorption — a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:4155–4170
Marinho BA, Cristóvao RO, Djellabi R et al (2018) Strategies to reduce mass and photons transfer limitations in heterogeneous photocatalytic processes : hexavalent chromium reduction studies. J Environ Manage 217:555–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.04.003
Mohamed HH, Alsanea AA, Alomair NA et al (2019) ZnO@ porous graphite nanocomposite from waste for superior photocatalytic activity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:12288–12301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04684-3
Monteiro RAR, Miranda SM, Vilar VJP et al (2015) N-modified TiO2 photocatalytic activity towards diphenhydramine degradation and Escherichia coli inactivation in aqueous solutions. Appl Catal B Environ 162:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.06.017
Nakata K, Fujishima A (2012) TiO 2 photocatalysis: design and applications. J Photochem Photobiol C: Photochem Rev 13:169–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2012.06.001
Nie AJ, Schneider J, Sieland F et al (2018) The role of Au loading for visible-light photocatalytic activity of Au-TiO2 (anatase). J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 366:111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.016
Prado NT, Oliveira LCA (2017) Nanostructured niobium oxide synthetized by a new route using hydrothermal treatment : high efficiency in oxidation reactions. Appl Catal B Environ 205:481–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.12.067
Putta T, Lu MC, Anotai J (2011) Photocatalytic activity of tungsten-doped TiO2 with hydrothermal treatment under blue light irradiation. J Environ Manag 92:2272–2276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2011.04.016
Ratova M, Redfern J, Verran J, Kelly PJ (2018) Highly efficient photocatalytic bismuth oxide coatings and their antimicrobial properties under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 239:223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.08.020
Rokhmat M, Wibowo E, Abdullah M (2017) Prototype of a flat-panel photoreactor using TiO2 nanoparticles coated on transparent granules for the degradation of methylene blue under solar illumination. Sustain Environ Res 27:172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2017.04.002
Sathasivam S, Bhachu DS, Lu Y et al (2015) Tungsten doped TiO2 with enhanced photocatalytic and optoelectrical properties via aerosol assisted chemical vapor deposition. Sci Rep 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10952
Spasiano D, Marotta R, Malato S et al (2015) Solar photocatalysis: materials, reactors, some commercial, and pre-industrialized applications. A comprehensive approach. Appl Catal B Environ 170–171:90–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.12.050
Stancl HON, Hristovski K, Westerhoff P (2015) Hexavalent chromium removal using UV-TiO2/Ceramic membrane reactor. Environ Eng Sci 32:676–683. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2014.0507
Tang J, Wang R, Liu M et al (2018) Construction of novel Z-scheme photocatalyst with enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance for degradation of norfloxacin. Chem Eng J 351:1056–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.171
Tugaoen HON, Garcia-Segura S, Hristovski K, Westerhoff P (2017) Challenges in photocatalytic reduction of nitrate as a water treatment technology. Sci Total Environ 599–600:1524–1551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.238
Tugaoen HON, Garcia-Segura S, Hristovski K, Westerhoff P (2018) Compact light-emitting diode optical fiber immobilized TiO2 reactor for photocatalytic water treatment. Sci Total Environ 613–614:1331–1338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.242
Turkten N, Cinar Z, Tomruk A, Bekbolet M (2019) Copper-doped TiO2 photocatalysts: application to drinking water by humic matter degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04474-x
United Nations (2018) Sustainable Developement Goals. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdg6. Accessed 10 Apr 2019
Veisi F, Zazouli MA, Ebrahimzadeh MA et al (2016) Photocatalytic degradation of furfural in aqueous solution by N-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:21846–21860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7199-7
Wang D, Pillai SC, Ho SH et al (2018) Plasmonic-based nanomaterials for environmental remediation. Appl Catal B Environ 237:721–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.05.094
Water.org (2019) Philippines’ water and sanitation crisis
Zangeneh H, Zinatizadeh AA, Feyzi M et al (2018) Photomineralization of recalcitrant wastewaters by a novel magnetically recyclable boron doped-TiO2-SiO2 cobalt ferrite nanocomposite as a visible-driven heterogeneous photocatalyst. J Environ Chem Eng 6:6370–6381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.10.001
Funding
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (NSC 101-2923-E-041-001-MY2) and the Engineering Research and Development for Technology—Department of Science and Technology, Philippines.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• CuSO4-doped TiO2 photocatalysts were synthesized by facile sol-gel method.
• Effect of doping and calcination temperature on visible photocatalytic activity described.
• CuSO4-doped TiO2 enabled visible light photocatalytic degradation of recalcitrant organics.
• Operational variables impact on CuSO4-doped TiO2 photocatalytic performance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Luna, M.D.G., Garcia-Segura, S., Mercado, C.H. et al. Doping TiO2 with CuSO4 enhances visible light photocatalytic activity for organic pollutant degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 24604–24613 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05789-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05789-5