Abstract
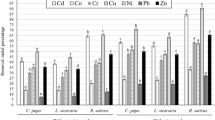
In order to evaluate the resistance of lawn plant to Co2+ at germination stage and discuss its concentration property at adult stage, four kinds of lawn plant which have some growth advantages in Co2+ polluted environment were selected as experimental materials in this research. They are tall fescue, timothy grass, inflorescences, and annual ryegrass. The results show that the evaluation of resistance to Co2+ of tall fescue’s seed is the highest; the evaluation of resistance to Co2+ of annual ryegrass seed is the lowest. The low consistence Co2+ could improve the seed germination. With Co2+ concentration increase, the accumulation coefficient of four plants increased at first and decreased later; the accumulation coefficient of underground portion is higher than the accumulation coefficient of aboveground; with Co2+ concentration increase, the transfer coefficient of four plants have a remarkable decline. In these plants, the accumulation coefficient of tall fescue and annual ryegrass is bigger than other two plants. As the concentration of Co2+ treatment increased to 100 mg/kg, the aboveground enrichment of Co2+ in F. elata reached 75 mg/kg, followed by L. multiflorum (68.9 mg/kg), P. pratense (48.8 mg/kg), and D. glomerata (27.2 mg/kg).The highest underground enrichment of Co2+ in F. elata reached 836.46 mg/kg, in contrast to the lowest underground enrichment in D. glomerata, 264.67 mg/kg. It shows that fescue and annual ryegrass have a better enrichment property to Co2+ and have a better prospect for the treatment of cobalt-contaminated soil. This research could provide some scientific basis and main technical approach for the soil contaminated by Co2+.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aery NC, Jagetiya BL (2000) Effect of cobalt treatments on dry matter production of wheat and dtpa extractable cobalt content in soils. Commun Soil Sci Plan. 31:1275–1286
Ahmad A, Alothman AAS (2014) Remediation rates and translocation of heavy metals from contaminated soil through Parthenium hysterophorus. Chem Ecol. 30:317–327
Bakkaus E, Gouget B, Gallien JP, Khodja H, Carrot F, Morel JL, Collins R (2005) Concentration and distribution of cobalt in higher plants: the use of micro-PIXE spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum.. Methods Phys. Res. B 231(1):350–356
Bano A, Hussain J, Akbar A, Mehmood K, Anwar M, Hasni MS, Sajid S, Ali I (2018) Biosorption of heavy metals by obligate halophilic fungi. Chemosphere 199:218–222
Barceloux DG (1999) Cobalt. J. Toxicol.-Clin. Toxic. 37:201–216
Barcelo J, Poschenrieder C, Gunse B (1985) Effect of chromium vi on mineral element composition of bush beans. J Plant Nutr. 8:211–217
Chaney RL, Baklanov IA (2017) Chapter Five - Phytoremediation and Phytomining: Status and Promise. In: Cuypers A, Vangronsveld J (eds) Advances in Botanical Research, vol 83. Academic Press, pp 189–221
Chen RX, Tang CB, Shang YS, Ben-Tian MO, Wang XL (2010) Introduction, selection and application of high quality forages in Guizhou. Pratacultural Science. 27:112–122
Chatterjee J, Chatterjee C (2000) Phytotoxicity of cobalt, chromium and copper in cauliflower. Environmental Pollution 109(1):69–74
Du WH (2003) Research advance in nutritive value, cultivation and utilization of timothy. Grassland & Turf. 4:7–11
He ZL, Yang XE, Stoffella PJ (2005) Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 19:125–140
Foy CD, And RLC, White MC (1978) The physiology of metal toxicity in plants. Ann Rev Plant Physio. 29:511–566
Guo Y (2018) Study on detection and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in rural soils. Environmental Science and Management. 43:163–166
Garba S, Osemeahon A, Sunday HM, Tsaware J (2012) Ethylenediaminetetraacetate (edta)-assisted phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by eleusineindica l. gearth. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotox. 4:103–109
Hao XC, Chen XM, Luo XG, Shou S (2016) Comparative study on growth and uranium enrichment of different forages under uranium stress. J. Nucl. Agr. 30:548–555
Hamon R, Wundke J, Mclaughlin M, Naidu R (1997) Availability of zinc and cadmium to different plant species. Soil Res. 35:1267–1277
Hussein H, Ibrahim SF, Kandeel K, Moawad H (2004) Biosorption of heavy metals from waste water using Pseudomonas sp. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 7, 7(1)
Irene C, Daniel R, Carolina K, Selvaraj T, Aminael SR, Manuel JG (2017) Erato polymnioides –A novel Hg hyperaccumulator plant in ecuadorian rainforest acid soils with potential of microbe-associated phytoremediation. Chemosphere. 188:633–641
Juwarkar AS, Shende GB (1986) Interaction of cadmium, lead: effect on growth, yield and content of cd, pb in barley, hordeumvulgare. Ind. J. Environ. Health 28:235–243
Lal S, Maurya AN (1981) Effects of zinc on onion. Haryana J. Hort. Sci. 10:231–235
Li H-F, Gray C, Mico C, Zhao F-J, McGrath SP (2009) Phytotoxicity and bioavailability of cobalt to plants in a range of soils. Chemosphere 75(7):979–986
Li NY, Guo B, Li H, Fu QL, Feng RW, Ding YZ (2016) Effects of double harvesting on heavy metal uptake by six forage species and the potential for phytoextraction in field. Pedosphere. 26:717–724
Li DM, Zhang XJ, Li GH, Deng DF, Zou H (2008) Effects of heavy metal ions on germination and physiological activity of Festucaarundinacea seed. Pratacultural Science. 25:98–102
Marchiol L, Sacco P, Assolari S, Zerbi G (2004) Reclamation of polluted soil: phytoremediation potential of crop-related brassica, species. Water Air Soil Poll. 158:345–356
Mosoarca G, Vancea C, Popa S, Boran S (2018) Adsorption, bioaccumulation and kinetics parameters of the phytoremediation of cobalt from wastewater using Elodea canadensis. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology 100(5):733–739
Murugesan K (1996) Influence of copper on the growth and yield of groundnut under Rhizobium sp. and Azotobacter sp. Geobios-Lyon. 23:45–49
Norcini JG, Aldrich JH, Martin FG (2004) Harvest season influences fertilizer effects on seed production of lanceleaf coreopsis. J. Environ. Hor. 12:229–233
Norcini JG, Aldrich JH, Martin FG (2006) Harvest season and fertilizer effects on seed production of Leavenworth’s coreopsis. J. Environ. Hor. 24:63–67
Dinh N, Antony VDE, David RM, Anh VN (2018) Zinc and lead accumulation characteristics and in vivo distribution of Zn2+ in the hyperaccumulator Noccaea caerulescens elucidated with fluorescent probes and laser confocal microscopy. Environmental and Experimental Botany. 147:1–12
Palit S, Sharma A, Talukder G (1994) Effects of cobalt on plants. The Botanical Review 60(2):149–181
Petros G, Marianthi T, Costas T (2008) Seed and cone diversity and seed germination of pinuspinea in strofylia site of the natura 2000 network. Biodivers Conserv. 17:2427–2439
Robinson TMM, Petit D, Fung LE, Green SR, Clothier BE (2000) Natural and induced cadmium-accumulation in poplar and willow: implications for phytoremediation. Plant and Soil 227:301–306
Simon L (2001) Heavy metals, sodium and sulphur in urban topsoils and in the indicator plant chicory (cichoriumintybus l.). Acta Agron Hung. 49:1–13
Singh SP, Nayyar VK (1990) Effect of cadmium and zinc on growth of corn in a coarse texture soil (typic ustipsamments). Int J Environ Stud. 34:57–63
Six J (2011) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 339:1–2
Thornber JP (1975) Chlorophyll-proteins: light-harvesting and reaction center components of plants. Ann Rev Plant Physio. 26:127–158
Venkataramana RP, Li KF, Dibyendu S, Ramakrishna W, Rupali D (2018) Comparative metabolic profiling of vetiver (Chrysopogon zizanioides) and maize (Zea mays) under lead stress. Chemosphere. 193:903–911
Vijayarengan P (2012) Changes in growth, biochemical constituents and antioxidant potentials in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) under cobalt stress. Int. J. Res. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2:74–82
Vijayarengan P, Lakshmanachary AS (1994) Differential nickel tolerance in greengram cultivars. Poll. Res. 13:291–296
Wan XM, Lei M, Chen TB (2016) Cost–benefit calculation of phytoremediation technology for heavy-metal-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 563–564:796–802
Wang PC, Mou Q, Wang XL, Zhao LL, Shu JH (2011) Response of weed invasion to mowing intensity in loliumperenne artificial pasture. Chinese Journal of Grassland. 33:117–120
Wang Y, Xin SG, Ma LJ, Dai BQ, Yu L, Wang LL (2007) Cu and Pb absorption and tolerance of Agrostis stolonifera and Festuca arundinacea. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology. 18:625
Wang ZK, Liao BH, Huang YX, Zeng QR (2006) Effects of Cd on growth of glycine max seedlings and Cd-tolerance differences of different varieties of glycine max. Journal of Agro- Environment Science. 25:1143–1147
Wen JG, Wei LF, Yang Y, Chen MH, Yang YD, Zou YH, Huang XJ, Wan J (2010) Study on cultivation and utilization of annual high-European ryegrass in Panzhihua area. Pratacult Anim Husb 7:16–17
Xie HK, Zhao CH, Peng XM, Deng GQ, Chen H, Huang M, Li X, Zhang LP (2013) Advances in research on repair of heavy metal cobalt contaminated soil. Mod. Agricul. Technol. 7:222–223
Xu DP, Wang D, Zeng C, He J, Wu PC (2014) On the dynamic change of cobalt accumulation and distribution in the broad bean. Journal of Safety & Environment Science. 14:294–298
Yadav SK (2010) Heavy metals toxicity in plants: an overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. South Afr. J. Bot. 76(2):167–179
Yoon J, Cao X, Zhou Q, Ma LQ (2006) Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated florida site. Sci Total Environ. 368:456–464
Zhang J, Wang G, Cheng W (2013a) Comparative trial of Minshan timothy and Japanese timothy. China Feed 2:26–27
Zhu H, Sun ZG, Yi HP, Ren P (2016) Spatial distribution of vanadium and cobalt content in different types of wetland soils in the Yellow River Estuary. J. Soil and Water Conserv. 30(01):315–320
Zhang S, Tang Y, Chen X, Wang D, Huang M (2013b) Accumulation and distribution of cobalt in rape and the effects of cobalt on the photosynthesis of rape leaves. Acta Botanica Boreali- OccidentaliaSinica. 33:1203–1209
Zhang ZH, Meney ZRK (2010) Cadmium accumulation and translocation in four emergent wetland species. Water Air Soil Poll 212:239–249
Acknowledgments
The National Defense Science and Technology Foundation of China (Grant No. 16ZG6101), the Major State Development Program of China (973 Program, No. 2014CB846003), Sichuan Province Foundation (Grant No. 18YYJC0927), and State Key Laboratory of NBC Protection for Civilian (SKLNBC2015–04) supported the study. We thank Dr. Imran Ali for his language help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chifu Zhuo had finished the data analysis and wrote manuscript in English. Xianghui Zhang had finished effects of Co2+ stress on relative GR and GE of four lawn plants; Chen Ruan had finished Co2+ enrichment characteristics of four lawn plants; Hao Chen had finished the Co2+ content analysis; Dan Wang had finished effects of Co2+ stress on seedling height and biomass of lawn plants; Xuegang Luo had directed assessment for Co2+ removal capacity; Xiaoming Chen’s duty was to direct the research and write manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuo, C., Chen, X., Zhang, X. et al. The evaluation of resistance to Co 2+ of lawn plant at seedling stage and its concentration property at adult stage . Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 17986–17995 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05243-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05243-6