Abstract
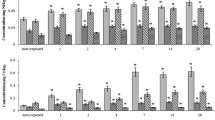
Environmental effects associated with the release of various metals even at maximum permissible concentrations (MPC) to the aquatic ecosystems are evident. In the present work, time-dependent increase in accumulated metals amount in gills of Anodonta cygnea after exposure to complex metal (Zn 0.1, Cu 0.01, Ni 0.01, Cr 0.01, Pb 0.005, and Cd 0.005 mg/L, MPC accepted for the inland waters in EU) mixture at various time points (1, 2, 4, 7, 14, and 28 days) was investigated. Statistically significant increase of Cu and Cd was determined in mussel’s gills after 7-day exposure, in comparison to control group; moreover, significantly elevated concentration of Cu was measured and after 14-day treatment (in comparison to control and pre-exposure group). Concentrations of five (Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, and Cd) out of 6 investigated metals were statistically increased in gills tissue after 28-day treatment. Moreover, complex metal mixture has demonstrated tissue- and time-dependent genotoxicity (∑Gentox) and cytotoxicity (∑Cytox) responses in mussels. After 4-day exposure, there were found the highest ∑Gentox levels in gills cells and haemocytes. Two-day treatment of mussels resulted in the highest and statistically significant induction of ∑Cytox level (in gills). Furthermore, after short-term (4 days) exposure, statistically significant inhibition of AChE activity in hemolymph of metal mixture–exposed mussels, in comparison to control and pre-exposure group, was found. Comparison of investigated responses in different tissue of A. cygnea discloses new information about metal mixture (at MPC) impacts at different treatment time. According to the obtained geno- and cytotoxicity data, it is suggested that gills are more sensitive tissue. Environmentally relevant trace metal concentrations when existing in mixture are able to cause adverse effects in A. cygnea; therefore, biological effects at different levels of organism are expected as a realistic scenario.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arjmand F, Mostafavi PG, Fazaeli R, Rad MHG, Vosoughi G (2012) The in vitro and in vivo effect of clinoptilolite on decreasing of copper ion and DNA damage of Anodonta cygnea. JACR 6(4):37–45
Bainy ACD, Gennari de Medeiros MH, Di Mascio P, de Almeida EA (2006) In vivo effects of metals on the acetylcholinesterase activity of the Perna perna mussel’s digestive gland. Biotemas 19(1):35–39
Baršienė J, Andreikėnaitė L, Rybakovas A (2006) Cytogenetic damage in perch (Perca fluviatilis L.) and Duck mussel (Anodonta anatina L.) exposed to crude oil. Ekologija 1:25–31
Baršienė J, Rybakovas A, Garnaga G, Andreikėnaitė L (2012) Environmental genotoxicity and cytotoxicity studies in mussels before and after the oil spill in marine oil terminal (Baltic Sea). Environ Monit Assess 184:2067–2078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2100-0
Baršienė J, Butrimavičienė L, Michailovas A, Grygiel W (2015) Assessing the environmental genotoxicity risk in the Baltic Sea: frequencies of nuclear buds in blood erythrocytes of three native fish species. Environ Monit Assess 187:4078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4078-x
Benali I, Boutiba Z, Merabet A, Chèvre N (2015) Integrated use of biomarkers and condition indices in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) for monitoring pollution and development of biomarker index to assess the potential toxic of coastal sites. Mar Pollut Bull 95:385–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.03.041
Bielen A, Bošnjak I, Sepčić K, Jaklič M, Cvitanić M, Lušić J, Lajtner J, Simčič T, Hudina S (2016) Differences in tolerance to anthropogenic stress between invasive and native bivalves. Sci Total Environ 543:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.049
Bourgeault A, Gourlay-France C, Vincent-Hubert F, Palais F, Geffard A, Biagianti Risbourg S, Pain-Devin S, Tusseau-Vuillemin MH (2010) Lessons from a transplantation of zebra mussels into a small urban river: an integrated ecotoxicological assessment. Environ Toxicol 25:468–478. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.20591
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1976.9999
Brown RJ, Galloway TS, Lowe D, Brown MA, Dissanayake A, Jones MB, Depledge MH (2004) Differential sensitivity of three marine invertebrates to copper assessed using multiple biomarkers. Aquat Toxicol 66(3):267–278
Burgos-Aceves MA, Faggio C (2017) An approach to the study of the immunity functions of bivalve haemocytes: physiology and molecular aspects. Fish Shellfish Immunol 67:513–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2017.06.042
Burgos-Aceves MA, Cohen A, Paolella G, Lepretti M, Smith Y, Faggio C, Lionetti L (2018) Modulation of mitochondrial functions by xenobiotic-induced microRNA: from environmental sentinel organisms to mammals. Sci Total Environ 645:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.109
Butrimavičienė L, Baršienė J, Greiciūnaitė J, Stankevičiūtė M, Valskienė R (2018) Environmental genotoxicity and risk assessment in the Gulf of Riga (Baltic Sea) using fish, bivalves, and crustaceans. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:24818–24828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2516-y
Canty MN, Hagger JA, Moore RTB, Cooper L, Galloway TS (2007) Sublethal impact of short term exposure to the organophosphate pesticide azamethiphos in the marine mollusc Mytilus edulis. Mar Pollut Bull 54(4):396–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.11.013
Cavas T, Garanko NN, Arkhipchuk VV (2005) Induction of micronuclei and binuclei in blood, gill and liver cells of fishes subchronically exposed to cadmium chloride and copper sulphate. Food Chem Toxicol 43(4):569–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2004.12.014
Ching EW, Siu WH, Lam PK, Xu L, Zhang Y, Richardson BJ, Wu RS (2001) DNA adduct formation and DNA strand breaks in green-lipped mussels (Perna viridis) exposed to benzo[a]pyrene: dose- and time-dependent relationships. Mar Pollut Bull 42:603–610
Crott JW, Mashiyama ST, Ames BN, Fenech M (2001) The effect offolic acid deficiency and MTHFR C677T polymorphism on chromosomedamage in human lymphocytes in vitro. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10:1089–1096
Czechowski W, Gajewski W, Garbaczewska G, Nowakowski E (1994) Biology. Państw. Wyd. Roln. Leśn, Warszawa (in Polish)
Dudgeon D, Arthington AH, Gessner MO, Kawabata Z, Knowler D, Lévêque C, Naiman RJ, Prieur-Richard AH, Soto D, Stiassny ML, Sullivan CA (2006) Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status, and conservation challenges. Biol Rev 81(2):163–182. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1464793105006950
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres VJ, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Faggio C, Tsarpali V, Dailianis S (2018) Mussel digestive gland as a model for assessing xenobiotics: an overview. Sci Total Environ 613:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.264
Falfushynska HI, Delahaut L, Stoliar OB, Geffard A, Biagianti-Risbourg S (2009) Multi-biomarkers approach in different organs of Anodonta cygnea from the Dnister Basin (Ukraine). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57(1):86–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9234-2
Falfushynska HI, Gnatyshyna LL, Farkas A, Vehovszky A, Gyori J, Stoliar OB (2010) Vulnerability of biomarkers in the indigenous mollusk Anodonta cygnea to spontaneous pollution in a transition country. Chemosphere 81:1342–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.08.016
Falfushynska H, Gnatyshyna L, Stoliar O, Mitina N, Skorokhoda T, Filyak Y, Zaichenko A, Stoika R (2012) Evaluation of biotargeting and ecotoxicity of Co2+-containing nanoscale polymeric complex by applying multi-marker approach in bivalve mollusk Anodonta cygnea. Chemosphere 88:925–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.02.087
Falfushynska H, Gnatyshyna L, Stoliar O (2013a) Effect of in situ exposure history on the molecular responses of bivalve mollusks Anodonta anatina (Unionidae) to trace metals. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 89:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.11.024
Falfushynska H, Gnatyshyna L, Stoliar O (2013b) In situ exposure history modulates the molecular responses to carbamate fungicide Tattoo in bivalve mollusk. Ecotoxicology 22:433–445. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-1037-6
Falfushynska GI, Gnatyshyna LL, Yurchak IV, Stoliar OB, Sokolova I (2016) Interpopulational variability of molecular responses to ionizing radiation. Sci Total Environ 568:444–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.175
Franco-Martinez L, Romero D, García-Navarro JA, Tecles F, Teles M, Tvarijonaviciute A (2016) Measurement of p-nitrophenyl acetate esterase activity (EA), total antioxidant capacity (TAC), total oxidant status (TOS) and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in gills and digestive gland of Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to binary mixtures of Pb, Cd and Cu. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(24):25385–25392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7677-y
Führer E, Rudolph A, Espinoza C, Díaz R, Gajardo M, Camaño N (2012) Integrated use of biomarkers (O: N ratio and acetylcholinesterase inhibition) on Aulacomya ater (Molina, 1782) (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) as a criteria for effects of organophosphate pesticide exposition. J Toxicol 2012:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/951568
Geist J (2011) Integrative freshwater ecology and biodiversity conservation. Ecol Indic 11:1507–1516. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.04.002
Govind P, Madhuri S (2014) Heavy metals causing toxicity in animals and fishes. Research Journal of Animal, Veterinary and Fishery. Sciences 2(2):17–23
Guidi P, Frenzilli G, Benedetti M, Bernardeschi M, Falleni A, Fattorini D, Regoli F, Scarcelli V, Nigro M (2010) Antioxidant, genotoxic and lysosomal biomarkers in the freshwater bivalve (Unio pictorum) transplanted in a metal polluted river basin. Aquat Toxicol 100:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.07.009
Hinzmann MF, Lopes-Lima M, Gonçalves J, Machado J (2013) Antiaggregant and toxic properties of different solutions on haemocytes of three freshwater bivalves. Toxicol Environ Chem 95(5):790–805. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2013.818149
Jackin E (1974) Enzyme responses to metals in fish. In: Vemberg EG, Vemberg WB (eds) Pollution and Physiology of Marine Organisms. Academic Press, New York, USA, pp 59–65
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN (2014) Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol 7(2):60–72. https://doi.org/10.2478/intox-2014-0009
Jaruga P, Coskun E, Kimbrough K, Jacob A, Johnson WE, Dizdaroglu M (2017) Biomarkers of oxidatively induced DNA damage in dreissenid mussels: a genotoxicity assessment tool for the Laurentian Great Lakes. Environ Toxicol 00:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.22427
Jindal R, Verma S (2015) In vivo genotoxicity and cytotoxicity assessment of cadmium chloride in peripheral erythrocytes of Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 118:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.04.005.
Jitar O, Teodosiu C, Oros A, Plavan G, Nicoara M (2015) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in marine organisms from the Romanian sector of the Black Sea. New Biotechnol 32(3):369–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2014.11.004
El Jourmi L, Amine A, Boutaleb N, Abouakil N, Lazar S, El Antri S (2014) Multimarker approach analysis in the brown mussel to evaluate the anthropogenic stress: a preliminary study. JMES 5(5):1326–1331
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35(4):495–516. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701320337
Eskandari S, Mozdarani H, Mashinchian Moradi A, Shahhosseiny MH (2012) Cytogenetic damage induced by crude oil in Anodonta cygnea (mollusca, bivalvia) assessed by the comet assay and micronucleus test. IJMASE 2(4):215–224
Kamel N, Attig H, Dagnino A, Boussetta H, Banni M (2012) Increased temperatures affect oxidative stress markers and detoxification response to benzo[a]pyrene exposure in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 63:534–543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-012-9790-3
Khan MI, Zahoo M, Khan A, Gulfam N, Khisroon M (2018) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and their genotoxic effect on freshwater mussel. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 102:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2492-4
Khazri A, Sellami B, Hanachi A, Dellali M, Eljarrat E, Beyrem H, Mahmoudi E (2017) Neurotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by permethrin in gills of the freshwater mussel Unio ravoisieri. Chem Ecol 33(1):88–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2016.1248948
Kolarević S, Knežević-Vukčević J, Paunović M, Kračun M, Vasiljević B, Tomović J, Vuković-Gačić B, Gačić Z (2013) Monitoring of DNA damage in haemocytes of freshwater mussel Sinanodonta woodiana sampled from the Velika Morava River in Serbia with the comet assay. Chemosphere 93:243–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04.073
Kolarević S, Kračun-Kolarević M, Kostić J, Slobodnik J, Liška I, Gačić Z, Paunović M, Knežević-Vukčević J, Vuković-Gačić B (2016) Assessment of the genotoxic potential along the Danube River by application of the comet assay on haemocytes of freshwater mussels: the Joint Danube Survey 3. Sci Total Environ 540:377–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.061
Kopecka-Pilarczyk J (2010) The effect of pesticides and metals on acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in various tissues of blue mussel (Mytilus trossulus L.) in short-term in vivo exposures at different temperatures. 2010. J Environ Sci Health B 45:336–346. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601231003704390
Lindberg HK, Wang X, Järventaus H, Falck GC, Norppa H, Fenech M (2007) Origin of nuclear buds and micronuclei in normal and folate-deprived human lymphocytes. Mutat Res 617:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2006.12.002
Lopes-Lima M, Sousa R, Geist J, Aldridge DC, Araujo R, Bergengren J, Bespalaya J et al (2017) Conservation status of freshwater mussels in Europe: state of the art and future challenges. Biol Rev 92:572–607. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12244
Matozzo V, Pagano M, Spinelli A, Caicci F, Faggio C (2016) Pinna nobilis: a big bivalve with big haemocytes? Fish Shellfish Immunol 55:529–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.06.039
Moreira SM, Coimbra J, Guilhermino L (2001) Acetylcholinesterase of Mytilus galloprovincialis LmK. hemolymph: a suitable environmental biomarker. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 67(4):470–475
Nepomuceno JC, Ferrari I, Spano MA, Centeno AC (1997) Detection of micronuclei in peripheral erythrocytes of Cyprinus carpio exposed to metallic mercury. Environ Mol Mutagen 30:293–297
Nugroho, A.P., Handayani, N.S.N., Pramudita, I.G.A., 2015. Effects of chromium (Cr) on freshwater mussel Anodonta woodiana (Lea, 1834): distribution, bioaccumulation, and genomic DNA damage. The 3rd International Conference on Biological Science 2013 (The 3rd ICBS-2013) Volume 2: 180. https://doi.org/10.18502/kls.v2i1.139
Pagano M, Porcino C, Briglia M, Fiorino E, Vazzana M, Silvestro S, Faggio C (2017) The influence of exposure of cadmium chloride and zinc chloride on haemolymph and digestive gland cells from Mytilus galloprovincialis. Int J Environ Res 11(2):207–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-017-0020-8
Palais F, Dedourge-Geffard O, Beaudon A, Pain-Devin S, Trapp J, Geffard O, Noury P, Gourlay-Francé C, Uher E, Mouneyrac C, Biagianti-Risbourg S, Geffard A (2012) One-year monitoring of core biomarker and digestive enzymeresponses in transplanted zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha). Ecotoxicology 21(3):888–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0851-1.
Perić L, Nerlović V, Žurga P, Žilić L, Ramšak A (2017) Variations of biomarkers response in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis to low, moderate and high concentrations of organic chemicals and metals. Chemosphere 174:554–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.138
Pourang N, Richardson CA, Mortazavi MS (2010) Heavy metal concentrations in the soft tissues of swan mussel (Anodonta cygnea) and surficial sediments from Anzali wetland, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 163(1-4):195–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0827-7
Rickwood CJ, Galloway TS (2004) Acetylcholinesterase inhibition as a biomarker of adverse effect A study of Mytilus edulis exposed to the priority pollutant chlorfenvinphos. Aquat Toxicol 67:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2003.11.004.
Robillard S, Beauchamp G, Laulier M (2003) The role of abiotic factors and pesticide levels on enzymatic activity in the freshwater mussel Anodonta cygnea at three different exposure sites. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C: Toxicol Pharmacol 135(1):49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1532-0456(03)00049-8
Rzymski P, Niedzielski P, Klimaszyk P, Poniedziałek B (2014) Bioaccumulation of selected metals in bivalves (Unionidae) and Phragmites australis inhabiting a municipal water reservoir. Environ Monit Assess 186(5):3199–3212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-013-3610-8.
Savorelli F, Manfra L, Croppo M, Tornambè A, Palazzi D, Canepa S, Trentini PL, Cicero AM, Faggio C (2017) Fitness evaluation of Ruditapes philippinarum exposed to nickel. Biol Trace Elem Res 177(2):384–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0885-y
Scarpato R, Migliore L, Barale R (1990) The micronucleus assay in Anodonta cygnea for the detection of drinking water mutagenicity. Mutat Res 245(4):231–237
Sen I, Shan dil A, Shrivastava VS (2011) Study for determination of heavy metals in fish species of River Yamuna (Delhi) by inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES). Adv Appl Sci Res 2(2):161–166
Serrano-García L, Montero-Montoya R (2001) Micronuclei and chromatid buds are the result of related genotoxic events. Environ Mol Mutagen 38(1):38–45. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.1048
Sohail M, Khan MN, Qureshi NA, Chaudhry AS (2017) Monitoring DNA damage in gills of freshwater mussels (Anodonta anatina) exposed to heavy metals. Pak J Zoo 49(1):305–311. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.pjz/2017.49.1.305.311
Stankevičiūtė M, Butrimavičienė L, Valskienė R, Greiciūnaitė J, Baršienė J, Vosylienė MZ, Svecevičius G (2016) Analysis of nuclear abnormalities in erythrocytes of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) treated with Cu and Zn and after 4-, 8-, and 12-day depuration (post-treatment recovery). Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 797:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.01.003
Stankevičiūtė M, Sauliutė G, Svecevičius G, Kazlauskienė N, Baršienė J (2017) Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity response to environmentally relevant complex metal mixture (Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd) accumulated in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Part I: importance of exposure time and tissue dependence. Ecotoxicology 26:1051–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1833-0
Stankevičiūtė M, Sauliutė G, Makaras T, Markuckas A, Virbickas T, Baršienė J (2018) Responses of biomarkers in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) following exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of complex metal mixture (Zn, Cu, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cd). Part II. Ecotoxicology 27:1069–1086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-018-1960-2
Strungaru SA, Jijie R, Nicoara M, Plavan G, Faggio C (2018) Micro (nano) plastics in freshwater ecosystems: abundance, toxicological impact and quantification methodology. Trends Anal Chem 110:116–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.10.025
Taleb ZM, Benali I, Gherras H, Ykhlef-Allal A, Bachir-Bouiadjra B, Amiard JC, Boutiba Z (2009) Biomonitoring of environmental pollution on the Algerian west coast using caged mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Oceanologia 51(1):63–84
Valskienė R, Baršienė J, Butrimavičienė L, Grygiel W, Stunžėnas V, Jokšas K, Stankevičiūtė M (2018) Environmental genotoxicity and cytotoxicity levels in herring (Clupea harengus), flounder (Platichthys flesus) and cod (Gadus morhua) inhabiting the Gdansk Basin of the Baltic Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 133:65–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.05.023
Huber V, Geist J (2017) Glochidial development of the freshwater swan mussel (Anodonta cygnea, Linnaeus 1758) on native and invasive fish species. Biol Conserv 209:230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2017.02.030
Torre A, Trischitta F, Faggio C (2013) Effect of CdCl2 on regulatory volume decrease (RVD) in Mytilus galloprovincialis digestive cells. Toxicol in Vitro 27:1260–1266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2013.02.017
Vidal-Liñán L, Bellas J, Etxebarria N, Nieto O, Beiras R (2014) Glutathione S-transferase, glutathione peroxidase and acetylcholinesterase activities in mussels transplanted to harbour areas. Sci Total Environ 470–471:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.073
Vidal-Liñán L, Bellas J, Salgueiro-Gonzalez N, Muniategui S, Beiras R (2015a) Bioaccumulation of 4-nonylphenol and effects on biomarkers, acetylcholinesterase, glutathione-S-transferase and glutathione peroxidase, in Mytilus galloprovincialis mussel gill. Environ Pollut 200:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.02.012
Vidal-Liñán L, Bellas J, Fumega J, Beiras R (2015b) Bioaccumulation of BDE-47 and effects on molecular biomarkers acetylcholinesterase, glutathione-S-transferase and glutathione peroxidase in Mytilus galloprovincialis mussels. Ecotoxicology 24:292–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1377-5
Vidal-Liñán L, Bellas J, Soriano JA, Concha-Graña E, Muniategui S, Beiras R (2016) Bioaccumulation of PCB-153 and effects on molecular biomarkers acetylcholinesterase, glutathione-S-transferase and glutathione peroxidase in Mytilus galloprovincialis mussels. Environ Pollut 214:885–891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.04.083
Vincent-Hubert F, Arini A, Gourlay-Francé C (2011) Early genotoxic effects in gill cells and haemocytes of Dreissena polymorpha exposed to cadmium, B[a]P and a combination of B[a]P and Cd. Mutat Res 723(1):26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.03.008
Woźnicki P, Lewandowska R, Brzuzan P, Ziomek E, Bardega R (2004) The level of DNA damage and the frequency of micronuclei in haemolymph of freshwater mussels Anodonta woodiana exposed to benzo(a)pyrene. Acta Toxicologica 12(1):41–45
Yahya AN, Mohamed SK, Mohamed AG (2018) Environmental pollution by heavy metals in the aquatic ecosystems of Egypt. OAJT 3(1):001–009. https://doi.org/10.19080/OAJT.2018.03.555603
Zhang YF, Chen SY, Qu MJ, Adeleye AO, Di YN (2017) Utilization of isolated marine mussel cells as an in vitro model to assess xenobiotics induced genotoxicity. Toxicol in Vitro 44:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2017.05.018
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Gerda Petkutė and Greta Ašmenaitė for the help during this experiment.
Funding
This study was funded by the Research Council of Lithuania through the project ACTIS S-MIP-17-10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Cinta Porte
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights:
•Six-metal mixture at the maximum permissible concentrations is geno- and cytotoxic to A. cygnea.
•The highest ∑Gentox levels in gills and haemocytes was determined after 4-day exposure.
•Significantly highest induction of ∑Cytox level was found in gills after 2-day treatment.
•Metal mixture possesses an inhibitory effect on the acetylcholinesterase activity in mussels.
•Significant decrease in AChE activity in A. cygnea was found after short-term (4 days) exposure.
•Significantly highest accumulation of trace metals has been determined after 28-day treatment.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Butrimavičienė, L., Stankevičiūtė, M., Kalcienė, V. et al. Genotoxic, cytotoxic, and neurotoxic responses in Anodonta cygnea after complex metal mixture treatment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 7627–7639 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04206-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04206-1