Abstract
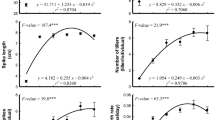
The safe disposal of industrial effluents always remained a challenging process because of their high level of nutrients, toxic elements, and salts. A pot experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of various concentrations (5%, 10%, 15%, and 20%) of sugar industry effluent spentwash (SW) fertigated with tab water (TW), on soil properties, crop growth, physiological parameters, yield components, and accumulation of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in rice (Oryza sativa L.) grains and straw. The results showed that soil physico-chemical properties were modified with rise in SW concentration. Application of 5% SW significantly enhanced the plant growth, and yield components. Photosynthesis rate, transpiration rate, and stomatal conductance were significantly higher under 5% SW concentration in comparison with control. However, SW concentrations of > 5% showed inhibitory effects for all growth, physiological, and yield components. Accumulation of PTEs showed increasing trend with rise in SW concentration. However, under 5% SW concentration, all the PTEs in rice grain and straw were within the permissible limits (PLs) recommended by FAO/WHO and no health hazards were detected by health risk assessment. Based on the study results, 5% SW fertigation with TW can be applied as fertilizer for enhancing the growth and productivity of rice.

Graphical abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agale M, Patel N, Patil A (2013) Impact of sugar industry effluents on the quality of groundwater from Dahiwad village, District Dhule (MS). Arch App Sci Res 5:58–60
Alfaraas A, Khairiah J, Ismail BS, Noraini T (2016) Effects of heavy metal exposure on the morphological and microscopical characteristics of the paddy plant. J Environ Biol 37:955–963
Alia PKVSK, Saradhi PP (1995) Effect of zinc on free radicals and proline in Brassica and Cajanus. Phytochemistry 39:45–47
Anjum SA, Tanveer M, Hussain S, Shahzad B, Ashraf U, Fahad S, Hassan W, Jan S, Khan I, Saleem MF, Bajwa AA (2016) Osmoregulation and antioxidant production in maize under combined cadmium and arsenic stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:11864–11875
Asati A, Pichhode M, Nikhil K (2016) Effect of heavy metals on plants: an overview. Int J App Engn Mnag 5:56–66
Assche FV, Clijsters H (2010) Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ 13:195–206
Belefant-Miller H (2007) Poultry litter induces tillering in rice. J Sustain Agric 31:151–160
Bellore SK, Mall LR (1975) Chlorophyll content as an ecological index of dry matter production. Indian J Bot Soc 54(1–2):75–77
Bose S, Bhattacharyya AK (2008) Heavy metal accumulation in wheat plant grown in soil amended with industrial sludge. Chemosphere 70:1264–1272
Cang L (2004) Heavy metals pollution in poultry and livestock feeds and manures under intensive farming in Jiangsu Province. China J Environ Sci 16:371–374
CEC (Council of the European Communities (1986) Council Directive of 12 June on the protection of environment and particular of the soil, when sewage sludge used in agriculture (86/278/EEC). Off J EurComm No. L181/6-12.
Chandra R, Bharagava RN, Yadav S, Mohan D (2009) Accumulation and distribution of toxic metals in wheat ( Triticum aestivum L.) and Indian mustard ( Brassica campestris L.) irrigated with distillery and tannery effluents. J of. Hazard Mater 162:1514–1521
Chandra R, Kumar K, Singh J (2004) Impact of anaerobically treated and untreated (raw) distillery effluent irrigation on soil microflora, growth, total chlorophyll and protein contents of Phaseolus aureus L. J Environ Biol 25:381–385
Chandra R, Yadav S, Mohan D (2008) Effect of distillery sludge on seed germination and growth parameters of green gram ( Phaseolus mungo L.). J Hazard Mater 152:431–439
Chandraju S, Basavaraju H (2007) Impact of distillery spent wash on Seed germination and growth of leaves Vegetables: an investigation. Sugar Journal (SISSTA) 38:20–50
Chandraju S, Basavaraju H, Kumar CC (2008) Investigation of impact of irrigation of distillery spentwash on the nutrients of pulses. Asian J Chem 20:6342–6348
Chidankumar CS, Chandraju S, Nagendraswamy R (2009) Impact of distillery spentwash irrigation on the yields of top vegetables (creepers). W App Sci J 6:1270–1273
Cui Y, Zhu YG, Zhai R, Huang Y, Qiu Y, Liang J (2005) Exposure to metal mixtures and human health impacts in a contaminated area in Nanning. China Environ Int 31:784–790
Das M, Chakraborty H, Singandhupe R, Muduli S, Kumar A (2010) Utilization of distillery wastewater for improving production in underproductive paddy grown area in India. J Sci Ind Res 69:560–563
Das SK (2014) Role of micronutrient in rice cultivation and management strategy in organic agriculture - a reappraisal. Agric Sci 05:765–769
Dikinya O, Areola OM (2011) Comparative effects of secondary treated waste water irrigation on soil quality parameters under different crop types. Global Science Books 5:41–55 http://www.globalsciencebooks.info/Journals/AJPSB.html
FAO (2000) Food and Agriculture Organization, National Institute of Health and National food nutrition survey. Islamabad, Food balance sheet, Rome http://www.fao.org/faostat
FAO (2004) Food statistics, Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome, Itlay; Available at: http:www.apps.fao.org
Fuentes A, Lloréns M, Sáez J, Aguilar MI, Ortuño JF, Meseguer VF (2004) Phytotoxicity and heavy metals speciation of stabilised sewage sludges. J Hazard Mater 108:161–169
Fytili D, Zabaniotou A (2008) Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods A review. Renewa Sust Ener Rev 12:116–140
Gahlot D, Kukreja K, Suneja S, Dudeja S (2011) Effect of digested distillery spent wash on nodulation, nutrient uptake and photosynthetic activity in chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Acta Agronomica Hungarica 59:73–85
Ge KY (1992) The status of nutrient and meal of Chinese in the 1990s. The peoples hygien press:415–434
Gee G, Bauder J (1986) Particle size analysis. p. 383–411. A. Klute (ed.) Methods of soil analysis. Part 1. Physical and mineralogical methods. Agron Monogr ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI 9:383–411
Govt Pak (2017) Government of Pakistan Economic Survey. Economic Advisors Wing Finance Division, Islamabad, Pakistan, pp 27–28 http://journal.plos.org/plosone/article/file
Harrison EZ, Mcbride MB, Bouldin DR (1999) Land Application of Sewage Sludges: An Appraisal of the U.S. Regulations. Int J Environ Pollut 11:1–36
Hasanuzzaman M, Ahamed K, Rahmatullah M, Akhter N, Nahar K, Rahman M (2010) Plant growth characters and productivity of wetland rice (Oryza sativa L.) as affected by application of different manures. Emir J Food Agr 22:46–58
Hati KM, Biswas AK, Bandyopadhyay K, Misra AK (2004) Effect of post-methanation effluent on soil physical properties under a soybean-wheat system in a Vertisol. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 167:584–590
Hussain A, Alamzeb S, Begum S (2013) Accumulation of heavy metals in edible parts of vegetables irrigated with waste water and their daily intake to adults and children, District Mardan, Pakistan. Food Chem 136:1515–1523
IRRI (2001) International Rice Research Institute. Philippines irri.org/blogs/irri-history/this-weekin-irri-history, Manila
Iyengar GV, Nair PP (2000) Global outlook on nutrition and the environment: meeting the challenges of the next millennium. Sci Total Environ 249:331–346
Jiang ZP, Li YR, Wei GP, Liao Q, Su TM, Meng YC, Zhang HY, Lu CY (2012) Effect of long-term vinasse application on physico-chemical properties of sugarcane field soils. Sugar Tech 14:412–417
Jones JB Jr, Case VW, Westerman RL (1990) Sampling, handling and analyzing plant tissue samples. Soil Testing and Plant Analysis. 3rd Ed Soil Sci Soc America 389–427
Kaloi GM, Memon M, Memon KS, Ahmad S, Sheikh SA, Jamro GM (2017) Effect of sugar industry spentwash (diluted) on the characteristics of soil and sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) growth in the subtropical environment of Sindh, Pakistan. Envoniron Mit Assess 189(3):127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5861-2
Kaloi GM, Memon M, Memon KS, Tunio S (2015) Integrated use of spent wash and mineral fertilizers on germination and initial growth of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). Soil Environ 34:1–8
Kauser S, 2007. Water use in vegetable production in district Faisalabad, MSc Thesis, Department of Environmental and Resource Economics, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan
Kaushik A, Nisha R, Jagjeeta K, Kaushik CP (2005) Impact of long and short term irrigation of a sodic soil with distillery effluent in combination with bioamendments. Bioresour Technol 96:1860–1866
Keeney DR, Nelson DW (1982) Nitrogen-Inorganic Forms 1. Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties, 643–698
Kettler TA, Doran JW, Gilbert TL (2001) Simplified method for soil particle-Size determination to accompany soil-quality analyses j series no. 13277 of the Agric. Res. Div., Univ. of Nebraska, Lincoln, NE. Soil Sci Soc Am J 65:849–852
Khalil S (2011) Agricultural use of untreated urban wastewater in Pakistan. Asian J Agric Rural Develop 1:21–26
Khaliq A, Matloob A, Hussain A, Hussain S, Aslam F, Zamir SI, Chattha MU (2015) Wheat residue management options affect crop productivity, weed growth, and soil properties in direct-seeded fine aromatic rice. CLEAN–Soil, Air, Water 43:1259–1265
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng YM, Huang YZ, Zhu YG (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing. China Environ Pollut 152:686–692
Khan F, Hussain S, Tanveer M, Khan S, Hussain HA, Iqbal B, Geng M (2018). Coordinated effects of lead toxicity and nutrient deprivation on growth, oxidative status, and elemental composition of primed and non-primed rice seedlings. Environ Sci Pollut Res doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2262-1
Krupa Z, Baszynski T (1995) Some aspects of heavy metals toxicity towards photosynthetic apparatus-direct and indirect effects on light and dark reactions. Acta Physiol Plant 2(17):177–190
Kumar A, Singh VK, And N, Kumar R (2014) Utilization of paddy straw as animal. Forage Res 40:154–158 http://www.forageresearch
Kumar V, Wati L, Fitzgibbon F, Nigam P, Banat IM, Singh D, Marchant R (1997) Bioremediation and decolorization of anaerobically digested distillery spent wash. Biotechnol Lett 19:311–314
Kumari K, Phogat VK (2009) Solubilization of phosphorus from low-grade Udaipur rock phosphate using spent wash. Indian J Agr Res 43:219–222
Liu H, Hussain S, Peng S, Huang J, Cui K, Nie L (2014) Potentially toxic elements concentration in milled rice differ among various planting patterns. Field Crop Res 168:19–26
Mahesh KS, Chandrashekara KT, Rajashekar N, Jagannath S (2013) Physiological behaviour of few Cultivars of Paddy (Oryza sativa L.) during Seed Germination and early Growth, subjecting to distillery Effluent Stress. Int Res J Biological Sci 2:5–10
Misra RN, Behera PK (1991) The effect of paper industry effluent on growth, pigments, carbohydrates and proteins of rice seedlings. Environ Pollut 72(2):159–167
Monni S, Salemaa M, Millar N (2000) The tolerance of Empetrum nigrum to copper and nickel. Environ Pollut 109:221–229
Murtaza G, Ghafoor A, Qadir M (2008) Accumulation and implications of cadmium, cobalt and manganese in soils and vegetables irrigated with city effluent. J Sci Food Agric 88:100–107
Mysliwa-Kurdziel B, Strzałka K (2002) Influence of metals on biosynthesis of photosynthetic pigments. Physiology and biochemistry of metal toxicity and tolerance in plants. Springer, Kluwer Academic Publ, Dordrecht, pp. 201–227
Narain K, Yazdani T, Bhat MM, Yunus M (2012) Effect on physico-chemical and structural properties of soil amended with distillery effluent and ameliorated by cropping two cereal plant spp. Environ Earth Sci 66:977–984
Naveed, S, Rehim, A, Imran, M, Bashir, MA, Anwar, MF, Ahmad, F (2018) Organic manures: an efficient move towards maize grain biofortification. Int J Rec Org Waste Agric. 1–9
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1996) Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. BT - Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. chemical methods. SSSA, Book Ser. 5.SSSA, Madison, WI. p, 961–1010
NEQS (1999) Nantioanl Environmental Quality Standard for municipal and liquid industries. Compiled and distributed by National Scientific Corporation. http://epd.punjab.gov.pk/neqs
Nickson RT, Mcarthur JM, Shrestha B, Kyaw-Myint TO, Lowry D (2005) Arsenic and other drinking water quality issues, Muzaffargarh District. Pakistan Appl Geochem 20:55–68
Oncel I, Keleş Y, Ustün AS (2000) Interactive effects of temperature and heavy metal stress on the growth and some biochemical compounds in wheat seedlings. Environ Pollut 107:315–320
Pandey SN, Nautiyal BD, Sharma CP (2008) Pollution level in distillery effluent and its phytotoxic effect on seed germination and early growth of maize and rice. J Environ Biol 29:267
Pant D, Adholeya A (2007) Biological approaches for treatment of distillery wastewater: a review. Bioresour Technol 98:2321–2334
PSMA (2014) Pakistan Sugar Mills Assocaition, annual report. Pakistan Pp:21–23. http://www.psmacentre.com/documents/annual report
Purushotham D, Rashid M, Lone MA, Rao AN, Ahmed S, Nagaiah E, Dar FA (2013) Environmental impact assessment of air and heavy metal concentration in groundwater of Maheshwaram watershed, Ranga Reddy district. Andhra Pradesh J Geol Soc India 81:385–396
Quartacci MF, Argilla A, Baker AJM, Navari-Izzo F (2006) Phytoextraction of metals from a multiply contaminated soil by Indian mustard. Chemosphere 63:918–925
Qureshi AL, Mahessar AA, Leghari EUH, Lashari BK, Mari FM (2015) Impact of Releasing Wastewater of Sugar Industries into Drainage System of LBOD,Sindh, Pakistan. Int J Environ Sci Develop 6:381–386
Ramana S, Biswas A, Kundu S, Saha J, Yadava R (2002) Effect of distillery effluent on seed germination in some vegetable crops. Bioresour Technol 82:273–275
Rath P, Biswal K, Misra M (2013) Effects of sugar factory distillery spentwash on germination and seedling growth of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int J Sci Innov Disc 3:191–201
Rath P, Pradhan G, Mishra MK (2010) Effect of sugar factory distillery spent wash (DSW) on the growth pattern of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) crop. J Phytopathol 2:33–39
Raverkar KP, Ramana S, Singh AB, Biswas AK, Kundu S (2000) Impact of post methanated spentwash (PMS) on the nursery raising, biological parameters of Glyricidia sepum and biological activity of soil. AnnPlant Res 2:161–168
Riaz M, Yan L, Wu X, Hussain S, Aziz O, Wang Y, Imran M, Jiang C (2018) Boron alleviates the aluminum toxicity in trifoliate orange by regulating antioxidant defense system and reducing root cell injury. J Environ Manag 208:149–158
Ryan J, Estefan G, Rashid A (2001) Soil and plant analysis laboratory manual. International Centre for Agricultural Research areas (ICARDA) Aleppo, Syria pp 172
Sarwar G, Schmeisky H, Tahir MA, Iftikhar Y, Sabah NU (2011) Application of green compost for the improvement of dry matter yield and chemical composition of Lolium perenne (grass). Japs J Animal Plant Sci 21:710–714
Sarwar N, Imran M, Shaheen MR, Ishaque W, Kamran MA, Matloob A, Rehim A, Hussain S (2017) Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: Modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 171:710–721
Singh R, Agrawal M (2009) Use of sewage sludge as fertiliser supplement for Abelmoschus esculentus plants: Physiological. biochemical and growth responses Int J Environ Waste Manag 3:91–106
Sinha S, Gupta M, Chandra P (1997) Oxidative stress induced by iron in Hydrilla verticillata (l.f.) Royle: response of antioxidants. Ecotox Environ Safe 38:286–291
Srivastava S, Jain R (2010) Effect of distillery spent wash on cytomorphological behaviour of sugarcane settlings. J Environ Biol 31:809–812
Stobart AK, Griffiths WT, Ameen-Bukhari I, Sherwood RP (2010) The effect of Cd on the biosynthesis of chlorophyll in leaves of barley. Physiol Plant 63:293–298
Subramani A, Saravanan S, Tamizhiniyan P, Lakshmanachary AS (1997) Influence of heavy metals on germination and early seedling growth of Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper. Pollut Res 16:29–31
Suganaya K, Rajannan G (2009) Effect of one time post-sown and pre-sown application of distillery spentwash on the growth and yield of maize crop. Bot Res Int 2:288–292
Sukanya TS, Meli SS (2010) Response of wheat to graded dilution of liquid distillery effluent (Spent wash) on plant nutrient contents, nutrient uptake, crop yield and residual soil fertility. Karnataka J Agr Sci 17:417–420
Swarup A, Yaduvansiii N (2000) Effects of Integrated Nutrient Management on Soil Properties and yield of rice in alkali soils. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 48:279–282
Thapliyal A, Vasudevan P, Dastidar MG, Tandon M, Mishra S (2011) Irrigation with domestic wastewater: responses on growth and yield of ladyfinger Abelmoschus esculentus and on soil nutrients. J Environ Biol 32:645–651
Timsina J, Jat ML, Majumdar K, Cakmak I (2010) Rice-maize systems of South Asia: current status, future prospects and research priorities for nutrient management. Plant Soil 335:65–82
Tuong TP, Bouman BAM, Kijne JW, Barker R, Molden D (2003) Rice production in water-scarce environments. Water Productivity in Agriculture Limits Opportunities for Improvement 4:53–67
United Nations (2003) Water for people, water for life. The United Nations World Water Development Report. UNESCO, Barcelona
USEPA (2002) United States of America Environmental Protection Agency Preliminary remediation gols. https://archive.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/web/pdf
USSL (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Handbook 60:147 http://www.ars.usda.gov/arsuserfiles/20360500/hb60.pdf
Wahid A, Ghani A, Ali I, Ashraf M (2007) Effects of cadmium on carbon and nitrogen assimilation in shoots of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] seedlings. J Agron Crop Sci 193:357–365
Wang X, Sato T, Xing B, Tao S (2005) Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Tianjin, China via consumption of vegetables and fish. Sci Total Environ 350:28–37
WHO (1993) World Health Organization, Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants. 41st report of the joint FAO?WHO expert committee on food additives. Technical report series, Geneva edition www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/jecfa-reports/en
Wintz H, Fox T, Vulpe C (2002) Responses of plants to iron, zinc and copper deficiencies. Biochemical Soc Trans 30:766–768
Yadana KL, Aung KM, Takeo, Kazuo O (2009) The effects of green manure (sesbania rostrata) on the growth and yield of rice. J Fac Agric Kyushu Univ 54:313–319
Zeng LS, Liao M, Chen CL, Huang CY (2007) Effects of lead contamination on soil enzymatic activities, microbial biomass, and rice physiological indices in soil–lead–rice (Oryza sativa L.) system. Ecotox Environ Safe 67:67–74
Zheng N, Wang Q, Zheng D (2007) Health risk of Hg, Pb, Cd, Zn, and Cu to the inhabitants around Huludao Zinc Plant in China via consumption of vegetables. Sci Total Environ 383:81–89
Acknowledgments
We would like to give our deep thanks to Professor Ying Ge from Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Marine Biology, College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, P.R. China, for his kind guidance and support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Elena Maestri
Highlights
• We applied different concentrations of spentwash to rice crop
• Low levels of spentwash enhanced rice growth, physiology, and yield
• Higher concentrations of spentwash reduced the crop production and increased the accumulation of micronutrients and heavy metals in plant tissues and grain
• Spentwash could be applied at lower concentration for rice production
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naveed, S., Rehim, A., Imran, M. et al. Effect of distillery spentwash fertigation on crop growth, yield, and accumulation of potentially toxic elements in rice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 31113–31124 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3067-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3067-y