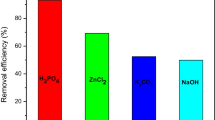
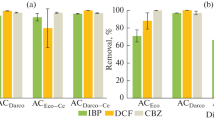
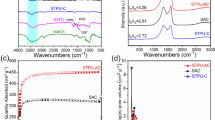
Abstract
Bisphenol A (BPA), diethyl phthalate (DEP), and carbamazepine (CBZ) have been widely used in chemical and pharmaceutical fields, and their residues are detected in various environments. Therefore, to find a suitable method for removing the compounds from an aqueous solution, an adsorption method by granular activated charcoal (AC) was studied. To investigate the adsorption properties of AC, its kinetics, equilibrium, pH effects, and regeneration of AC were examined. Moreover, its surface properties (i.e., surface area, pore volume, functional groups, and surface charge) were characterized by N2 adsorption and desorption isotherm, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), and zeta potential analyses. Experimental results show that AC has high removal efficiencies for the target compounds at the low initial concentration as well as high estimated adsorption capacities (qm) for DEP, BPA, and CBZ, whose values were 293.4 ± 18.8, 254.9 ± 16.2, and 153.3 ± 1.61 mg/g, respectively. In comparison with other adsorbents based on previously reported results, AC was shown to have generally higher removability for the three compounds than others. Moreover, it was observed that AC’s ability to adsorb DEP and BPA was dependent on pH because of hydrolysis and ionization, respectively. Meanwhile, there is no pH effect for CBZ adsorption by AC. After 3 cycles of adsorption/desorption, AC still maintained 92, 100, and 82% of initial adsorption capacities for DEP, BPA, and CBZ, respectively. Therefore, the AC is an effective adsorbent for the removal of endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pharmaceuticals from aqueous solution.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar J, Amin NAS, Shahzad K (2015) A review on removal of pharmaceuticals from water by adsorption. Desalin Water Treat 57:12842–12860. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1051121
Al-Khateeb LA, Almotiry S, Salam MA (2014) Adsorption of pharmaceutical pollutants onto graphene nanoplatelets. Chem Eng J 248:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.023
Ben-Ali S, Jaouali I, Souissi-Najar S, Ouederni A (2017) Characterization and adsorption capacity of raw pomegranate peel biosorbent for copper removal. J Clean Prod 142:3809–3821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.081
Benotti MJ, Trenholm RA, Vanderford BJ, Holady JC, Stanford BD, Snyder SA (2009) Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in U.S. drinking water. Environ Sci Technol 43:597–603. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801845a
Cartwright CD, Owen SA, Thompson IP, Burns RG (2000) Biodegradation of diethyl phthalate in soil by a novel pathway. FEMS Microbiol Lett 186:27–34
Cohen-Ofri I, Weiner L, Boaretto E, Mintz G, Weiner S (2006) Modern and fossil charcoal: aspects of structure and diagenesis. J Archaeol Sci 33:428–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jas.2005.08.008
Dai CM, Zhang J, Zhang YL, Zhou XF, Duan YP, Liu SG (2013) Removal of carbamazepine and clofibric acid from water using double templates-molecularly imprinted polymers. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20:5492–5501. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1565-5
Delgado LF, Charles P, Glucina K, Morlay C (2012) The removal of endocrine disrupting compounds, pharmaceutically activated compounds and cyanobacterial toxins during drinking water preparation using activated carbon—a review. Sci Total Environ 435-436:509–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.07.046
Deng J, Shao Y, Gao N, Xia S, Tan C, Zhou S, Hu X (2013) Degradation of the antiepileptic drug carbamazepine upon different UV-based advanced oxidation processes in water. Chem Eng J 222:150–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.045
Domínguez JR, González T, Palo P, Cuerda-Correa EM (2011) Removal of common pharmaceuticals present in surface waters by Amberlite XAD-7 acrylic-ester-resin: influence of pH and presence of other drugs. Desalination 269:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.065
Ganiyu SO, van Hullebusch ED, Cretin M, Esposito G, Oturan MA (2015) Coupling of membrane filtration and advanced oxidation processes for removal of pharmaceutical residues: a critical review. Sep Purif Technol 156:891–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.09.059
Gao DW, Wen ZD (2016) Phthalate esters in the environment: a critical review of their occurrence, biodegradation, and removal during wastewater treatment processes. Sci Total Environ 541:986–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.148
Ghosh S, Badruddoza AZM, Hidajat K, Uddin MS (2013) Adsorptive removal of emerging contaminants from water using superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles bearing aminated β-cyclodextrin. J Environ Chem Eng 1:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.04.004
Guo W, Hu W, Pan J, Zhou H, Guan W, Wang X, Dai J, Xu L (2011) Selective adsorption and separation of BPA from aqueous solution using novel molecularly imprinted polymers based on kaolinite/Fe3O4 composites. Chem Eng J 171:603–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.04.036
Khanday WA, Marrakchi F, Asif M, Hameed BH (2017) Mesoporous zeolite–activated carbon composite from oil palm ash as an effective adsorbent for methylene blue. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 70:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.10.029
Lewis DL, Holm HW, Kollig HP, Hall TL (1984) Transport and fate of diethyl phthalate in aquatic ecosystems. Environ Toxicol Chem 3:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620030205
Liu G, Ma J, Li X, Qin Q (2009) Adsorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solution onto activated carbons with different modification treatments. J Hazard Mater 164:1275–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.038
Liu FF, Zhao J, Wang S, Du P, Xing B (2014) Effects of solution chemistry on adsorption of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) by graphenes and carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 48:13197–13206. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5034684
Lv L, He J, Wei M, Duan X (2006) Kinetic studies on fluoride removal by calcined layered double hydroxides. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:8623–8628
Nam SW, Choi DJ, Kim SK, Her N, Zoh KD (2014) Adsorption characteristics of selected hydrophilic and hydrophobic micropollutants in water using activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 270:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.01.037
Nitayaphat W, Jiratumnukul N, Charuchinda S, Kittinaovarat S (2009) Mechanical properties of chitosan/bamboo charcoal composite films made with normal and surface oxidized charcoal. Carbohydr Polym 78:444–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.04.027
Pan B, Lin D, Mashayekhi H, Xing B (2008) Adsorption and hysteresis of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinyl estradiol on carbon nanomaterials. Environ Sci Technol 42:5480–5485. https://doi.org/10.1021/es8001184
Pastor-Villegas J, Meneses Rodríguez JM, Pastor-Valle JF, García García M (2007) Changes in commercial wood charcoals by thermal treatments. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 80:507–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2007.05.001
Pehlivan E, Altun T, Parlayici S (2012) Modified barley straw as a potential biosorbent for removal of copper ions from aqueous solution. Food Chem 135:2229–2234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.07.017
Qin Z, Liu S, S-x L, Kang Q, Wang J, Zhao C (2016) Advanced treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater with combined micro-electrolysis, Fenton oxidation, and coagulation sedimentation method. Desalin Water Treat 57:25369–25378
Rivera-Utrilla J, Sanchez-Polo M, Ferro-Garcia MA, Prados-Joya G, Ocampo-Perez R (2013) Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere 93:1268–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.059
Tan IAW, Hameed BH, Ahmad AL (2007) Equilibrium and kinetic studies on basic dye adsorption by oil palm fibre activated carbon. Chem Eng J 127:111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2006.09.010
To M-H, Hadi P, Hui C-W, Lin CSK, McKay G (2017) Mechanistic study of atenolol, acebutolol and carbamazepine adsorption on waste biomass derived activated carbon. J Mol Liq 241:386–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.05.037
Wang F, Yao J, Sun K, Xing B (2010) Adsorption of dialkyl phthalate esters on carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 44:6985–6991. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101326j
Xu Z, Cheng L, Shi J, Lu J, Zhang W, Zhao Y, Li F, Chen M (2014) Kinetic study of the removal of dimethyl phthalate from an aqueous solution using an anion exchange resin. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:6571–6577. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2556-x
Yen CH, Lien HL, Chung JS, Yeh HD (2017) Adsorption of precious metals in water by dendrimer modified magnetic nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 322:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.02.029
Yim B, Nagata Y, Maeda Y (2002) Sonolytic degradation of phthalic acid esters in aqueous solutions. Acceleration of hydrolysis by sonochemical action The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 106:104-107 https://doi.org/10.1021/jp011896c
Zhou M, Wu YN, Qiao J, Zhang J, McDonald A, Li G, Li F (2013) The removal of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions by MIL-53(Al) and mesostructured MIL-53(Al). J Colloid Interface Sci 405:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.05.024
Funding
This work was supported by the Korean Government through NRF (2017R1A2A1A05001207, 2017R1A6A3A04003316) grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 530 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Cho, CW., Cui, L. et al. Adsorptive removal of endocrine-disrupting compounds and a pharmaceutical using activated charcoal from aqueous solution: kinetics, equilibrium, and mechanism studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 33897–33905 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2617-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2617-7